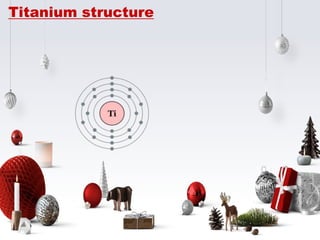
Titanium is a lustrous, silvery gray metal that is strong yet lightweight. It is resistant to corrosion from sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in 1791 and is the ninth most abundant element in the Earth's crust. It is commonly used in aircraft due to its high strength and ability to withstand temperature extremes. About 65% of titanium is used for aerospace applications, with the remainder used in products like golf clubs, laptops, and bicycles. Titanium readily reacts with oxygen and is difficult to produce due to contamination sensitivity.