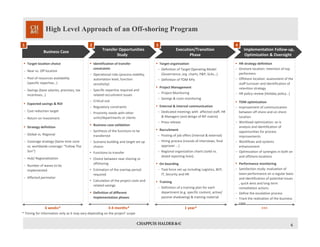
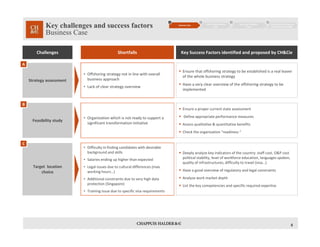
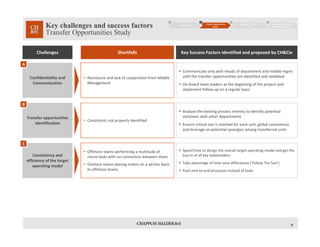
This document discusses an offshoring program and provides an overview of the key considerations and approach. It outlines the main business drivers for offshoring such as reducing costs through lower salaries and premises costs. It then presents a high-level approach involving a transfer opportunities study, execution/transition phase, and ongoing implementation follow-up and optimization. Some of the main challenges discussed include choosing the right target location, developing a clear strategy, identifying all transfer opportunities, ensuring a smooth transition of processes, and recruiting and retaining skilled resources in the offshore location. Success factors center around thorough planning, clear communication, consistency in the target operating model, and change management.