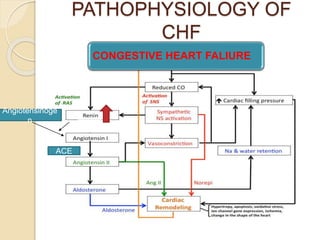
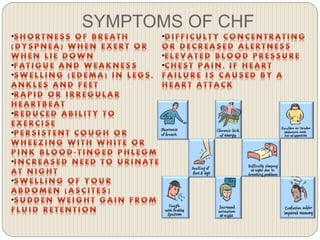
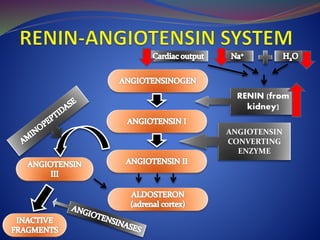
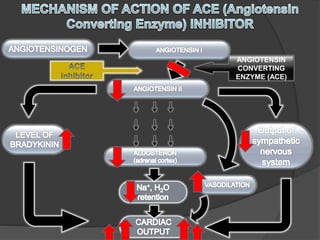
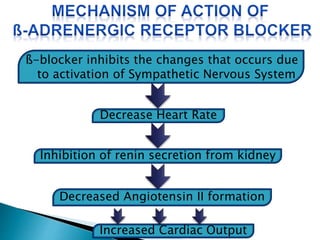
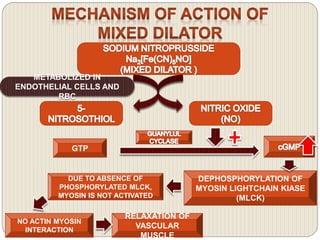
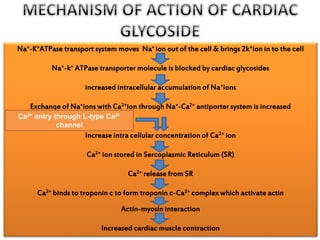
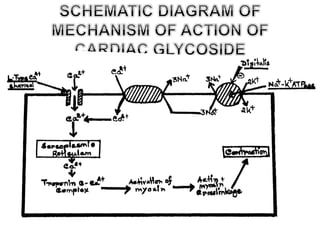
This document provides an overview of congestive heart failure (CHF), including its etiology, pathophysiology, symptoms, management, and treatment with various drugs. CHF is defined as the heart's inability to pump sufficient blood due to problems with filling or ejecting blood. Common causes include intrinsic pump failure, increased workload, impaired filling, and poor oxygen/nutrient supply. The pathophysiology involves neurohormonal activation leading to fluid retention. Symptoms include fatigue, shortness of breath, and edema. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes, medications like ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics, and vasodilators to block neurohormonal activation and reduce preload and afterload. Ad