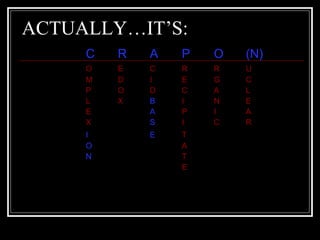
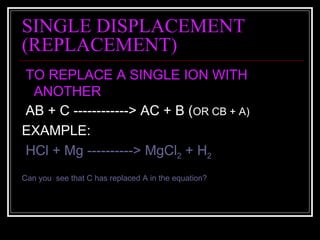
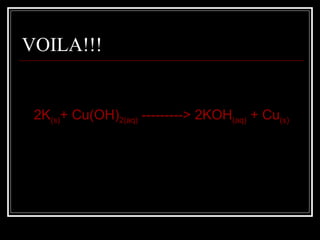
A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction that balances the reactants and products to show the states of matter. Chemical equations can be classified into different types of reactions such as synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, and combustion. Solubility rules determine whether combining chemicals will form an insoluble precipitate.