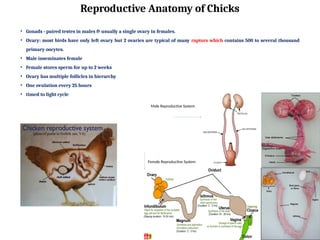
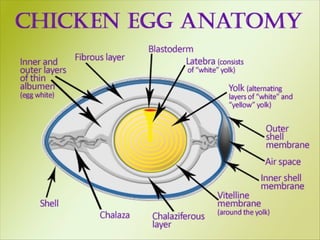
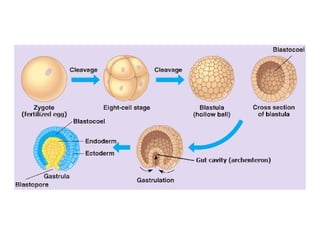
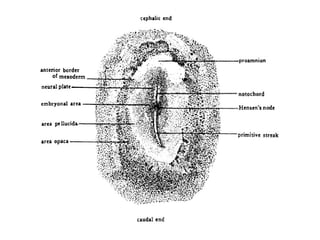
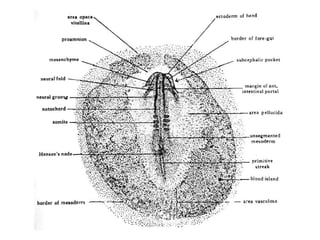
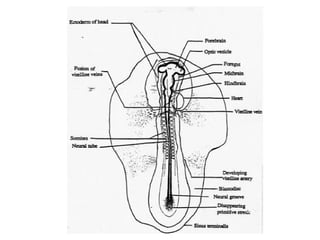
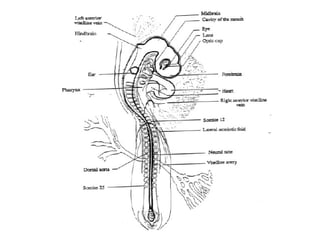
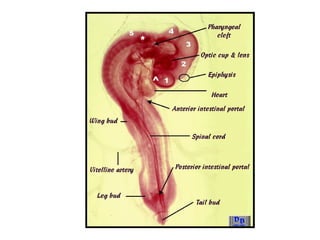
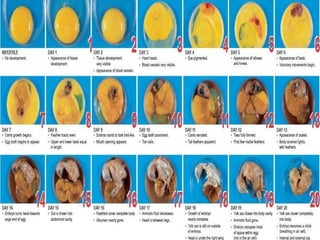
The document outlines the developmental biology of chick embryos, detailing the reproductive anatomy and the stages of embryonic development from fertilization to hatching. It describes processes such as ovulation, sperm storage, and various embryonic structures forming over specific timeframes, including the formation of the primitive streak, notochord, and brain vesicles. Additionally, it covers the differentiation of the heart and blood vessels, emphasizing significant structural developments at specified intervals up to 72 hours post-fertilization.