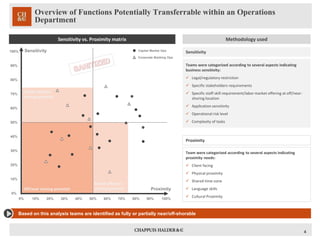
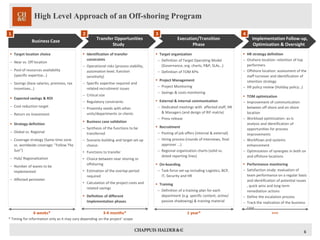
The document outlines a comprehensive study on the offshoring relocation opportunity, focusing on business drivers like cost reduction, efficiency improvements, and the creation of shared services centers. It discusses methodologies for assessing functions eligible for offshoring, key challenges, and factors for successful execution, including the importance of stakeholder engagement and performance monitoring. Additionally, it highlights the need for strategic alignment with overall business objectives to ensure a successful offshoring initiative.