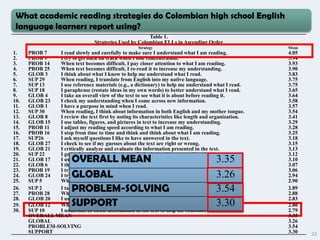
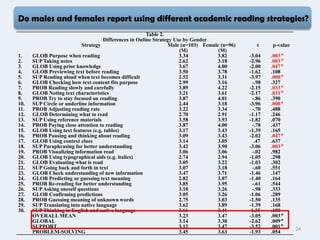
Colombian high school English learners reported using the following reading strategies most frequently:
1) Reading slowly and carefully to ensure understanding;
2) Getting back on track when losing concentration; and
3) Paying closer attention when text becomes difficult.
The strategies were used at least sometimes based on mean responses between 3 to 5 on a Likert scale.