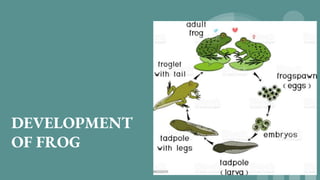
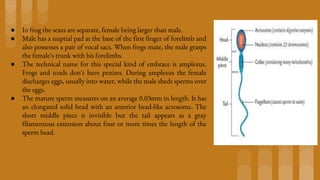
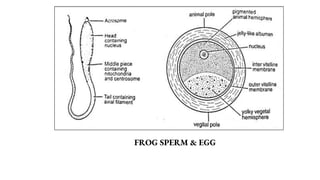
1. The document summarizes the development of frog sperm, eggs, fertilization, and early embryonic development. It describes how the male and female frogs mate and the structure of their sperm and eggs.
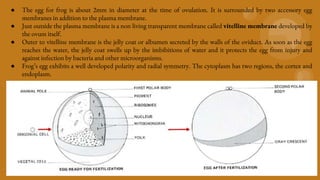
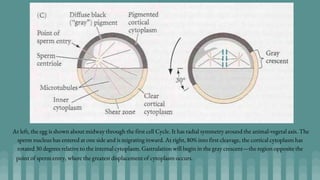
2. During fertilization, one sperm fuses with the egg to form a zygote. This triggers formation of a fertilization membrane and grey crescent on the egg surface, establishing the embryo's polarity.
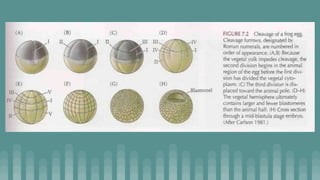
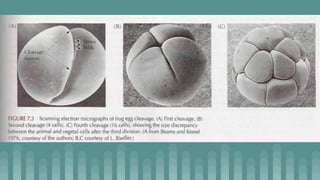
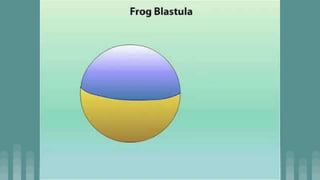
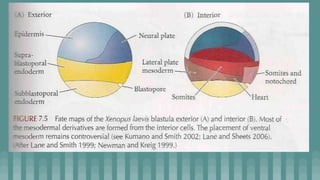
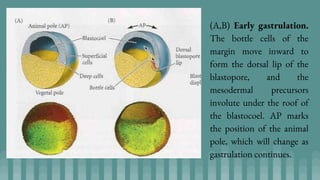
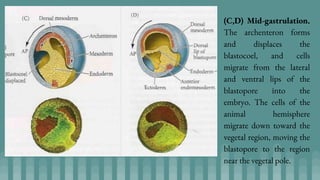
3. Cleavage and blastulation occur, forming a blastula. Gastrulation then transforms the blastula into a three-layered embryo through invagination, involution, and epiboly.