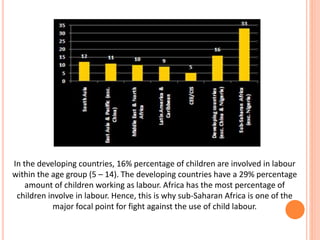
Child labor refers to the employment of children in work that deprives them of their childhood, with around 215 million children affected globally, often in hazardous conditions. The document discusses the prevalence of child labor, particularly in Pakistan's Sialkot province, where economic conditions force families to engage their children in labor to survive. It highlights the need for government enforcement of laws prohibiting child labor and the importance of addressing underlying causes such as poverty and lack of education.