1) Early philosophers proposed the idea of atoms as the smallest indivisible units of matter. Rutherford's gold foil experiment in the early 1900s showed that atoms have a small, dense nucleus at their center.
2) Bohr's model improved on Rutherford's model by proposing that electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed energy levels. This explained the emission spectra of hydrogen. Later models incorporated the dual wave-particle nature of electrons and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
3) Modern atomic theory describes electrons as existing in electron clouds around the nucleus, with their locations defined by quantum numbers like principal, azimuthal, magnetic, and spin quantum numbers. This quantum mechanical model best explains the structure and behavior of atoms






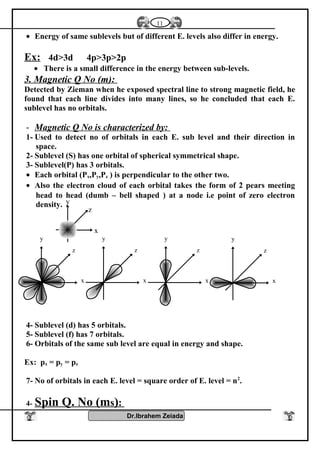

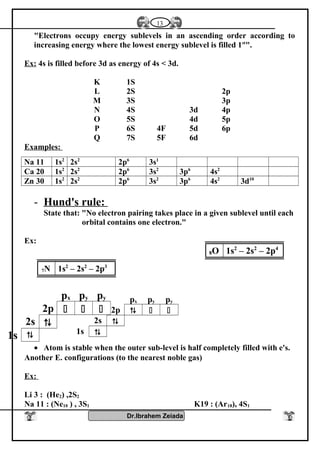





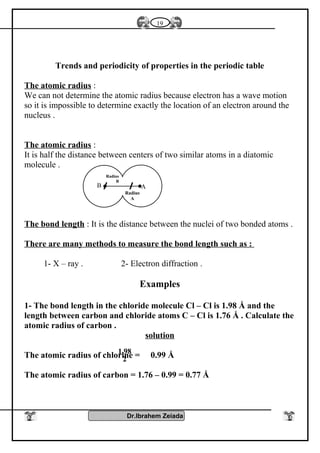



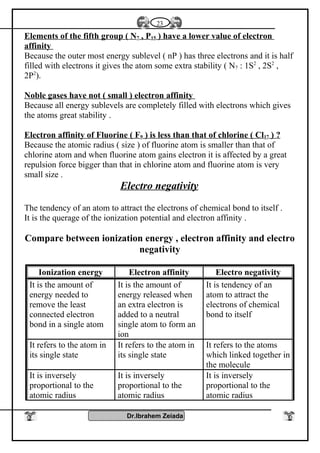




























![General properties
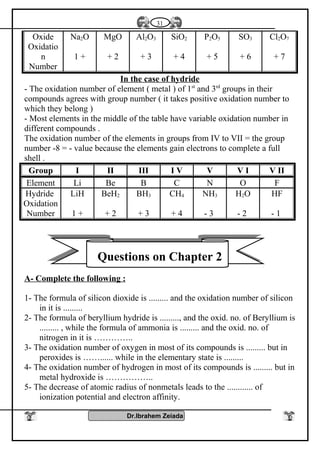
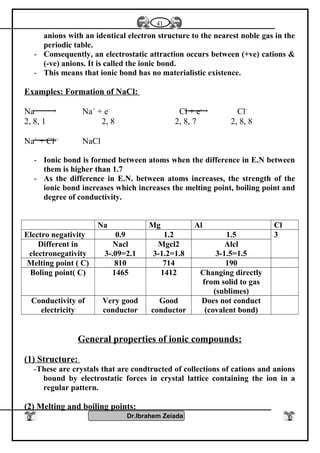
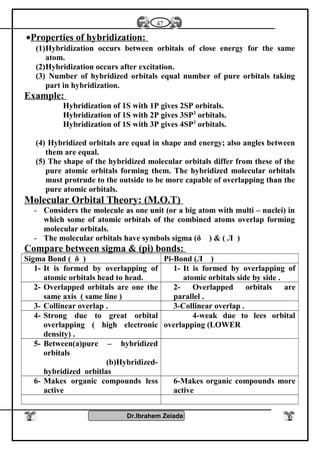
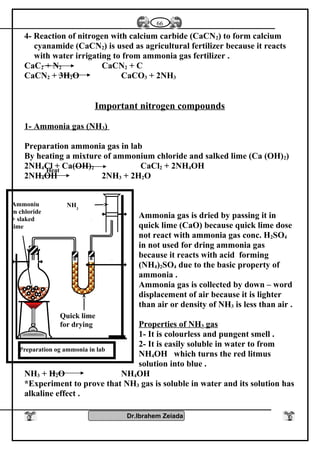
1- Oxidation number : Elements of group [5 – A] have several oxidation
numbers because they gain electrons from 1 to 3 through covalent
sharing or electrons from 1 to 5 electron and reach to the stability state
.
2- With oxygen : All elements of this group form oxides are acidic
(decreases with increasing the atomic number) such as N2O3, N2O5,
P2O3, P2O5 while other are amphoteric Sb2O3 or Bi2O3 or basic
(increases with increasing the atomic number) Bi2O3 .
3- With hydrogen : Most of elements of this group reacts with hydrogen
to form hydrides such as NH3 , PH3 , phosphene , Arsine AsH3
These compounds (NH3- PH3) can form coordinate bonds due to presence
of pair of electrons in valence shell so it can give this electrons to the
outer atoms or ions to form coordinate bond
NH3 + H+
NH4 , PH3 + H+
PH4
These compounds are basic because atom of element has one pair of
electrons donated to positive proton of hydrogen which is found in the
molecule of water therefore the negative hydroxyl group separated from
molecule of water .
NH3 + H+
OH-
NH4
+
OH-
- The polarity of hydrogen compounds in this group decreases with
increasing atomic number .
- The thermally stability and the solubility in water are decreases with
increasing the atomic in this group (NH4
+
) is more polarity than (PH4
+
) is
more polarity than (AsH4
+
)
Dr.Ibrahem Zeiada
64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e8f54776-da50-41ee-8ffe-c690d9ce250f-161012114403/85/chemistry-2nd-sec-full-sheet-64-320.jpg)

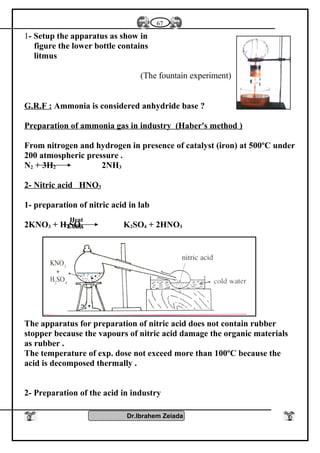














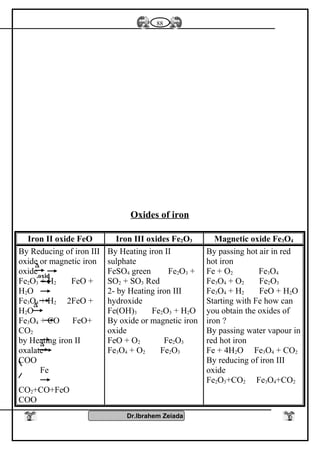
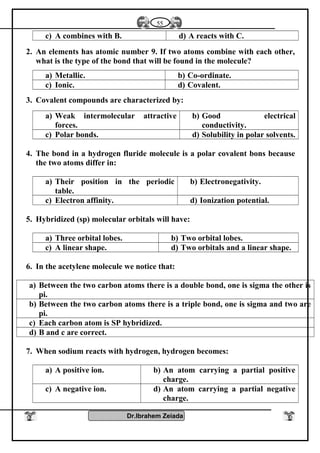
![Iron II oxide is formed
because CO is reducing
agent it prevents the
lormatgon of iron III
oxide
Fe3O4Fe2O3FeO
It is a black colourIt is a blood red colour
oxide
It is a black solid oxide
Effect of heat
Fe3O4+ 1/2 O2 Fe2O3
Fe3O4 + H2SO4
Fe2(SO4) FeSO4 + H2O
Two types of iron salts
because FeO, Fe2O3
Effect of heat
Fe2O3 Fe3O4+ O2
Fe2O3 + H2SO4
Fe2O3( SO4)3 + H2O
Effect of heat
FeO+ O2 Fe2O3
FeO + H2SO4 FeSO4
+ H2O
Diagram shows the important reaction of iron
Oxygen converterMidrex furnaceBlast furnace
Charge [ load ]
molten pig iron
Charge [ load ]
Fe2O3
1- Charge (load)
Fe2O3 + C + CaCO3
reducing agent .Reducing agent a
mixture of CO + H2
from natural gas
Reducing agent
Co from coke
Oxidizing agent
current pure oxygen
Oxidizing agentOxidizing agent
Type of iron produced
steel iron
Type of iron produced
pig iron
Type of iron produced
pig iron
Detection of iron II and iron III cations:
Dr.Ibrahem Zeiada
89](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e8f54776-da50-41ee-8ffe-c690d9ce250f-161012114403/85/chemistry-2nd-sec-full-sheet-89-320.jpg)



