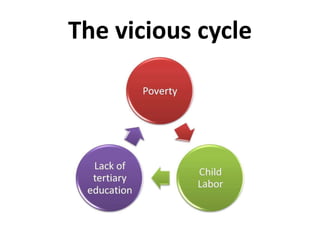
This document discusses child labor in Bangladesh. It defines child labor according to number of work hours by age. Over 1 million children have never been to school in Bangladesh where child labor is widely accepted. Common work areas include brick breaking, rickshaw pulling, and domestic work. Poverty is a main driver of child labor as nearly 1/3 of some families' incomes come from children. Child labor negatively impacts education and health, and risks abuse and trafficking. Solutions proposed include donating to NGOs, increasing education awareness, and strictly enforcing laws against child labor.