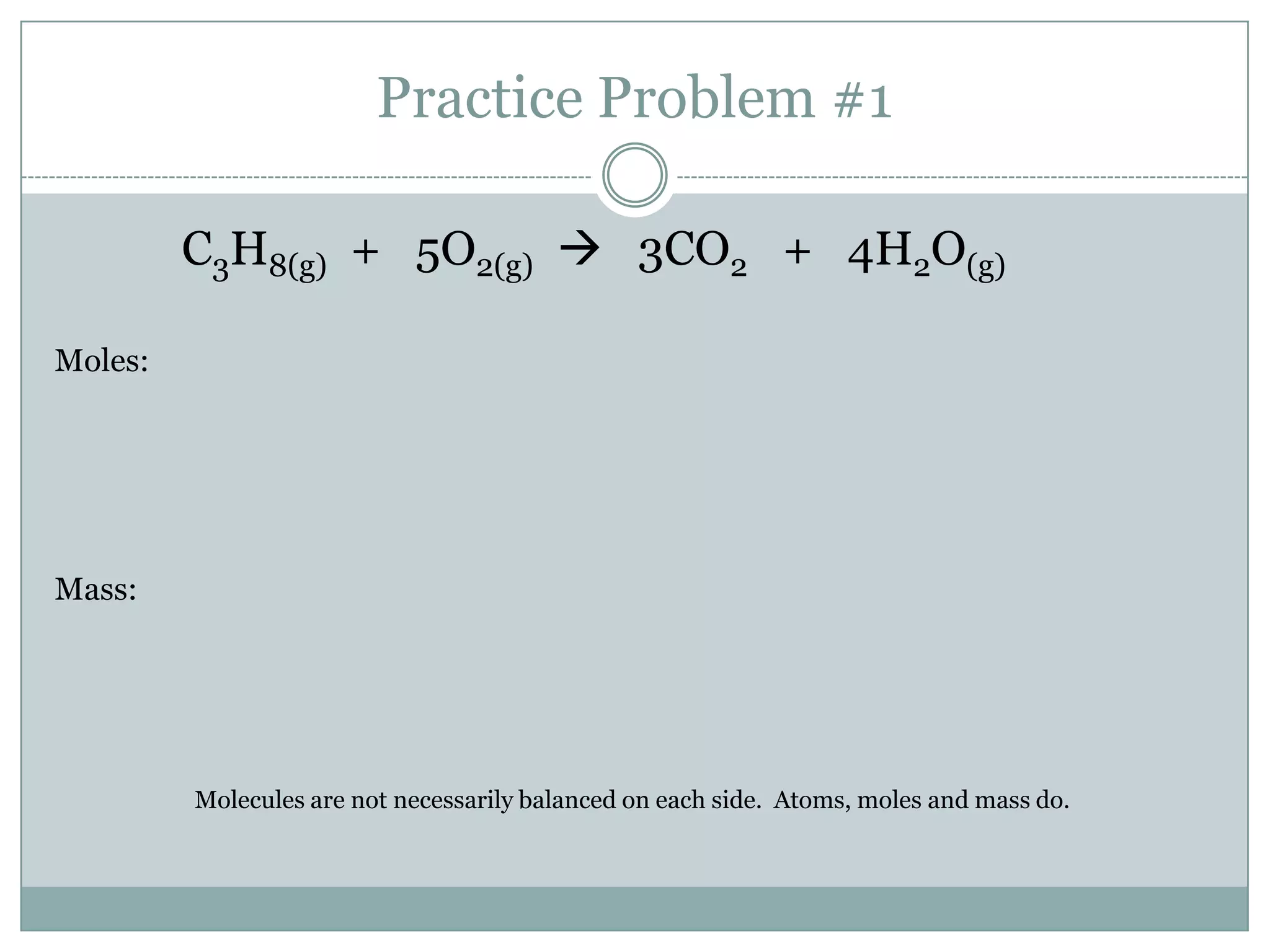
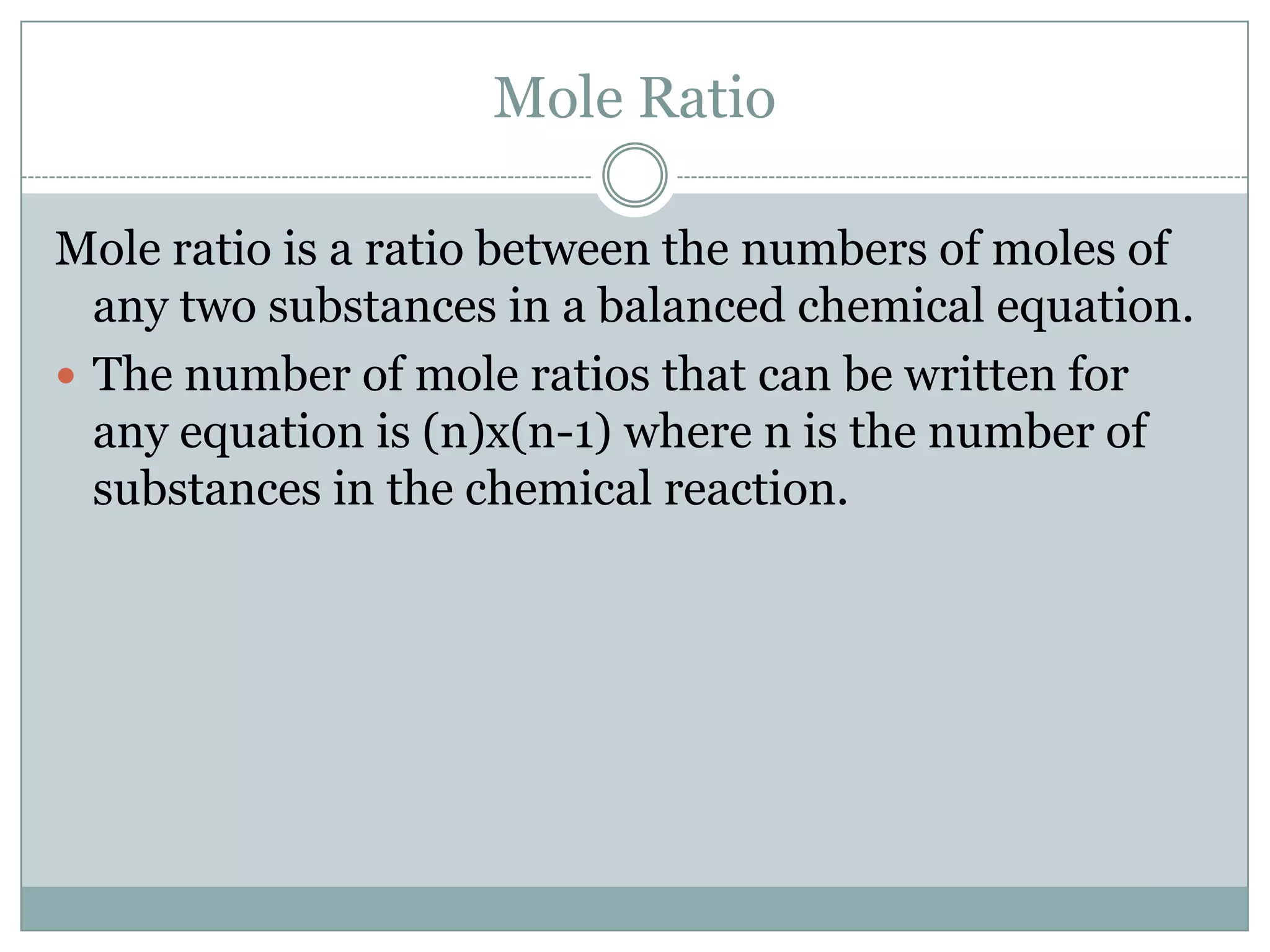
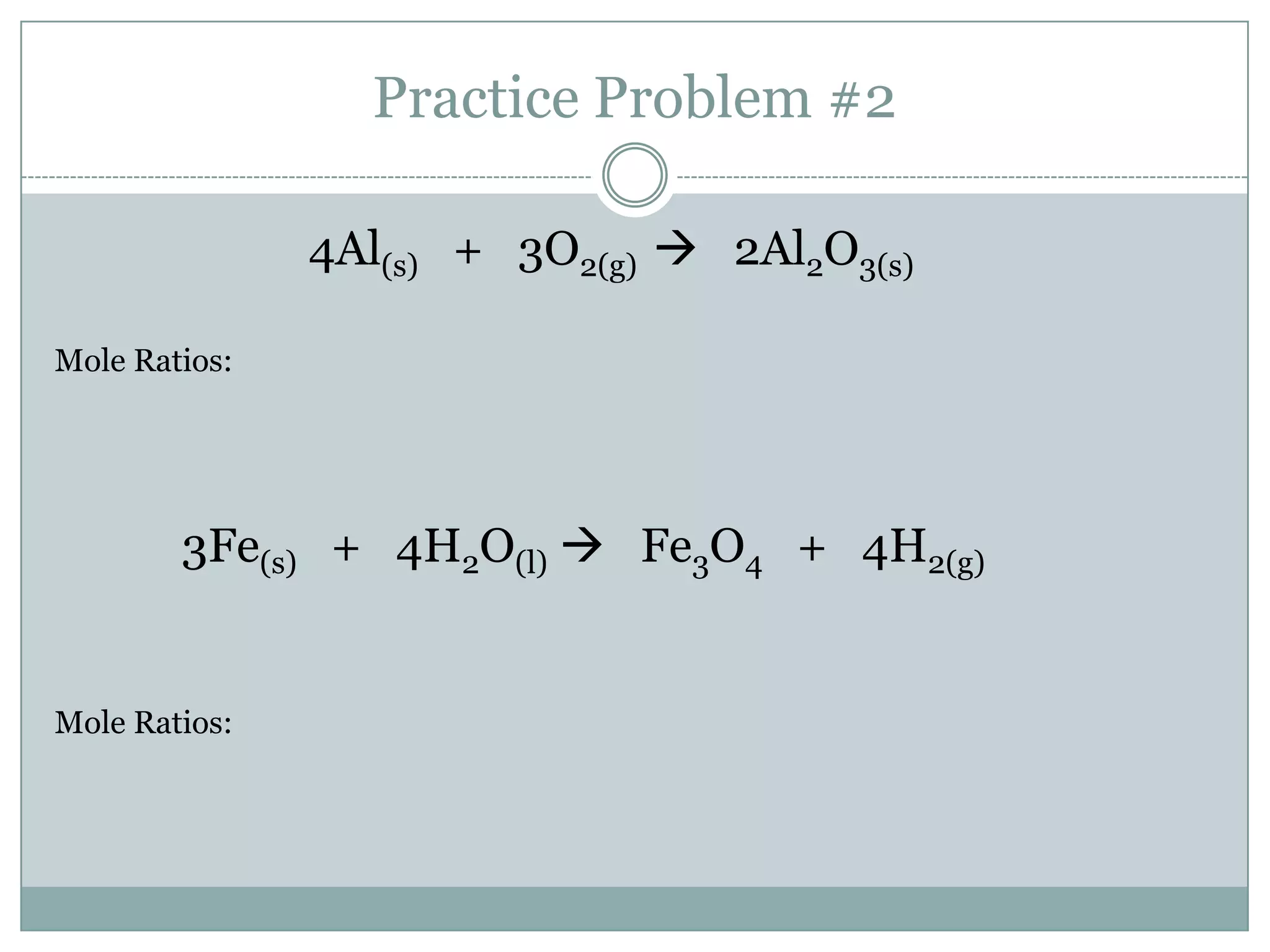
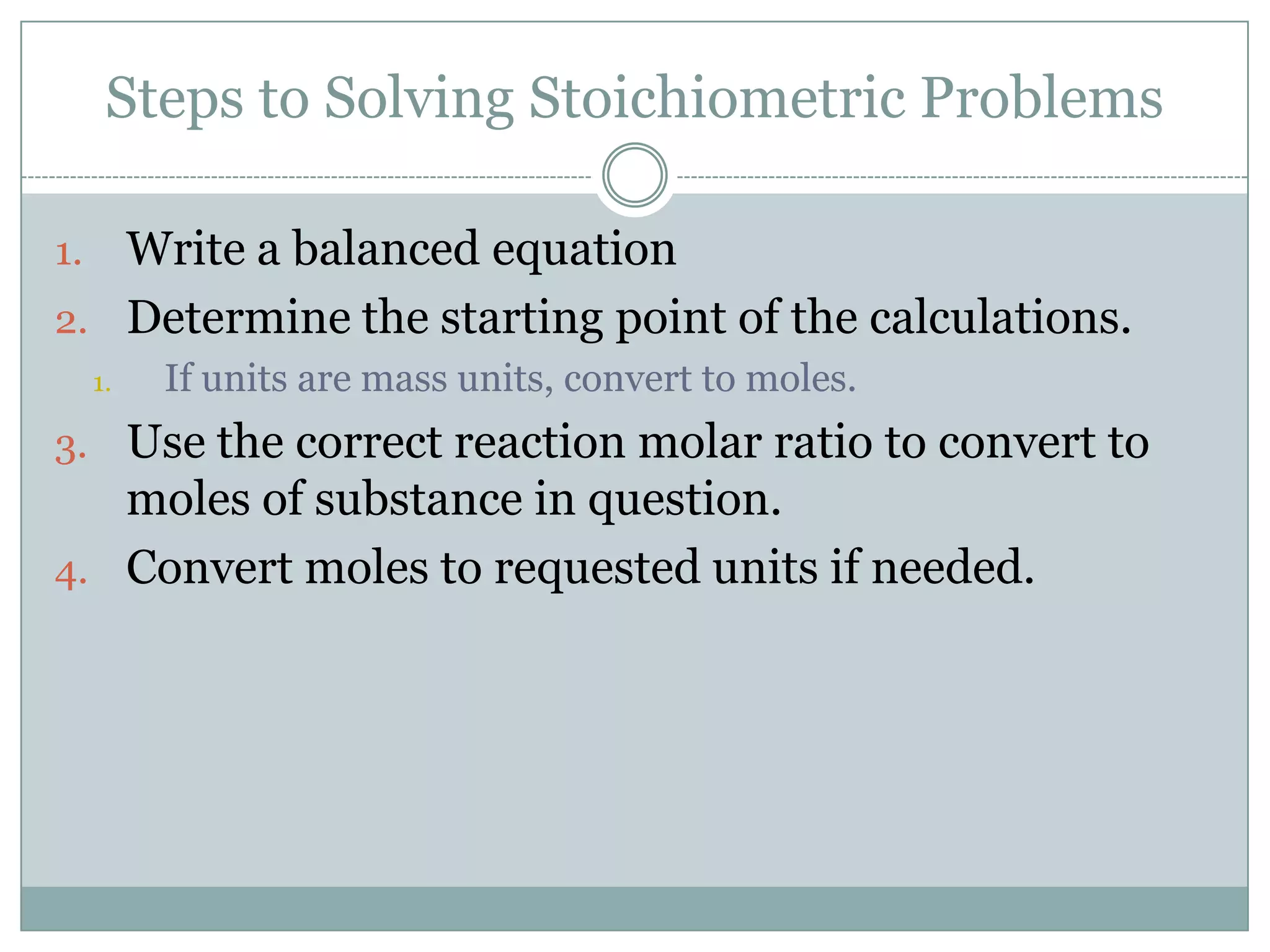
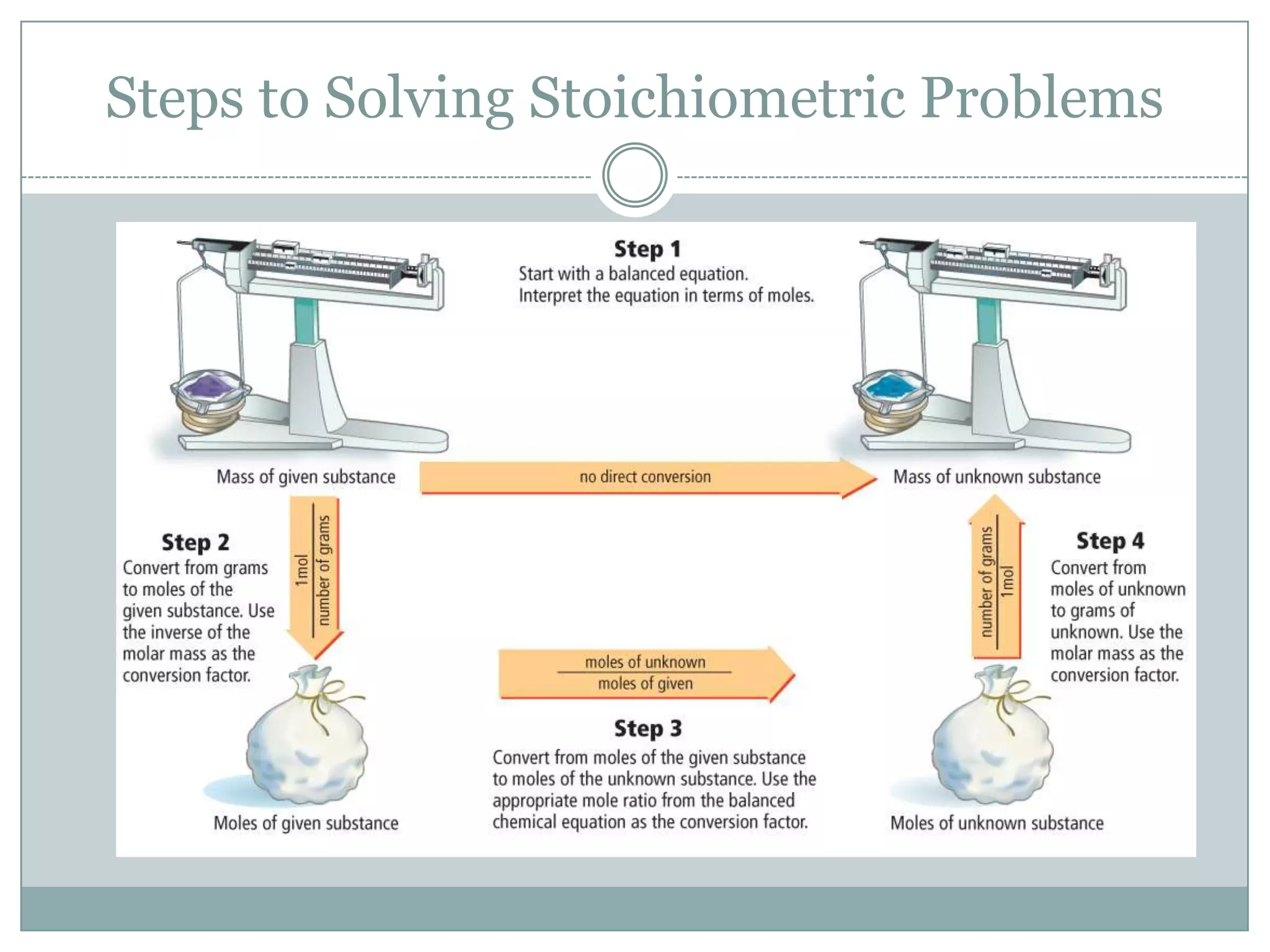
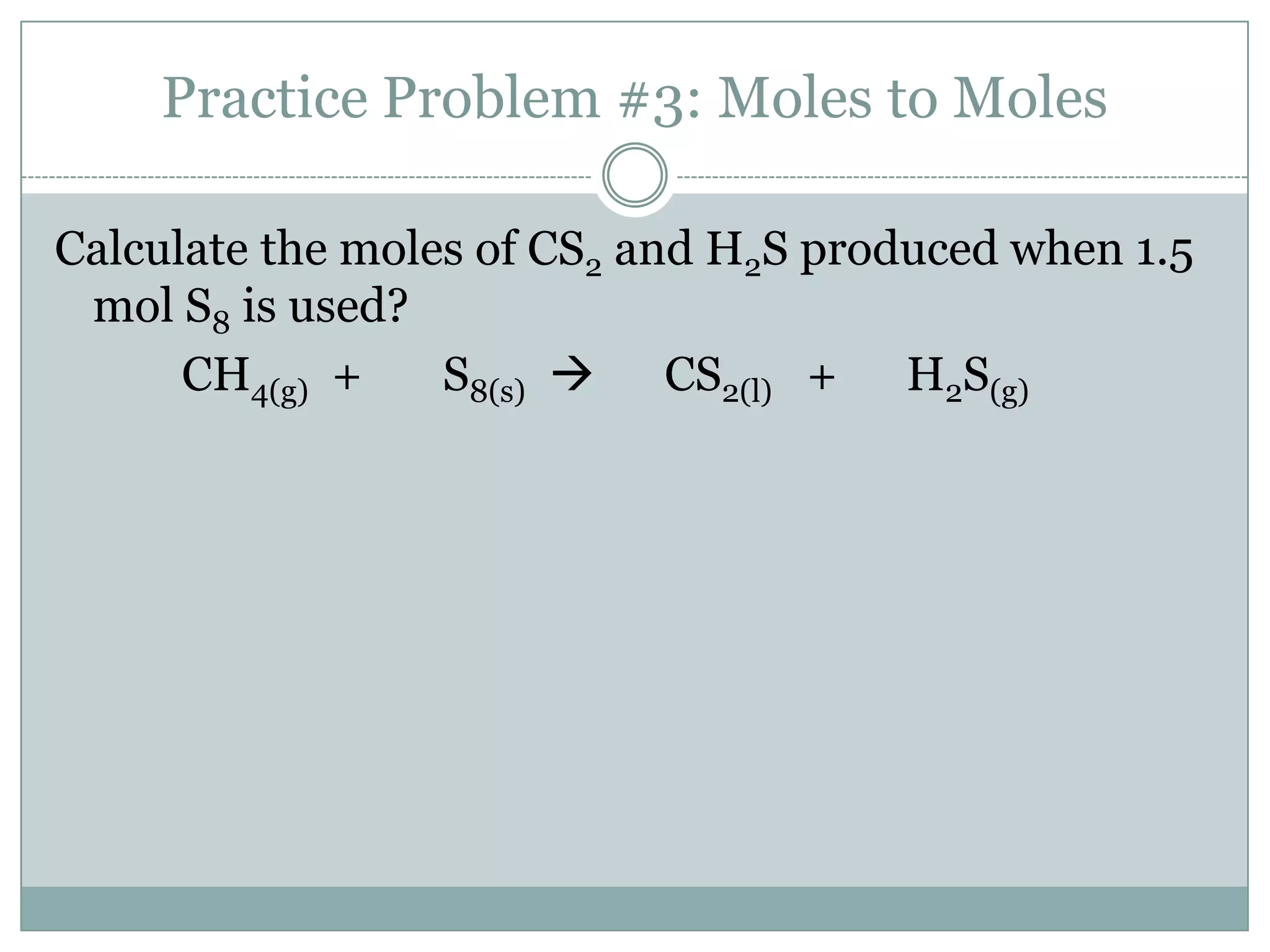
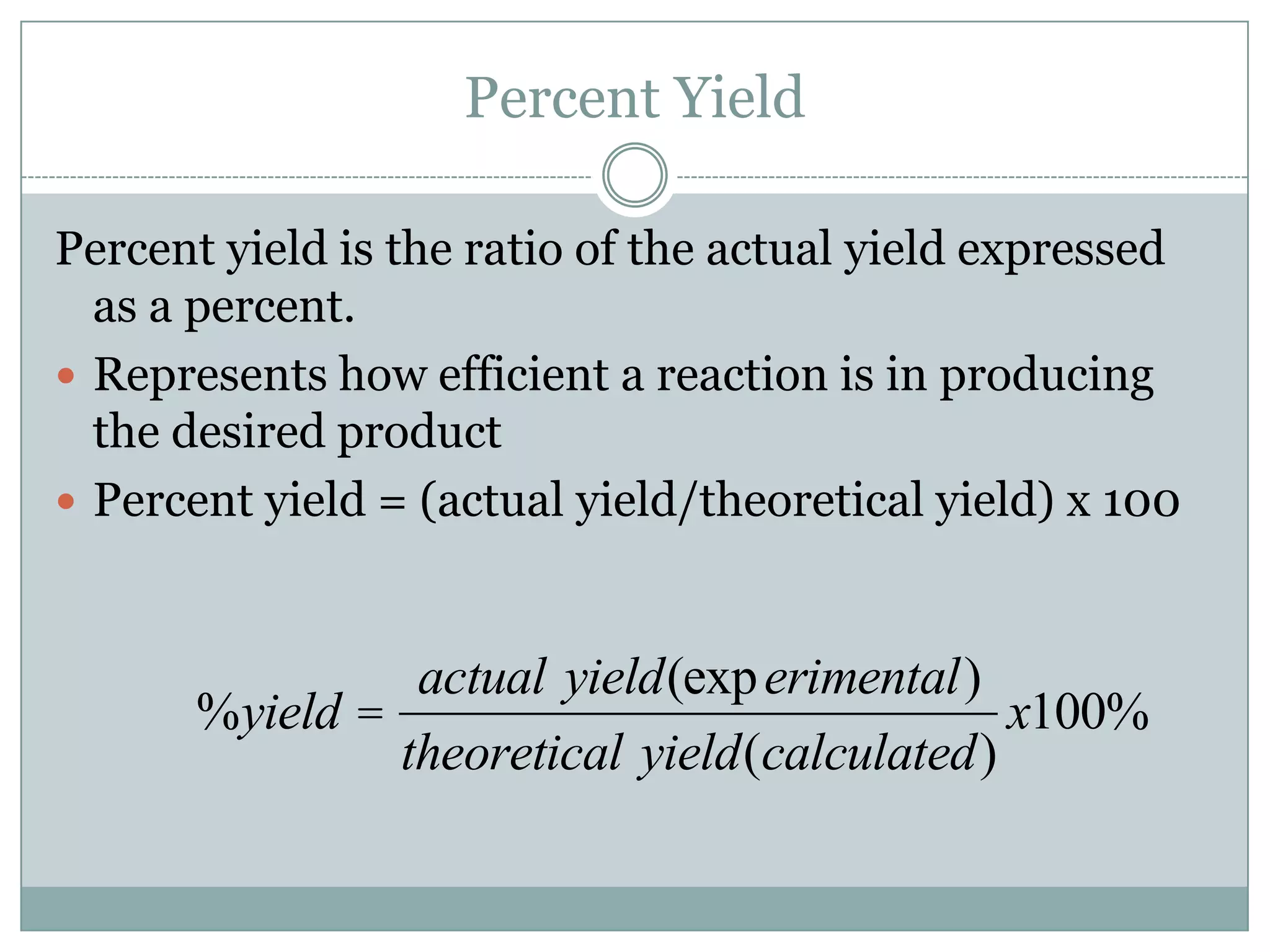
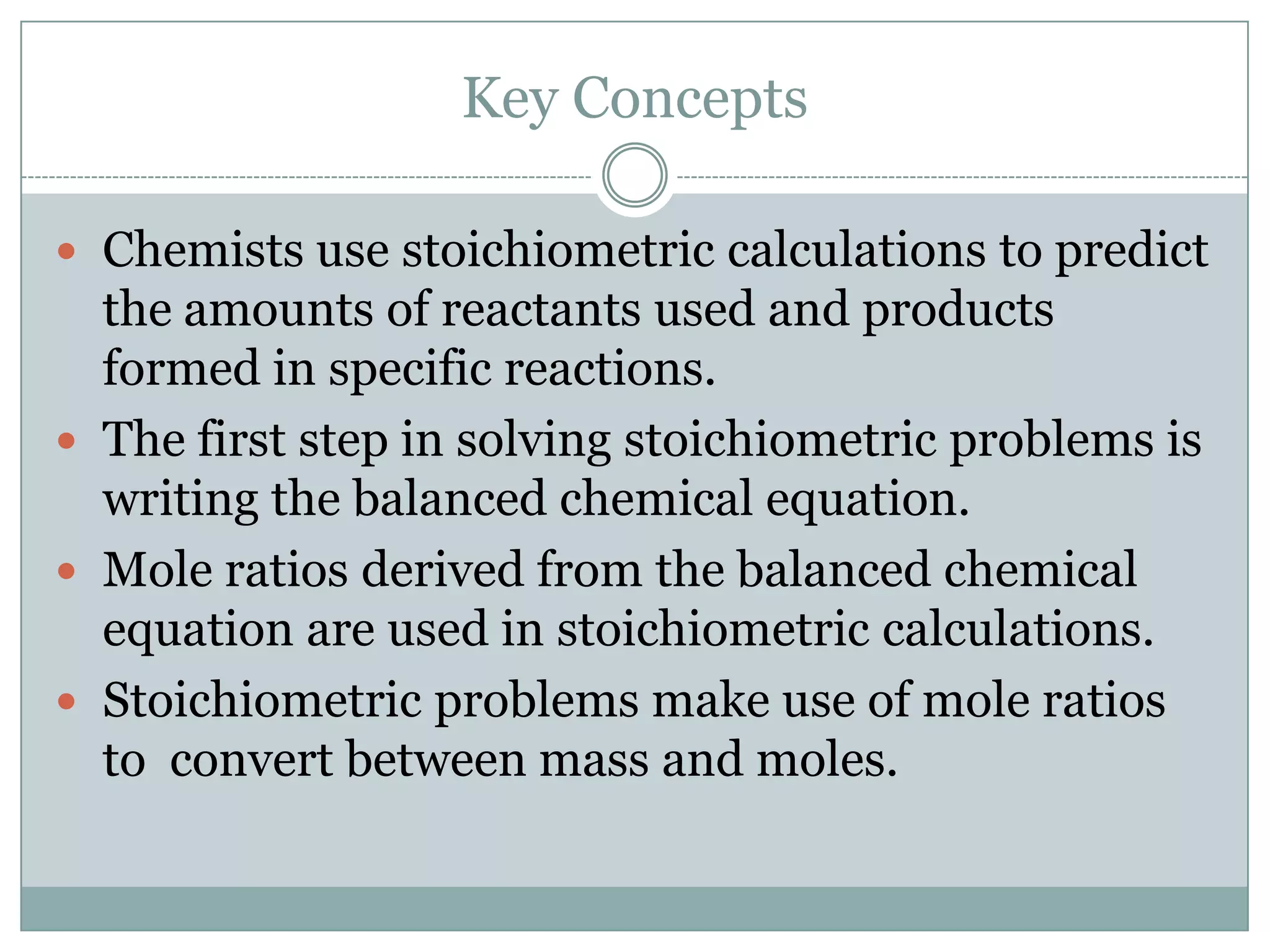
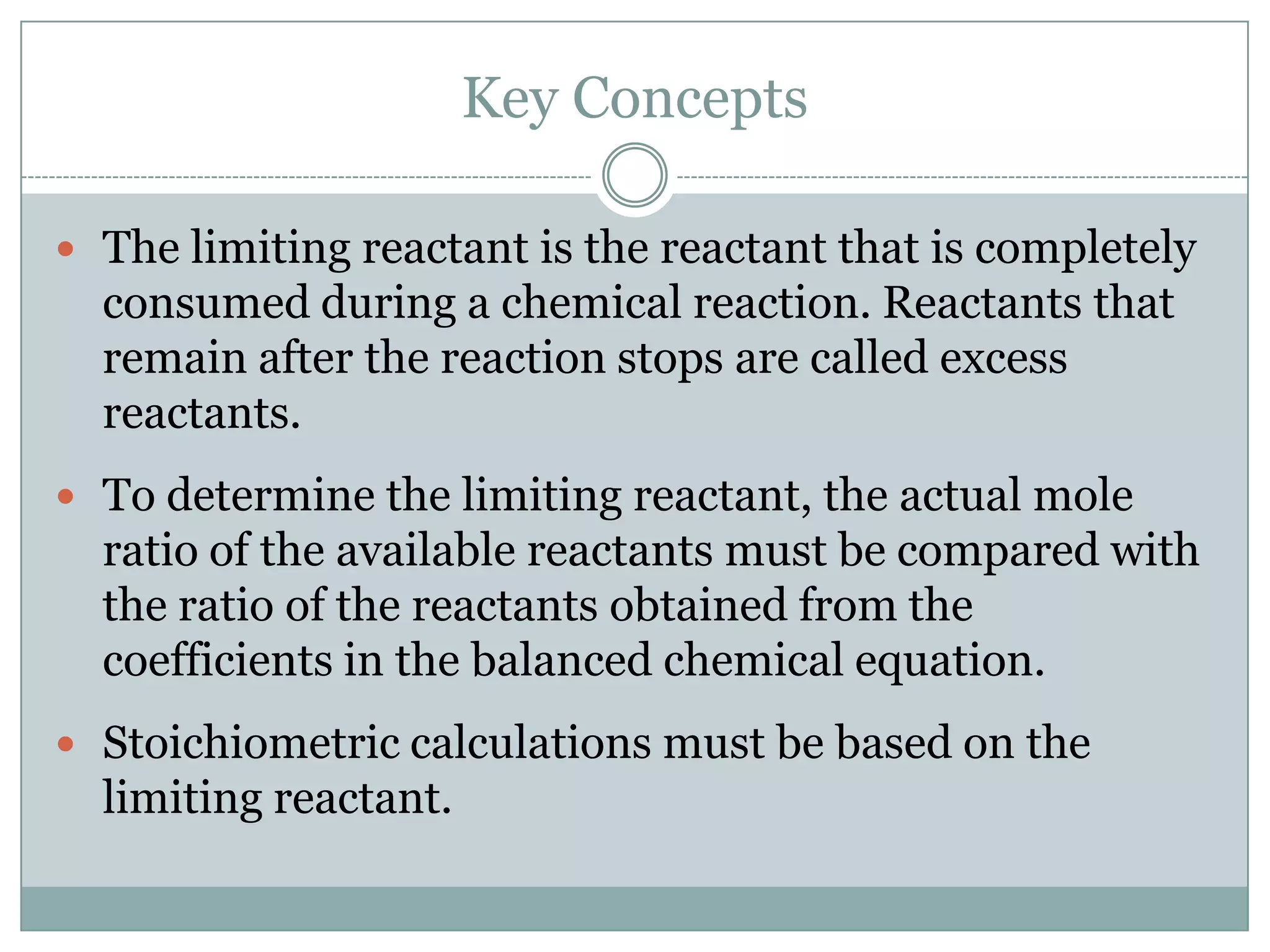
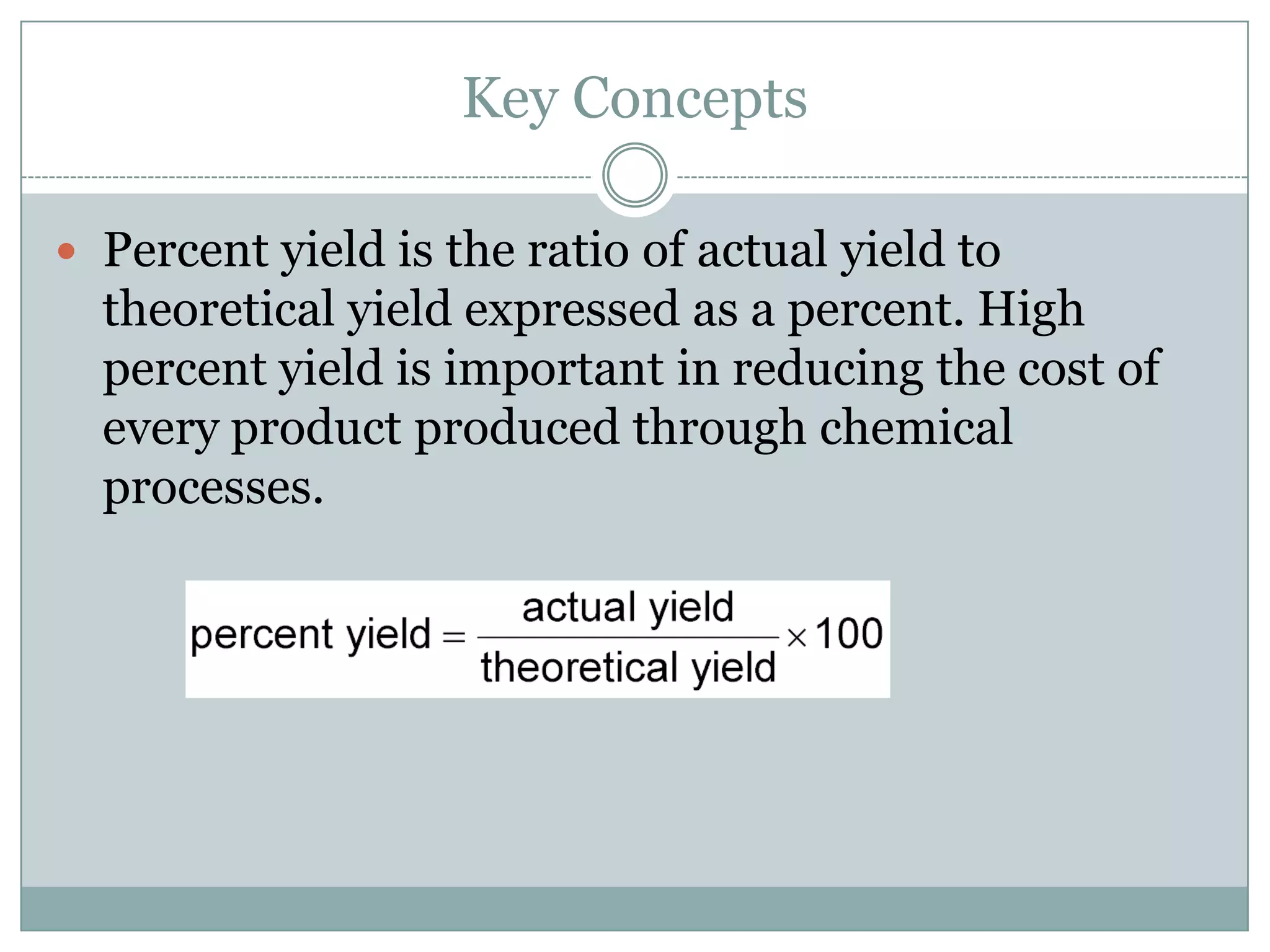
Stoichiometry is the study of quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions based on mole ratios from balanced equations. Key concepts include:
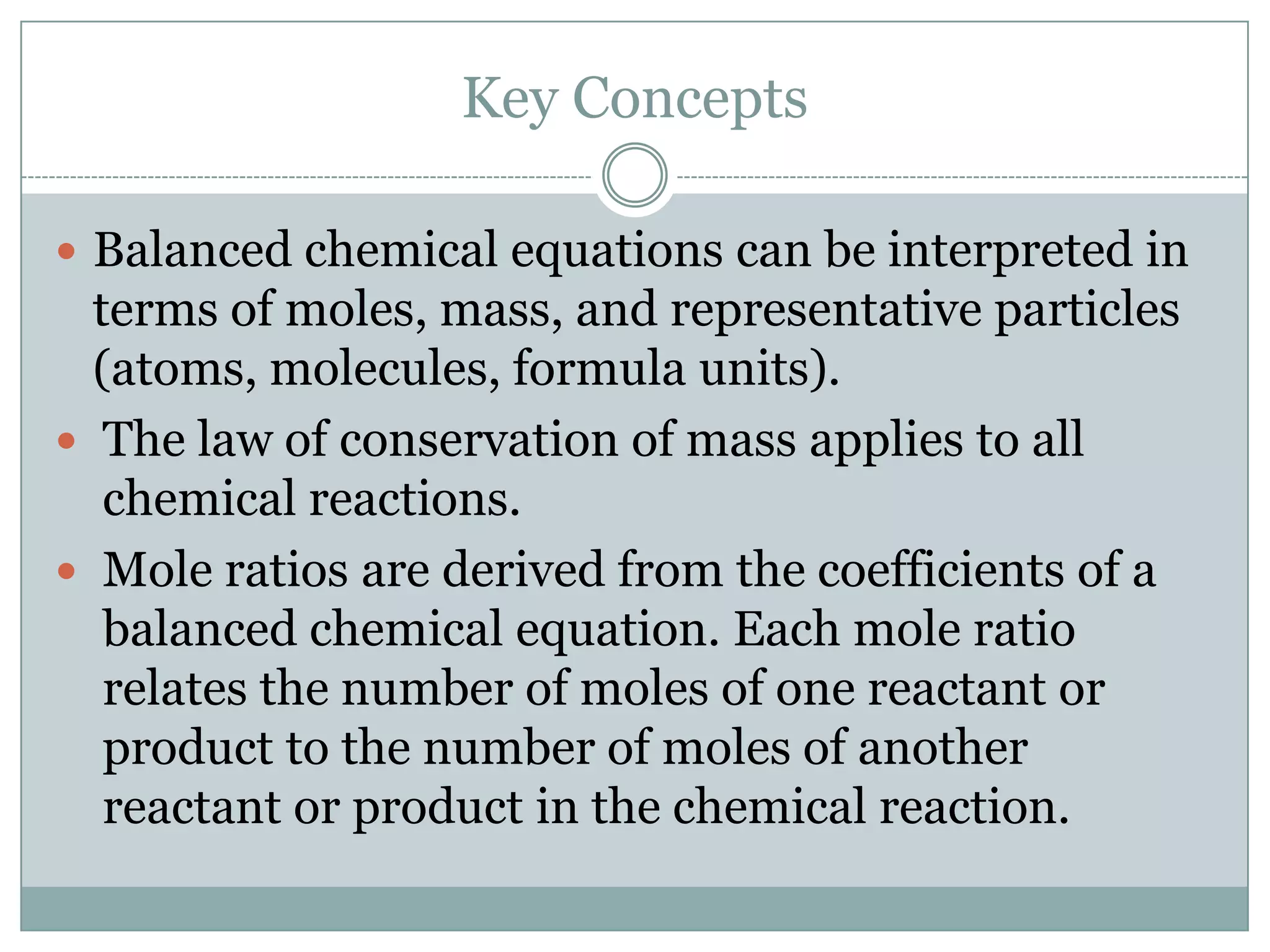
1) Balanced equations show mole, mass, and particle relationships between reactants and products
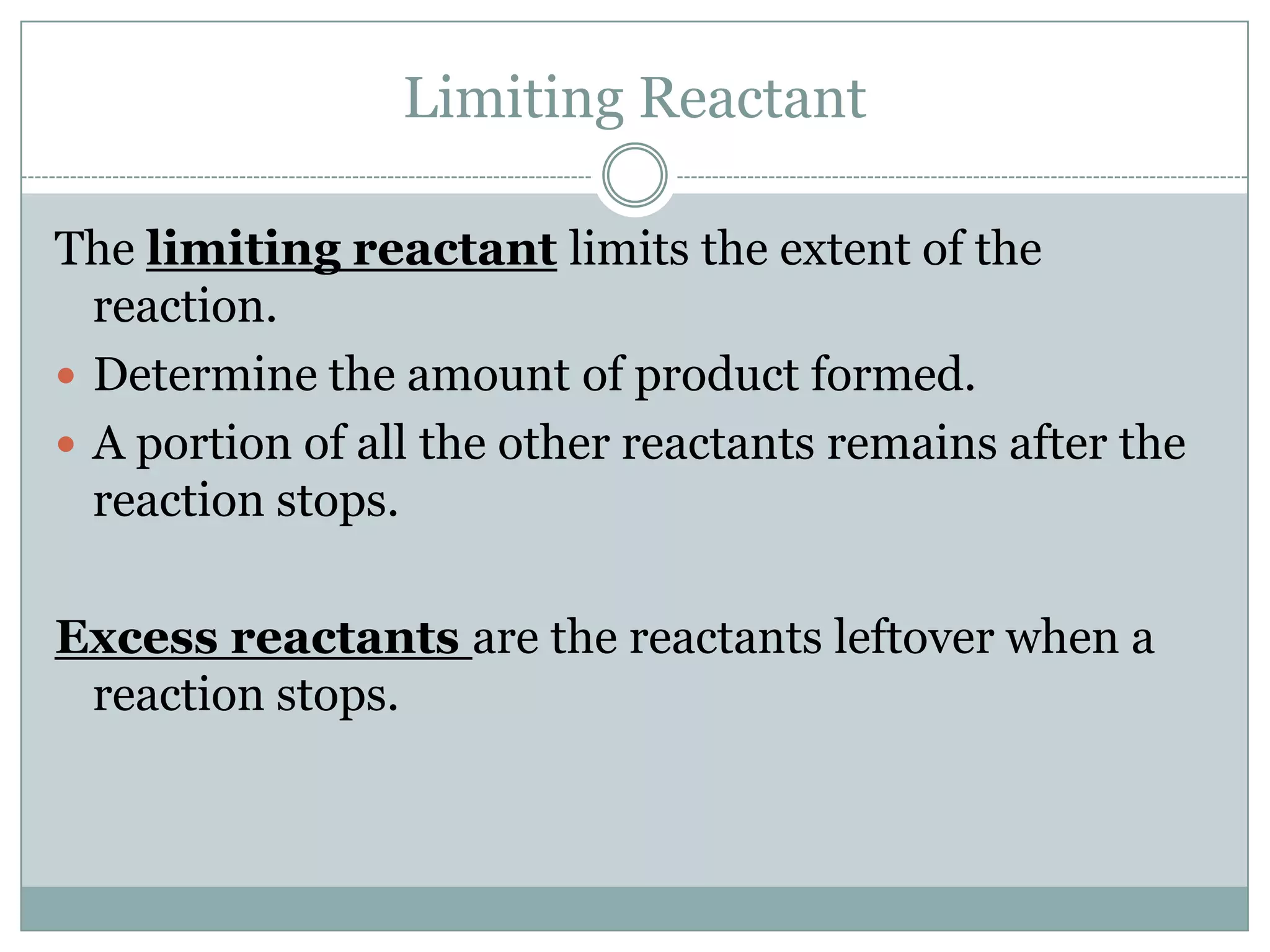
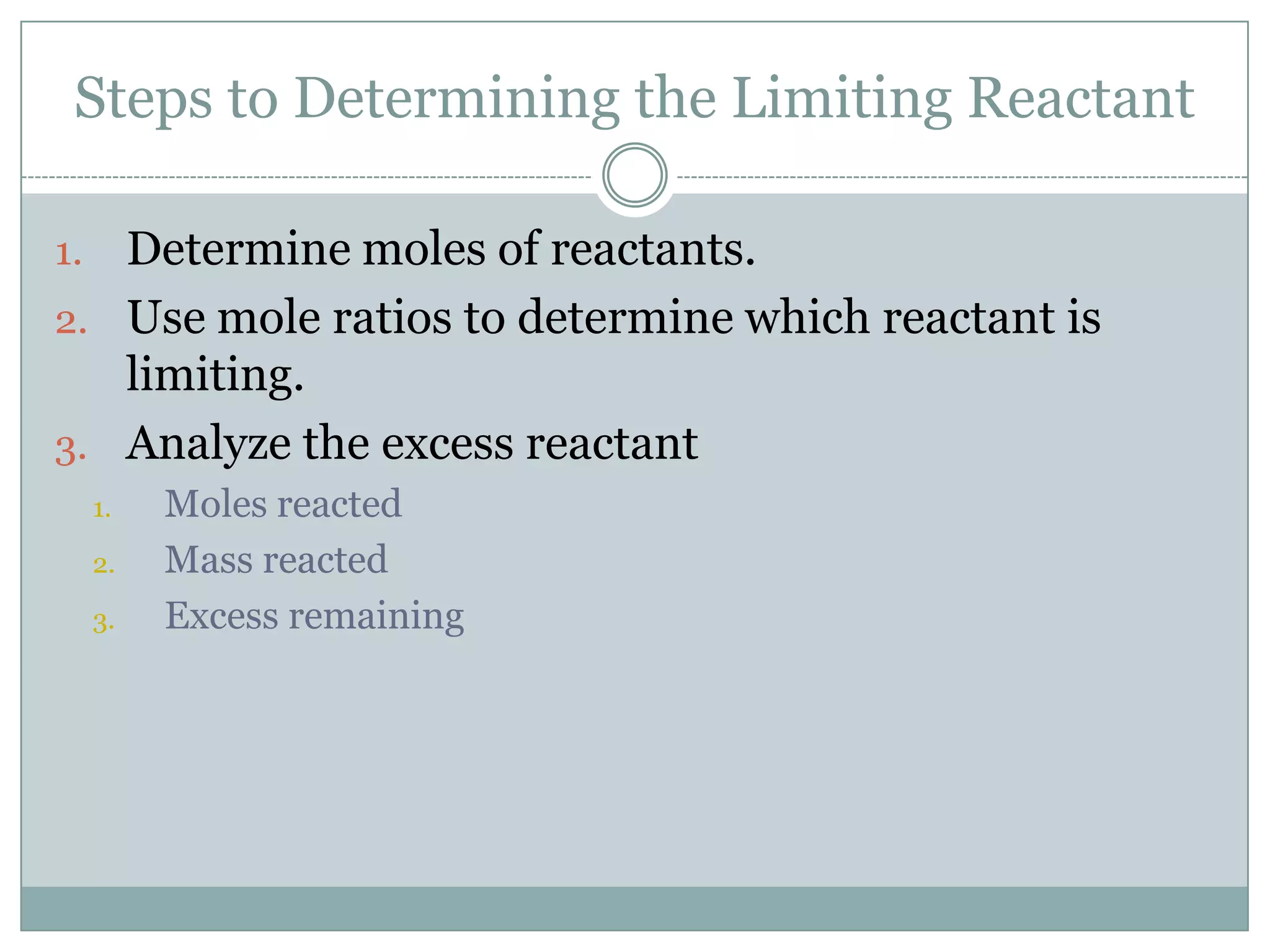
2) Limiting reactants determine the maximum amount of product that can be formed
3) Excess reactants remain after the limiting reactant is used up in the reaction