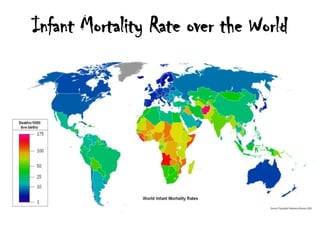
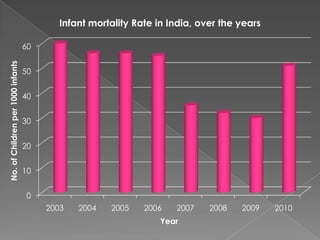
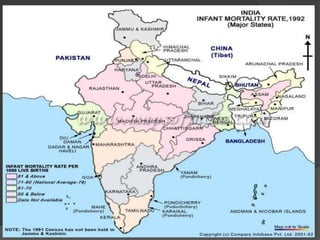
The infant mortality rate (IMR) is the number of infant deaths per 1000 live births. IMR is an important indicator of a country's development level and standard of living. Globally, IMR has significantly declined since 1960 due to improved healthcare, though it remains much higher in less developed countries. Common causes of infant mortality include low birth weight, respiratory issues, SIDS, and lack of essentials like food, shelter and water. Reducing behaviors like smoking during pregnancy and improving literacy, prenatal care, and access to health services can help lower IMR.