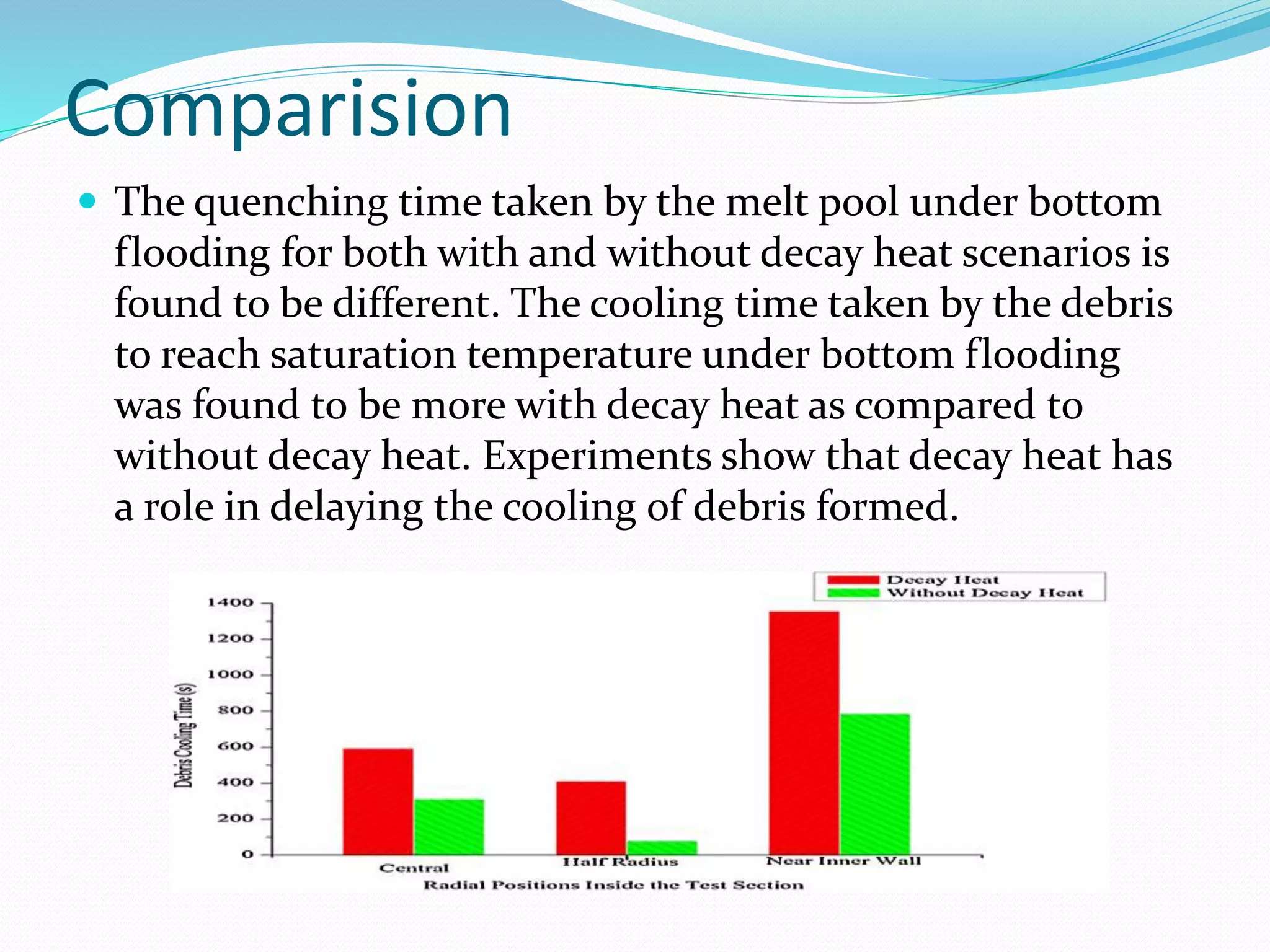
Experiments are carried out to analyze corium simulant materials. Calcium oxide and boron trioxide mixtures are used as simulants in varying weight percentages. The mixtures are ball milled and heat treated at different temperatures before characterization. Techniques like FTIR, UV-Vis-IR and DSC are used to analyze the samples' thermal and vibrational properties. Bottom flooding is found to be the most effective method for cooling corium, taking only a few minutes compared to hours for other methods. Decay heat is also found to delay cooling.



![Nuclear safety
Nuclear safety defined as “The achievement of proper operating
conditions, prevention of accidents or mitigation of accident
consequences, resulting in protection of workers, the public and
the environment from undue radiation hazards".[1]
The IAEA defines nuclear security as "The prevention and
detection of and response to, theft, sabotage, unauthorized
access, illegal transfer or other malicious acts involving nuclear
material, other radioactive substances or their associated
facilities.”
This covers nuclear power plants and all other nuclear facilities,
transportation of nuclear materials and the use and storage of
nuclear material for medical, power, industry and military use.
Nuclear reactor are always improved time by time, but 100 %
safety is not guaranteed. Nuclear accident can be controlled( not
100% guarantee). Nuclear safety includes cooling of corium after
melt down.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-4-2048.jpg)

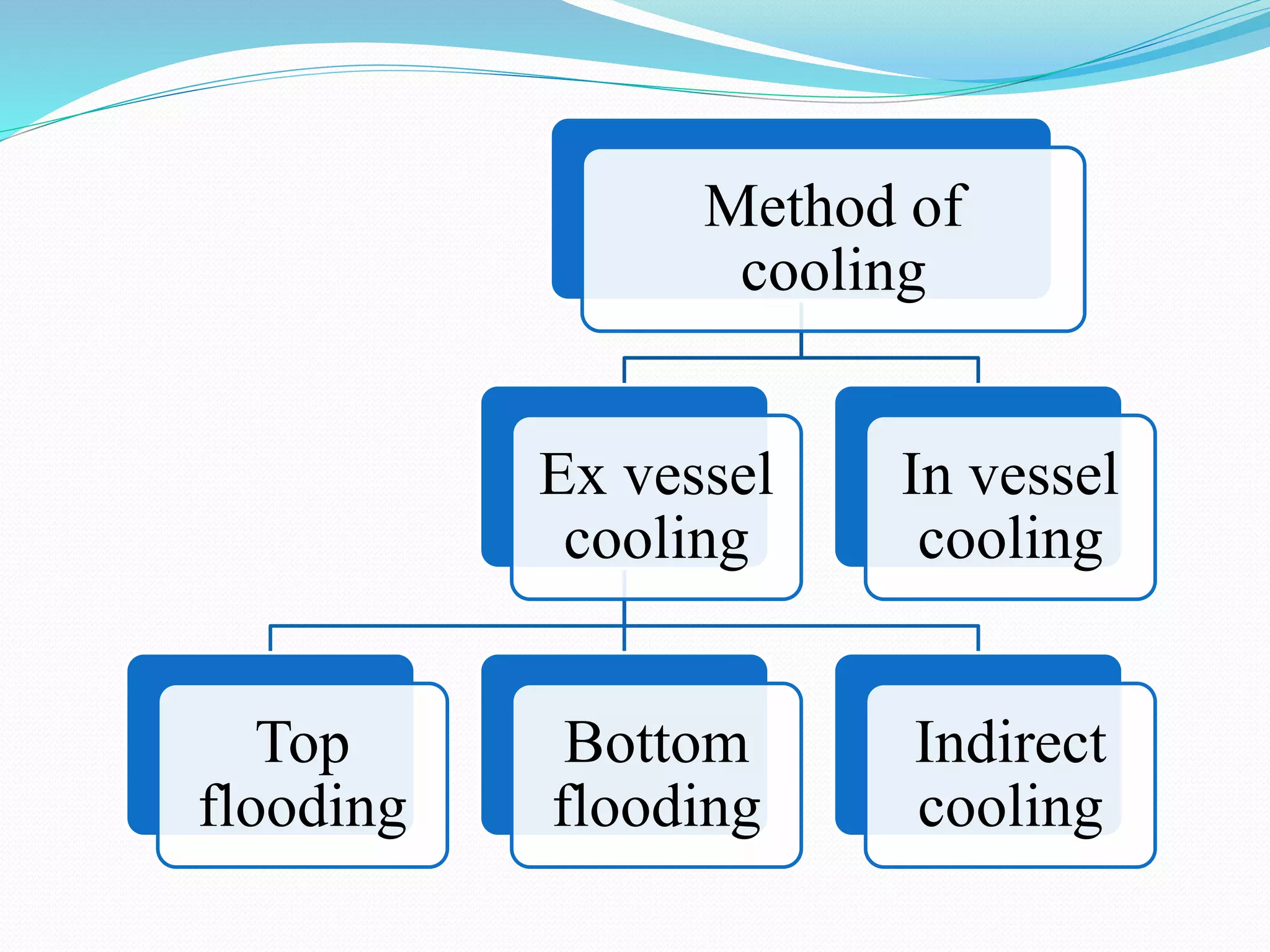
![Melt coolability
Melt coolability can be done by in-vessel and ex-vessel technique. In ex-vessel
technique, three method are top flooding, bottom flooding and indirect
flooding are classified.
Cooling method are classified in two main parts:
In vessel cooling:[8]
In vessel cooling is cooling in which cooling is done in inner part of vessel.
Ex vessel cooling:[9]
In vessel cooling is cooling in which cooling is done in outer part of vessel.
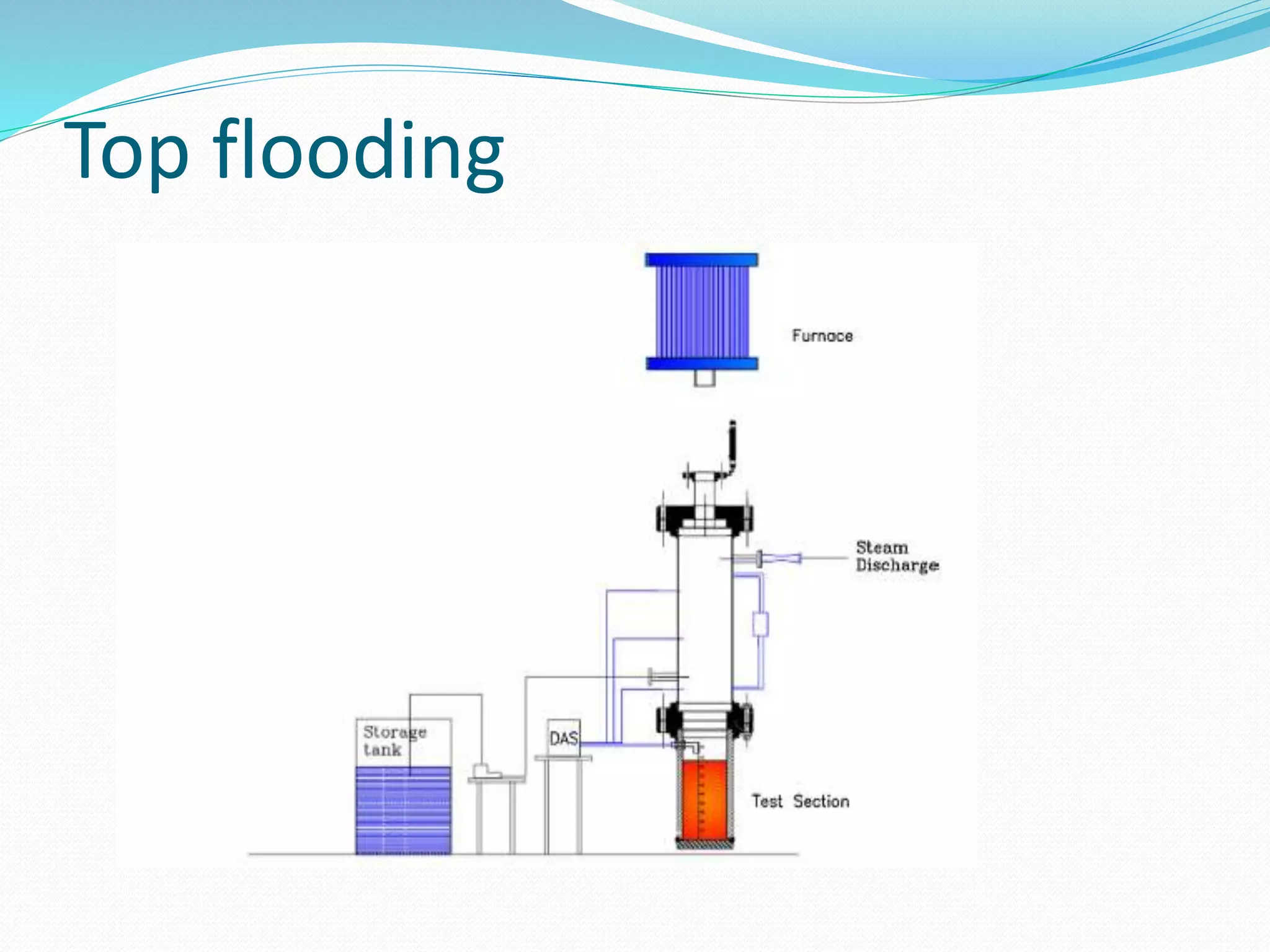
2.1.Top flooding:[10][11]
In vessel cooling is cooling in which water is flow from top of nuclear reactor.
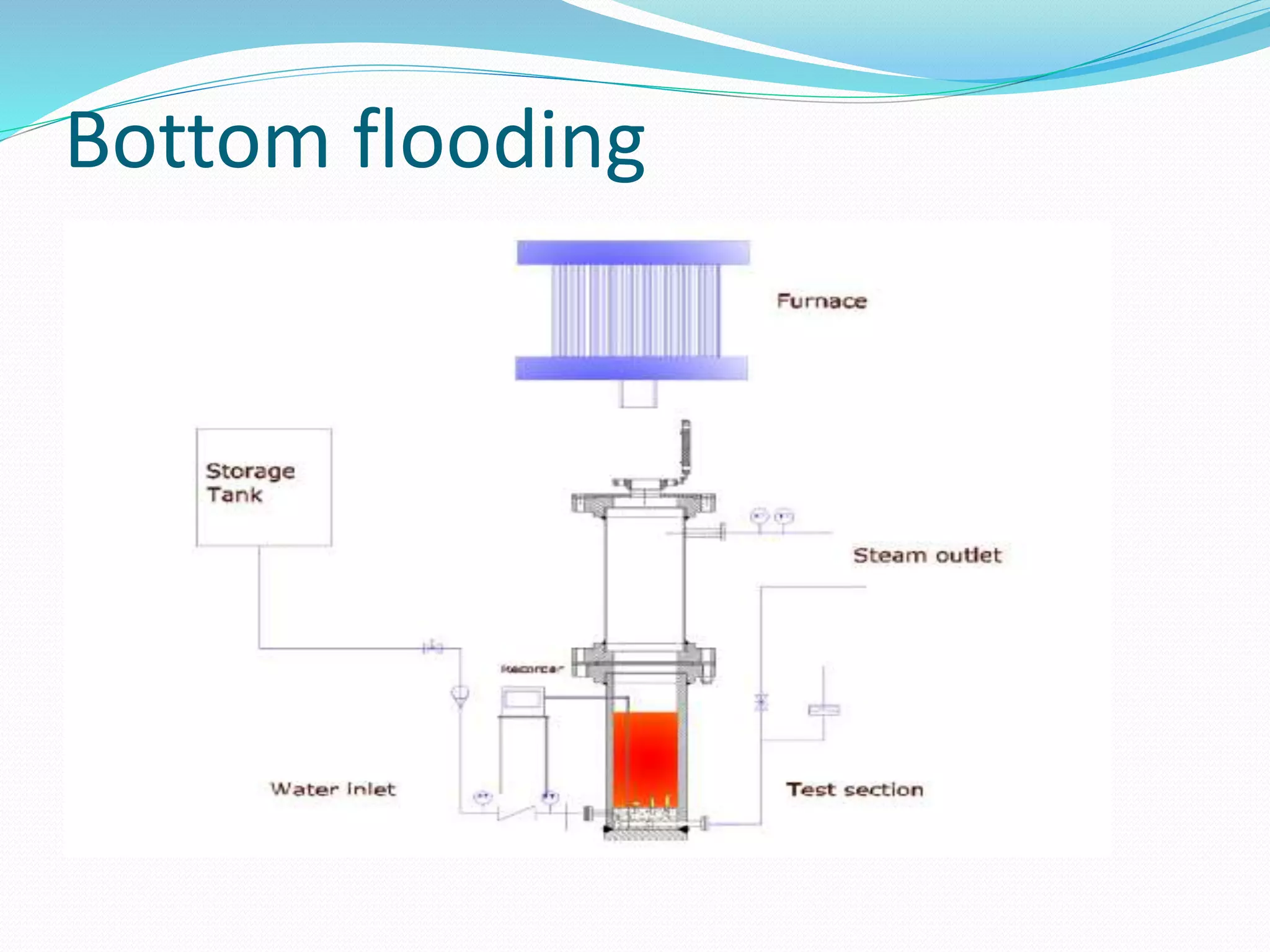
2.2.Bottom flooding:[12]
In vessel cooling is cooling in which water is flow from bottom of nuclear
reactor.
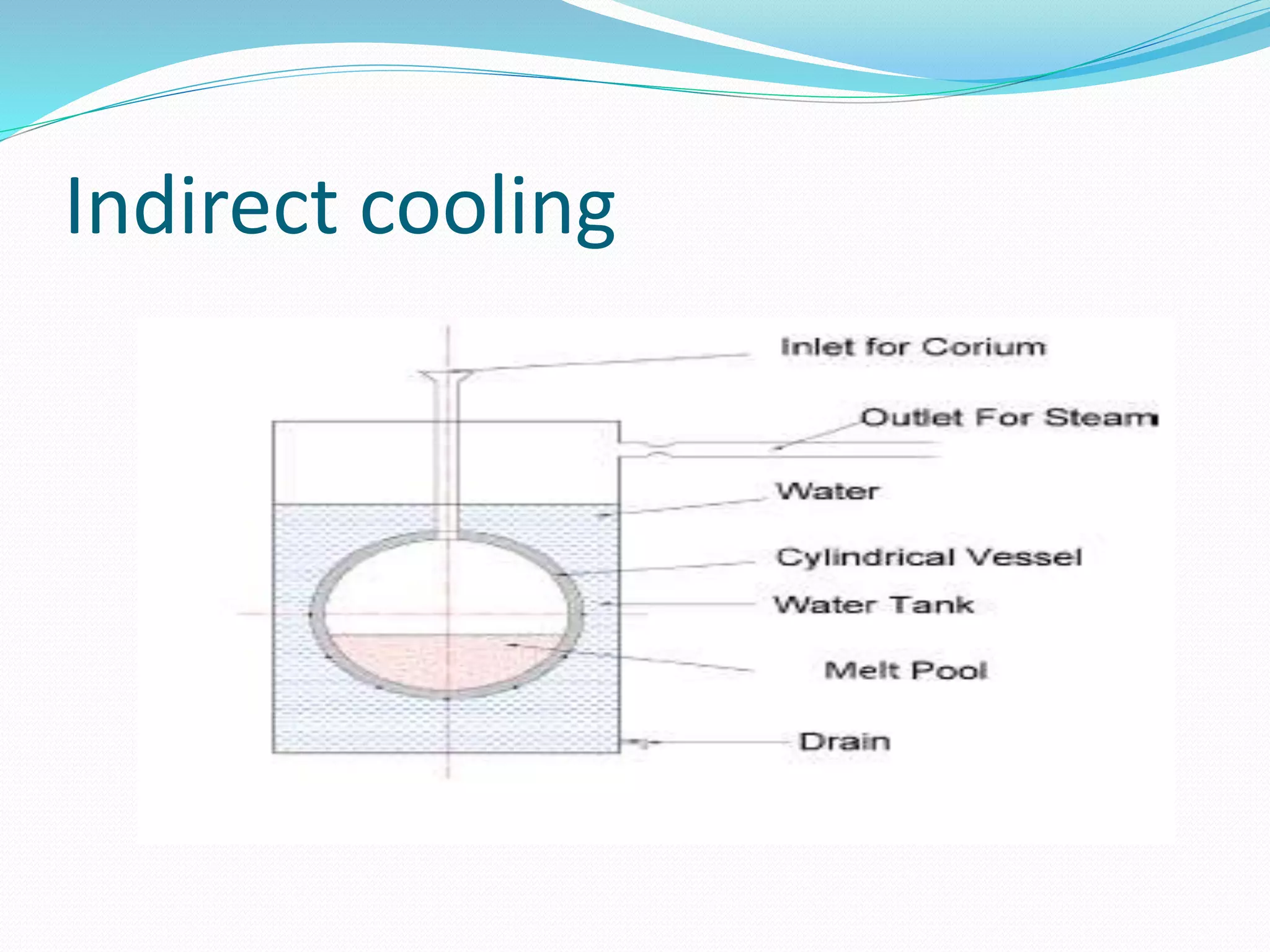
2.3.Indirect cooling:[11]
In vessel cooling is cooling in which water is flow at around of nuclear reactor.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-6-2048.jpg)






![Corium
Corium(fuel containing material) or lava like fuel
containing material is created in nuclear reactor core
during nuclear meltdown. Corium material depends on the
design, type of reactor, specifically on materials used in
control rods, coolant and reactor vessel structural
materials. It is most dangerous and most radioactive, lava
flow material in human history.
List of Different composition of Corium:[17][18][19]
Calcium oxide[33] Boron trioxide Iron(III) oxide Indium(I) oxide
Indium(II) oxide Indium(III) oxide Zirconium oxide
Uranium oxide CaO-B2O3 (by 30:70 weight percentage)
Sodium + borosilicate UO2 + ZrO3 (by 80:20 weight percentage)
Al2O3:10.7%,CaO:13.6%,Fe2O3:3.21%,MgO:1.0%,K2O:2.41%,SiO2:59.0%,Na2
O:1.89%,TiO2:0.6% and H2O: 5.28%.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-18-2048.jpg)


![Ball milling
Ball milling is milling or abrasion process used to properly
mix powder or to reduce powder size. [44][45] In this case, no
milling is done and there is no reduction in powder size.
For powder mixing, rotation speed of 100 rpm is taken and
time for mixing is 1 hour. Ball weight to powder weight ratio
is 3:1. Powder weight is 20 gm and ball weight is 60 gm.Low
speed is taken for mixing purpose and high speed is taken
for milling purpose.[49]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-21-2048.jpg)


![FTIR
Fourier Transform Infra-Red spectroscopy (FTIR) is technique used to obtain
infrared spectrum of absorption or emission of solid, liquid or gas.[46][71][72][73]
FTIR spectrometer simultaneously collects high spectral resolution data over
wide spectral range (in our cases we use wavelength from 400 cm-1 to 4000 cm-
1) [47]. This confers significant advantage over dispersive spectrometer, which
measures intensity over a narrow range of wavelength at a time. [48]
The term Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy originates from fact that
Fourier transform is required to convert the raw data into the actual
spectrum.[54]
FTIR Spectrum is compact, easy to use, powerful instrument with fully
integrated, universal sampling system for measurements in the range of 4000-
400 cm-1 for liquid (KBr cell) and solid (KBr pellets) samples. FTIR machine
used to get FTIR spectrum is shown in figure.
FTIR is used for following applications:
Pharmaceuticals and Nutraceuticals[54] , IR sampling, spectral and field based
analysis[61][66][69] , Polymers, Environmental[55], In-service lubricants and fuels.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-25-2048.jpg)

![UV Vis IR
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy (UV–Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or
reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region.[46] This
means it uses light in the visible and adjacent ranges.[47] The absorption or
reflectance in the visible range directly affects perceived color of the
chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic
spectrum, atoms and molecules undergo electronic transitions.[48] Absorption
spectroscopy is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in
that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground
state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the
excited state.[58]
UV Vis IR machine is shown in figure. LAMBDA 750 (Perkin Elmer) UV-Vis
NIR Spectrophotometer instrument is a bench-top, true double-beam, double-
monochromator design providing high stability & accuracy performance for
samples in the area of chemical sciences, biochemistry, materials science,
nanoscience and technology.
UV Vis IR machine’s uses are following:
4.2.1.Use:
Application areas range from surface characterization of solids to the
photometric analysis of turbid, colloidal, transparent and translucent samples.
Typical uses encompass quality assurance testing and product development
measurements on textiles, dyes, paper and glass.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-27-2048.jpg)

![Differential scanning calorimetry
Differential scanning calorimetry is thermo-analytical technique in which difference in
amount of heat required to increase temperature of sample and reference is measured as
function of temperature.[52] Both the sample and reference are maintained at nearly the
same temperature throughout experiment.[53] Temperature program for a DSC analysis is
designed such that the sample holder temperature increases linearly as a function of
time. The reference sample should have a well-defined heat capacity over range of
temperatures to be scanned.[56]
Technique was developed by E. S. Watson and M. J. O'Neill in 1962, and introduced
commercially at the 1963 Pittsburgh conference. First adiabatic differential scanning
calorimeter that could be used in biochemistry was developed by P. L. Privalov and D. R.
Monaselidze in 1964 at Institute of Physics in Tbilisi, Georgia. Term DSC was coined to
describe this instrument, which measures energy directly and allows precise
measurements of heat capacity.
Types of DSC:
Power-compensated DSC, keeps power supply constant and Heat-flux DSC, keeps heat flux
constant
DSC is be done by NETZSCH DSC machine.This machine is shown in figure. It uses
Nitrogen environment with 60 ml/minute. Crucible used is DSC/TG pan Al2O3.
Use:
Melting/crystallization behaviour , Solid-solid transitions , Polymorphism , Glass
transitions , Cross linking reactions , Oxidative stability, Purity determination, Specific
heat and Thermo-kinetics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-29-2048.jpg)

![FESEM
Microscopy techniques are used to produce real-space magnified images of a
surface showing what it looks like.[42][38] In general, microscopy information
concerns surface crystallography(how the atoms are arranged at the surface)[47],
surface morphology (shape and size of topographic features making the
surface), [49] and surface composition (elements and compounds the surface is
composed of). [50][51]
Field-emission microscopy (FEM) was invented by Erwin Müller in 1936. In
FEM, the phenomenon of field electron emission was used to obtain an image
on the detector on the basis of the difference in work function of the various
crystallographic planes on the surface.
Nova Nano FE-SEM 450 (FEI) provides ultra high resolution characterization &
analysis giving precise, true nanometer scale information.
Advanced optics & detection, including beam deceleration, in lens ETD(SE),
TLD (custom), lens mounted DBS & LVD offer best selection of information &
image optimization. Beam landing energy can go down from 30 keV to 50 eV. 3.
It gives a resolution of 1.4 nm at 1 kV (TLD-SE) & 1 nm at 15 kV (TLD-SE). The
FE-SEM is coupled to EDAX detector for measuring the elemental chemical
composition of materials. FESEM machine is shown in figure.
FESEM can be used for following applications:
Applications: Metallic materials[43] Ceramics and composites, Polymeric
materials, Geology and mineralogy , Dental materials and Electrolyte[57]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-31-2048.jpg)



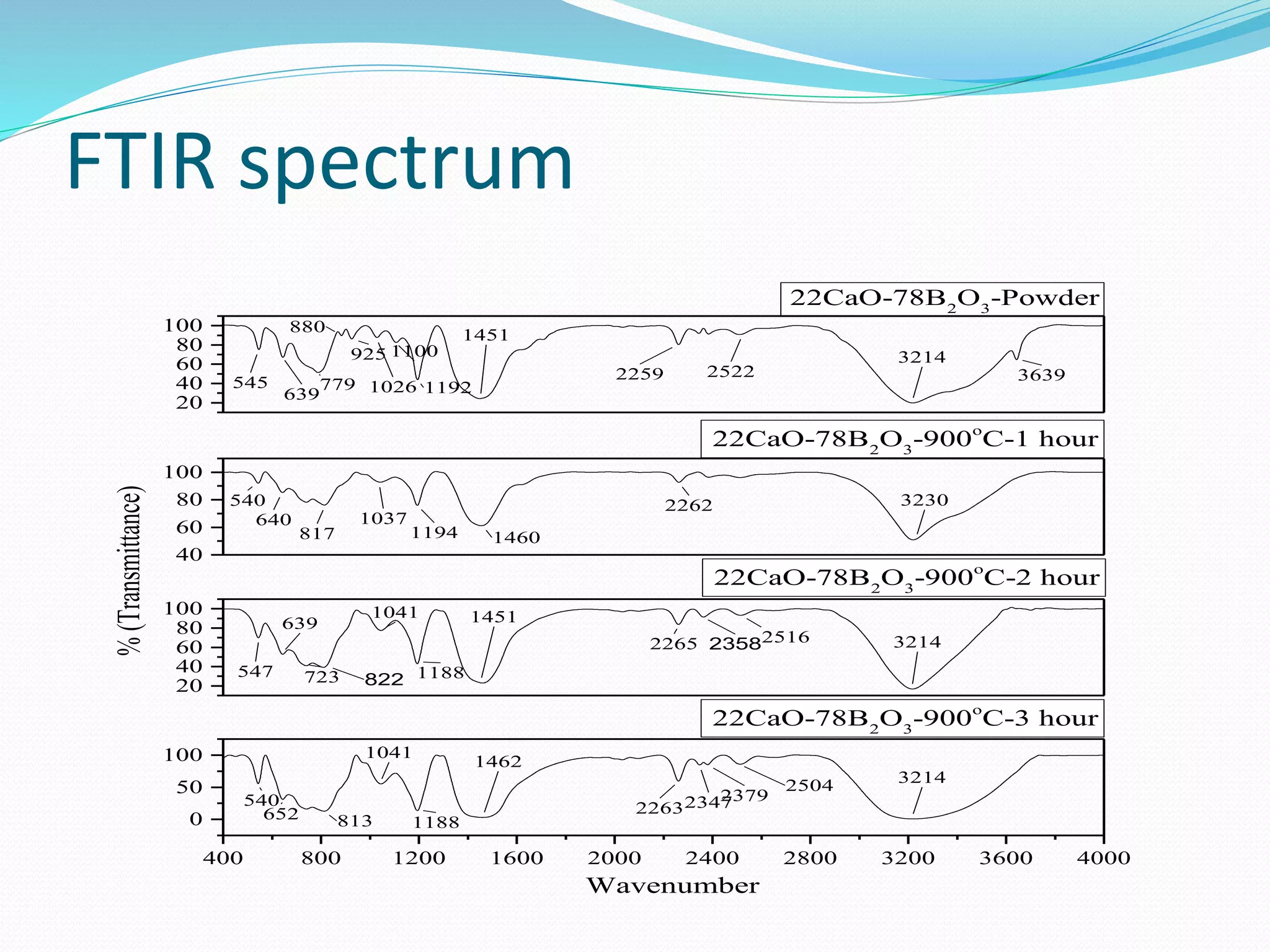
![FTIR analysis
The broad bands are due to combination of factors such as high degeneracy of
vibrational state, thermal broadening of lattice dispersion band and also
mechanical scattering in the debris glass. CaO[30][35] and B2O3[38][40][41][42]
are shown in mixture. The band at around 540 cm-1 is assigned to the
characteristic vibration of Ca cation[8][9][10]In the infrared spectral region,
the vibrational modes of borate show three regions , the first region at 1200-
1600 cm-1 band is due to an asymmetric stretching of relaxation of the B-O
bond of trigonal BO3 units, the second region at 800-1200 cm-1 due to the B-O
bond stretching of tetrahedral BO4 units[3], and third region bands at 600-800
cm-1 is originating from the bending vibrations of B-O-B linkages in borate
network.[4] In the present debris of glass, the absence of peak at 800 cm-1
indicates the absence of boroxol ring.[5] The substitution of boroxol rings by
triborate and tetraborate groups has been observed.[6]
Broad band at 3200 cm-1 is due to the hydroxyl group (due to stretching of OH-
). It’s value decrease with increase of soaking time. The band at 1400-1600 cm-1
is due the stretching of B-O bonds of various borate arrangements containing
planar six membered groups, exhibiting a compositional dependence that
originates from different species. Its value is high for 1 hour, low for 2 hour and
high for 3 hour. Big band at 1000-1200 cm-1, [3] is due to stretching vibrations of
B-O in BO4 units from tri-, tetra-, and penta borate groups. Its value increase
with increase in soaking period. At 600-800 cm-1 is originating from the
bending vibrations of B-O-B linkages in borate network[4]. Its value low for 1
hour , high for 2 hour and again high for 3 hour. The band at 541 cm-1 is
assigned to characteristic vibration of Ca cation. Its value is low for 1 hour
,high for 2 hour and again low for 3 hour. [8][9][10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-36-2048.jpg)
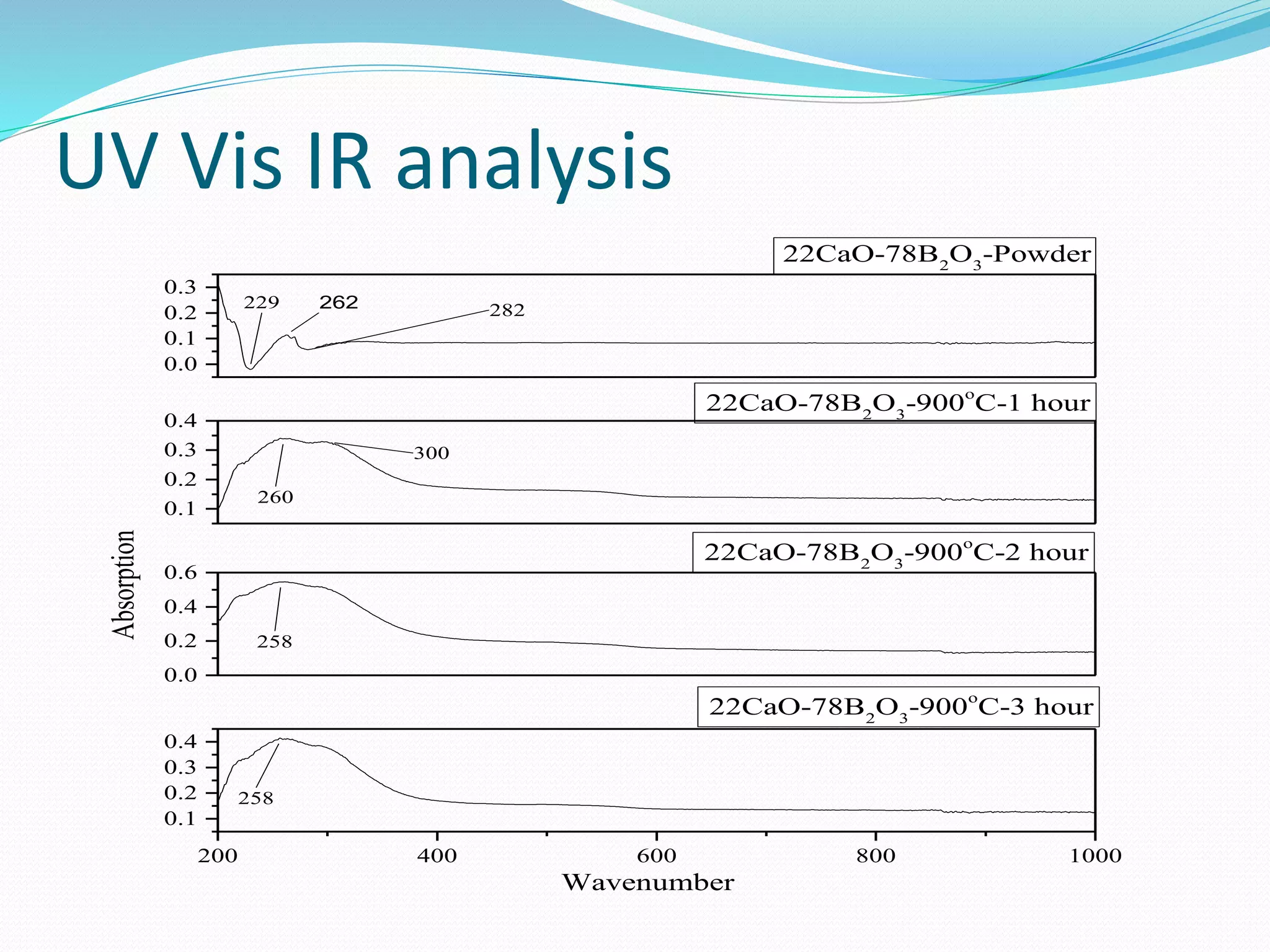
![UV Vis IR analysis
Main peak show at 260 cm-1 for 900°C and 1 hour, 258 cm-1 for
900°C and 2 hour and 260 cm-1 for 900°C and 3 hour. For initial
sample it shows peak at 229 cm-1,262 cm-1 and 282 cm-1. For
900°C and 1 hour, it shows second peak at 300 cm-1.
UV Vis show peak at 260 for 1 hour, 258 for 2 hour and 258 for 3
hour for 900°C heating temperature. Its value decreases with
increase in soaking time for same heating temperature.
The ability of a material to absorb light is measured by its optical
absorption coefficient. The spectrum of the glass film exhibits a
maximum transmittance of from 30 to 50% in the visible region.
The spectrum magnified in the inset of Fig. 2 clearly shows that
the as prepared glass samples have an intense absorption tail
within 250–270. The transmission curves can be divided broadly
into regions of strong absorption near the optical band gap and a
region with medium or weak absorption, where the effects due to
interference are observed.[3]The other transitions are not
observed because the interference pattern suppresses the effect
due to these transitions. This may be due to formation complex
oxide particles.[27]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-38-2048.jpg)
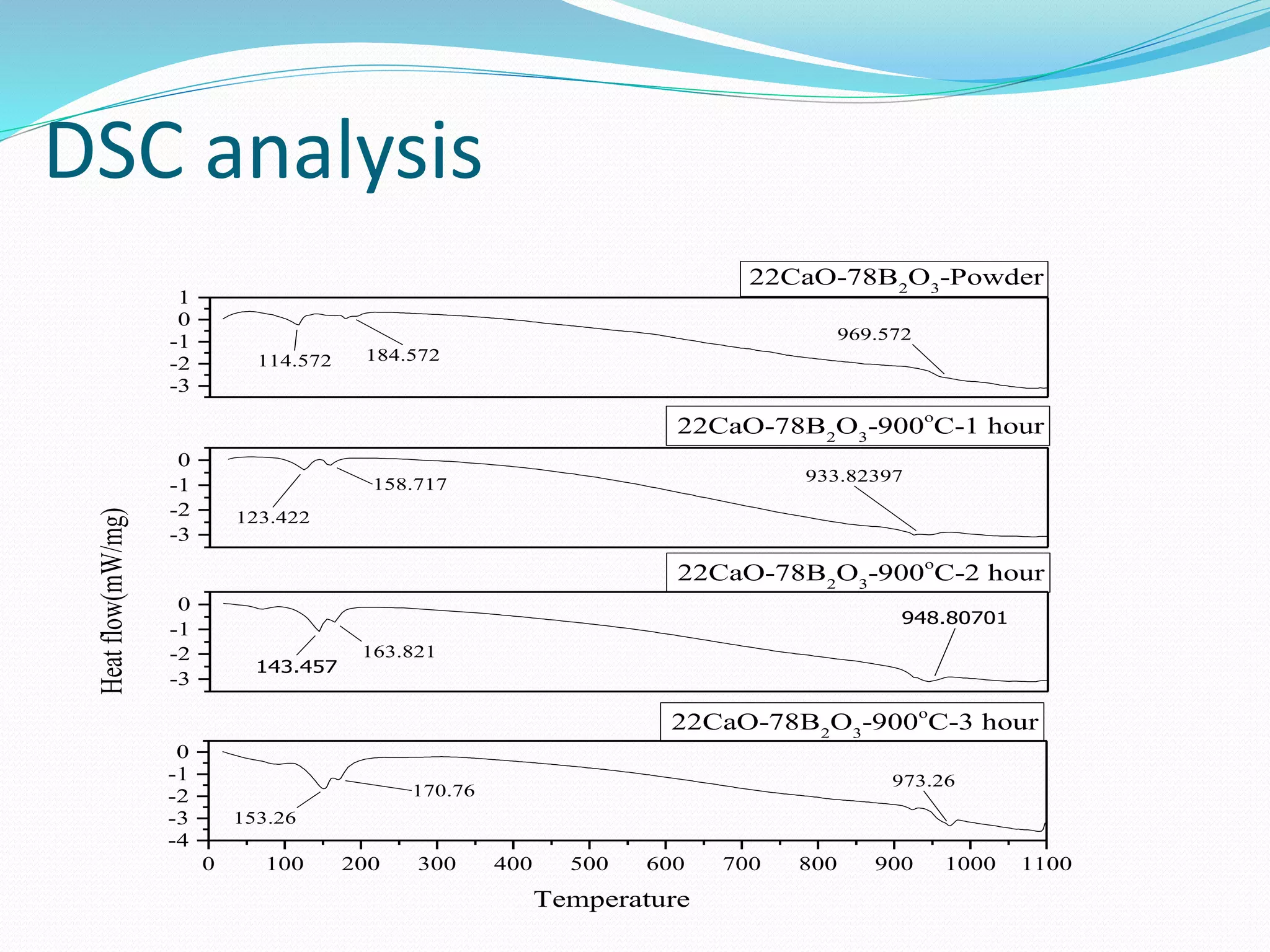
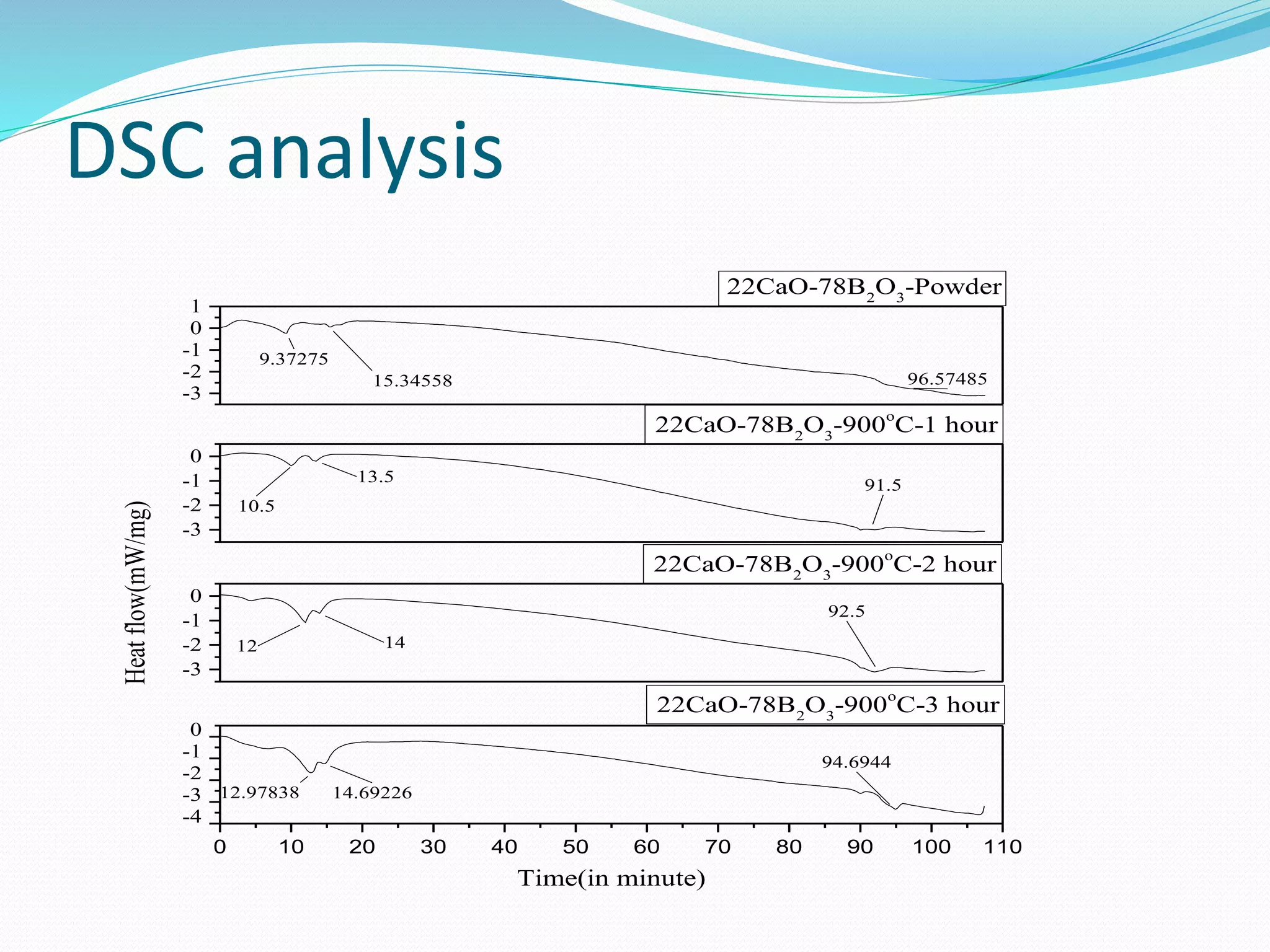
![DSC analysis
DSC curve of CaO-B2O3 debris shows in figure recorded under a
constant heating rate of 10 K/min. A glass debris composition of CaO-
B2O3 exhibited a glass transition marked by endothermic base line shift
within the temperature range of 940- 980°C. [5][25] The glass
transition temperature of 30%CaO+ 70%B2O3 was 745± 2 °C. The sharp
crystallization peaks was observed at 960±10 °C.
For intial sample peak position at 962°C. [5][25] For 900°C-1hour, its
position at 933°C, For 900°C-2hour, its position at 948°C, For 900°C-
3hour, its position at 973°C. Peak position shows melting point for
respective sample. This is mixture of Calcium oxide and boron trioxide,
so it takes time for melting. Melting point can not be defined as single
point, but it takes range of temperature for melting. In our case, it takes
950°C to 970°C.
For same heating temperature, its value increase with increase in
soaking period.
For powder initial peak position at 114°C and 182°C. For 900°C-1hour, its
initial position at 123°C and 158°C, For 900°C-2hour, its initial position
at 143°C and 163°C, For 900°C-3hour, its initial position at 153°C and
170°C. Initial Peak position shows melting of water moisture and
impurity for respective sample. Water moisture and impurity mixture
are melted and having peak at approximate above 100°C. Second peak
observed at approximate 160°C to 180°C. It’s because of impurity.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-41-2048.jpg)
![Structural analysis
Analysis of SEM images are shown above. [1][6][7][8][10] This are images generated by
Nova Nano FE-SEM 450 (FEI) machine. EDS can be done by EDAX detector. It gives
elemental chemical composition of material. By elemental analysis, we conclude that we
have CaO and B2O3 in composition. All experiments are done at high voltage 15 kV and 30
kV respectively, so we have resolution of 1 nm for 15 kV. It uses low vaccum mode,
pressure of 6.58*10-3 and 2.27*10-3 Pascal respectively. All images are generated at
different magnification of 500X,1000X,2000 X, 2500 X, 5000 X, 10000 X, 20000 X, 30000
X and 50000 X and for different resolution from 1 micrometer to 100 micometer. But, we
only compare results for resolution of 5 micrometer, 50 micrometer and 100 micrometer.
The surface morphology of CaO-B2O3 mixture for initial sample and after heat treatment
are shown in figure. The energy dispersion spectrum of the present glass samples
revealed the existence of different non-crystalline phases.[42] The surface area and
porosity of sorbents are important structural parameters, because the sorbents sorption
performance has directly relationship with these structures.[36] Surface morphology
confirmed that elements present in the samples are Ca,B and O as shown in figure. It
have homogeneous surface morphology. Fine microstructure with extremely small pores
distributed homogenously found in mixture. It consist of 78 mole% B2O3 and 22% mole
percentage of CaO.[31][32] It consist of CaO and B2O3 identified by FTIR.[39] Heat
treatment is done for different heating temperature and for same soaking time. Heat
treatment is done for same heating temperature and for different soaking time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-43-2048.jpg)


![FTIR analysis
The broad bands are due to combination of factors such as high
degeneracy of vibrational state, thermal broadening of lattice
dispersion band and also mechanical scattering in the debris
glass. CaO[30][35] and B2O3[38][40][41][42] are shown in
mixture. The band at around 540 cm-1 is assigned to the
characteristic vibration of Ca cation[8][9][10]In the infrared
spectral region, the vibrational modes of borate show three
regions , the first region at 1200-1600 cm-1 band is due to an
asymmetric stretching of relaxation of the B-O bond of trigonal
BO3 units, the second region at 800-1200 cm-1 due to the B-O
bond stretching of tetrahedral BO4 units[3], and third region
bands at 600-800 cm-1 is originating from the bending vibrations
of B-O-B linkages in borate network.[4] In the present debris of
glass, the absence of peak at 800 cm-1 indicates the absence of
boroxol ring.[5] The substitution of boroxol rings by triborate
and tetraborate groups has been observed.[6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-46-2048.jpg)
![FTIR analysis
Broad band at 3200 cm-1 is due to the hydroxyl group (due to
stretching of OH-). It’s value is highest for 800°C, low at 900°C
and again high at 950°C. The band at 1400-1600 cm-1 is due the
stretching of B-O bonds of various borate arrangements
containing planar six membered groups, exhibiting a
compositional dependence that originates from different species.
It’s value is lowest for 800°C, high at 900°C and again low at
950°C. Big band at 1000-1200 cm-1, [3] is due to stretching
vibrations of B-O in BO4 units from tri-, tetra-, and penta borate
groups. Its value decrease with increase in heating temperature.
At 600-800 cm-1[4] is originating from the bending vibrations of
B-O-B linkages in borate network. It’s value is lowest for 800°C,
high at 900°C and again low at 950°C. The band at 541 cm-1 is
assigned to characteristic vibration of Ca cation. Its value
decrease with increase in heating temperature. [8][9][10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-47-2048.jpg)
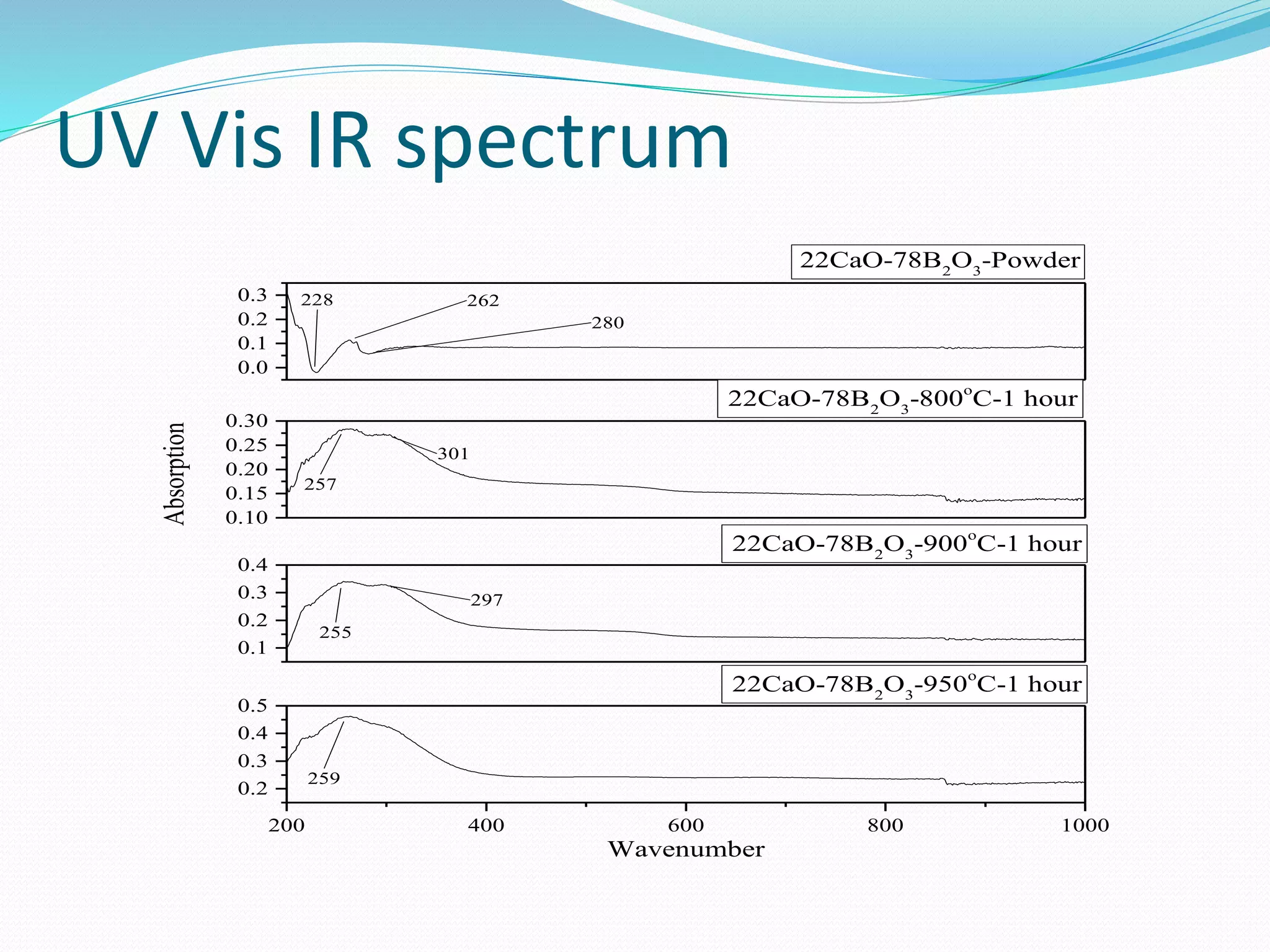
![UV Vis IR
Main peak show at 257 cm-1 for 800°C and 1 hour, 255 cm-1 for 900°C
and 1 hour and 259 cm-1 for 950°C and 1 hour.[3][4][27] For initial
sample it shows peak at 228 cm-1,262 cm-1 and 280 cm-1. For 800°C and 1
hour, 900°C and 1 hour , it shows second peak at 301 cm-1 and 297 cm-1
respectively.
UV Vis IR spectra shows peak at 258±3 cm-1. Its value is high for 800°C,
low for 900°C and again high for 950°C for same soaking time.
The ability of a material to absorb light is measured by its optical
absorption coefficient. The spectrum of the glass film exhibits a
maximum transmittance of from 30 to 50% in the visible region. The
spectrum magnified in the inset of Fig. 2 clearly shows that the as
prepared glass samples have an intense absorption tail within 250–270.
The transmission curves can be divided broadly into regions of strong
absorption near the optical band gap and a region with medium or
weak absorption, where the effects due to interference are
observed.[3]The other transitions are not observed because the
interference pattern suppresses the effect due to these transitions. This
may be due to formation complex oxide particles.[27]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-48-2048.jpg)
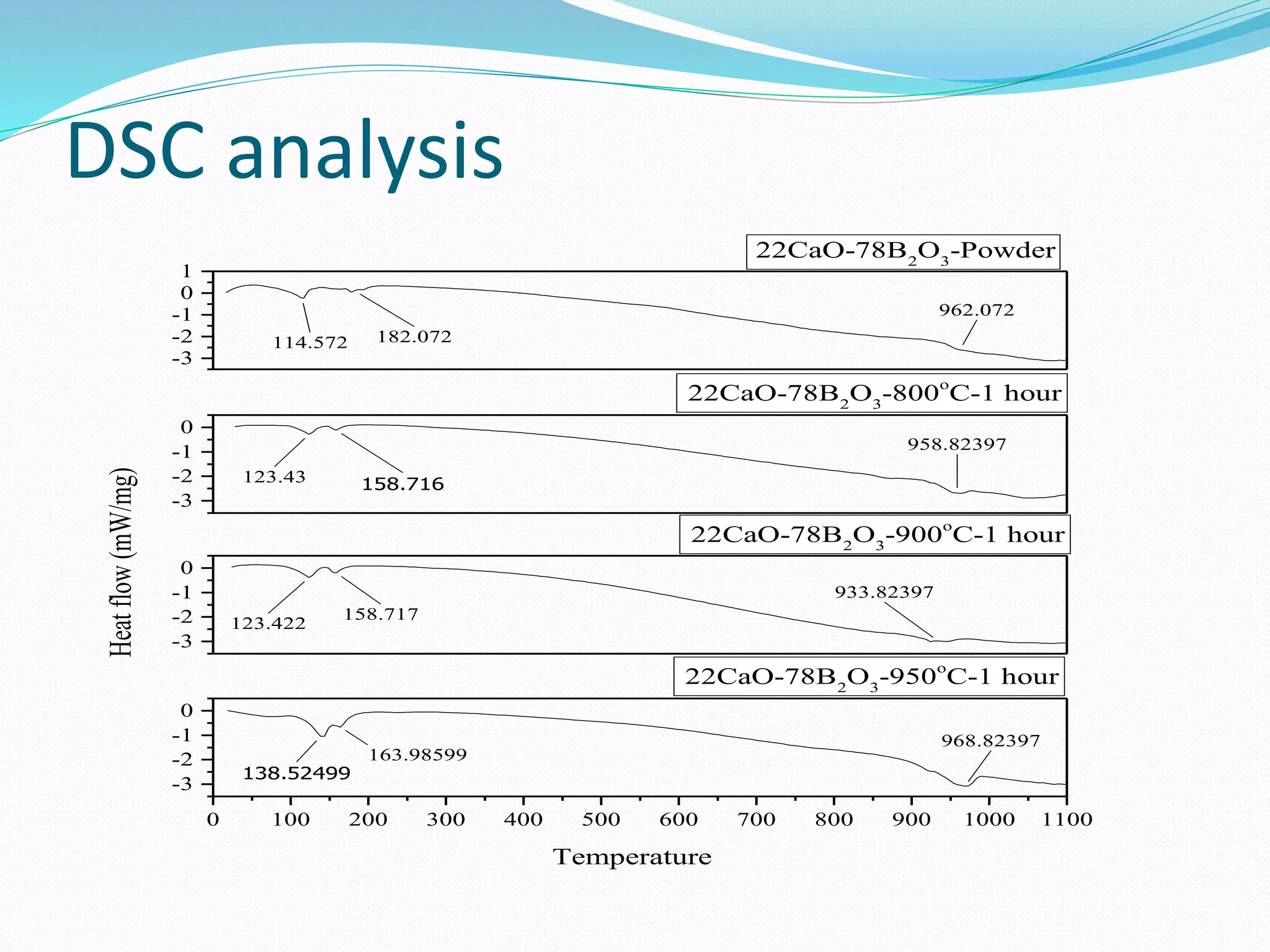
![DSC analysis
DSC curve of CaO-B2O3 debris shows in figure recorded under a constant
heating rate of 10 K/min. A glass debris composition of CaO-B2O3 exhibited a
glass transition marked by endothermic base line shift within the temperature
range of 940- 980°C. [5][25] The glass transition temperature of 30%CaO+
70%B2O3 was 745± 2 °C. The sharp crystallization peaks was observed at 960±10
°C.
For intial sample peak position at 962°C. For 800°C-1hour, its position at 958°C,
For 900°C-1hour, its position at 933°C, For 950°C-1hour, its position at
962°C.[5][25] Peak position shows melting point for respective sample. This is
mixture of Calcium oxide and boron trioxide, so it takes time for melting.
Melting point can not be defined as single point, but it takes range of
temperature for melting. In our case, it takes 950°C to 970°C.
For same soaking time, its value high for 800°C , low for 900°C and again high
at 950°C.
For powder initial peak position at 114°C and 182°C. For 800°C-1hour, its initial
position at 123°C and 158°C, For 900°C-1hour, its initial position at 123°C and
158°C, For 950°C-1hour, its initial position at 138°C and 163°C. Initial Peak
position shows melting of water moisture and impurity for respective sample.
Water moisture and impurity mixture are melted and having peak at
approximate above 100°C. Second peak observed at approximate 160°C to
180°C. It’s because of impurity.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-50-2048.jpg)

![Structural analysis
Analysis of SEM images are shown above.[1][6][7][8][10] This are images
generated by Nova Nano FE-SEM 450 (FEI) machine. EDS can be done by
EDAX detector. It gives elemental chemical composition of material. By
elemental analysis, we conclude that we have CaO and B2O3 in composition. All
experiments are done at high voltage 15 kV and 30 kV respectively, so we have
resolution of 1 nm for 15 kV. It uses low vaccum mode, pressure of 6.58*10-3 and
2.27*10-3 Pascal respectively. All images are generated at different magnification
of 500X,1000X,2000 X, 2500 X, 5000 X, 10000 X, 20000 X, 30000 X and 50000
X and for different resolution from 1 micrometer to 100 micometer. But, we
only compare results for resolution of 5 micrometer, 50 micrometer and 100
micrometer.
The surface morphology of CaO-B2O3 mixture for initial sample and after heat
treatment are shown in figure. The energy dispersion spectrum of the present
glass samples revealed the existence of different non-crystalline phases.[42]
The surface area and porosity of sorbents are important structural parameters,
because the sorbents sorption performance has directly relationship with these
structures.[36] Surface morphology confirmed that elements present in the
samples are Ca,B and O as shown in figure. It have homogeneous surface
morphology. Fine microstructure with extremely small pores distributed
homogenously found in mixture. It consist of 78 mole% B2O3 and 22% mole
percentage of CaO.[31][32] It consist of CaO and B2O3 identified by FTIR.[39]
Heat treatment is done for different heating temperature and for same soaking
time. Heat treatment is done for same heating temperature and for different
soaking time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-54-2048.jpg)


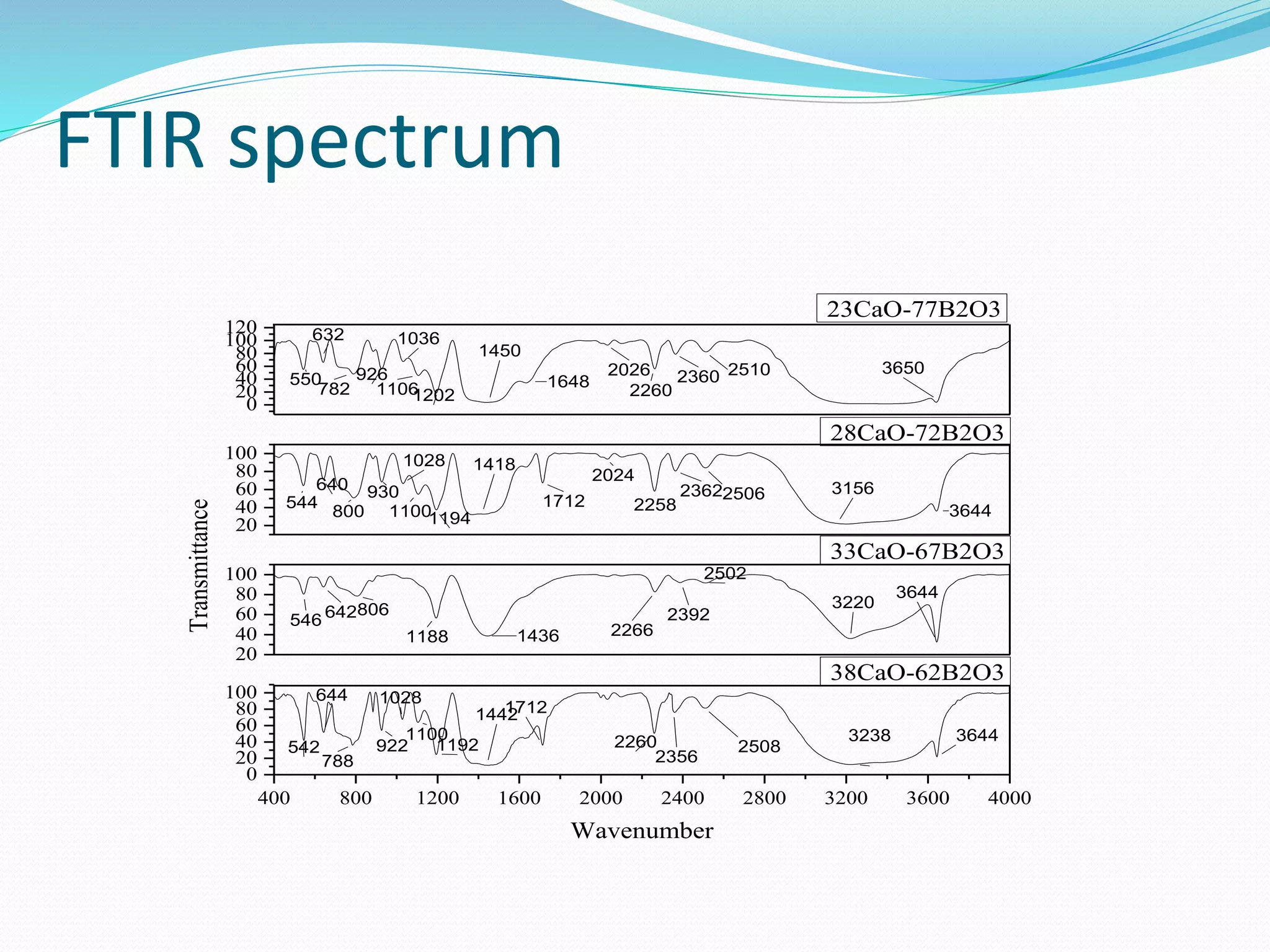
![FTIR analysis
23%CaO-77%B2O3:
FTIR peak show at 3650,
2516,2360,2260,2026,1648,1450,1202,1106,1036,926,782,632 and 550 cm-1. The
band at 550 cm-1 is assigned to the characteristic vibration of Ca
cation[8][9][10]. The band at 632 cm-1 is due to the bending vibrations of B-O-B
linkage in the borate network, a big band at 1202 cm-1, is due to stretching
vibrations of B-O in BO4 units from tri-, tetra-, and penta borate groups. The
band at 1450 cm-1 is due the stretching of B-O bonds of various borate
arrangements containing planar six membered groups, exhibiting a
compositional dependence that originates from different species.
28%CaO-72%B2O3:
FTIR peak show at
3644,3156,2506,2362,2258,2024,1712,1418,1194,1100,1028,930,800,640 and 544 cm-
1. The band at 544 cm-1 is assigned to the characteristic vibration of Ca
cation[8][9][10]. The band at 640 cm-1 is due to the bending vibrations of B-O-
B linkage in the borate network, a big band at 1194 cm-1, is due to stretching
vibrations of B-O in BO4 units from tri-, tetra-, and penta borate groups. The
band at 1418 cm-1 is due the stretching of B-O bonds of various borate
arrangements containing planar six membered groups, exhibiting a
compositional dependence that originates from different species. Broad band
at 3156 cm-1 is due to the hydroxyl group (due to stretching of OH-).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-58-2048.jpg)
![FTIR analysis
33%CaO-67%B2O3:
FTIR peak show at 3644,3220,2562,2392,2266,1436,1188,806,642 and 546 cm-1. The band
at 546 cm-1 is assigned to the characteristic vibration of Ca cation[8][9][10]. The band at
642 cm-1 is due to the bending vibrations of B-O-B linkage in the borate network, a big
band at 1188 cm-1, is due to stretching vibrations of B-O in BO4 units from tri-, tetra-, and
penta borate groups. The band at 1436 cm-1 is due the stretching of B-O bonds of various
borate arrangements containing planar six membered groups, exhibiting a compositional
dependence that originates from different species. Broad band at 3220 cm-1 is due to the
hydroxyl group (due to stretching of OH-).
38%CaO-62%B2O3:
FTIR peak show at 3646, 3238,2506,2356,,2260,1712,1445,1192,1106,1028,922,788,644 and
542 cm-1. The band at 542 cm-1 is assigned to the characteristic vibration of Ca
cation[8][9][10]. The band at 644 cm-1 is due to the bending vibrations of B-O-B linkage
in the borate network, a big band at 1192 cm-1, is due to stretching vibrations of B-O in
BO4 units from tri-, tetra-, and penta borate groups. The band at 1445 cm-1 is due the
stretching of B-O bonds of various borate arrangements containing planar six membered
groups, exhibiting a compositional dependence that originates from different species.
Broad band at 3238 cm-1 is due to the hydroxyl group (due to stretching of OH-).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-59-2048.jpg)
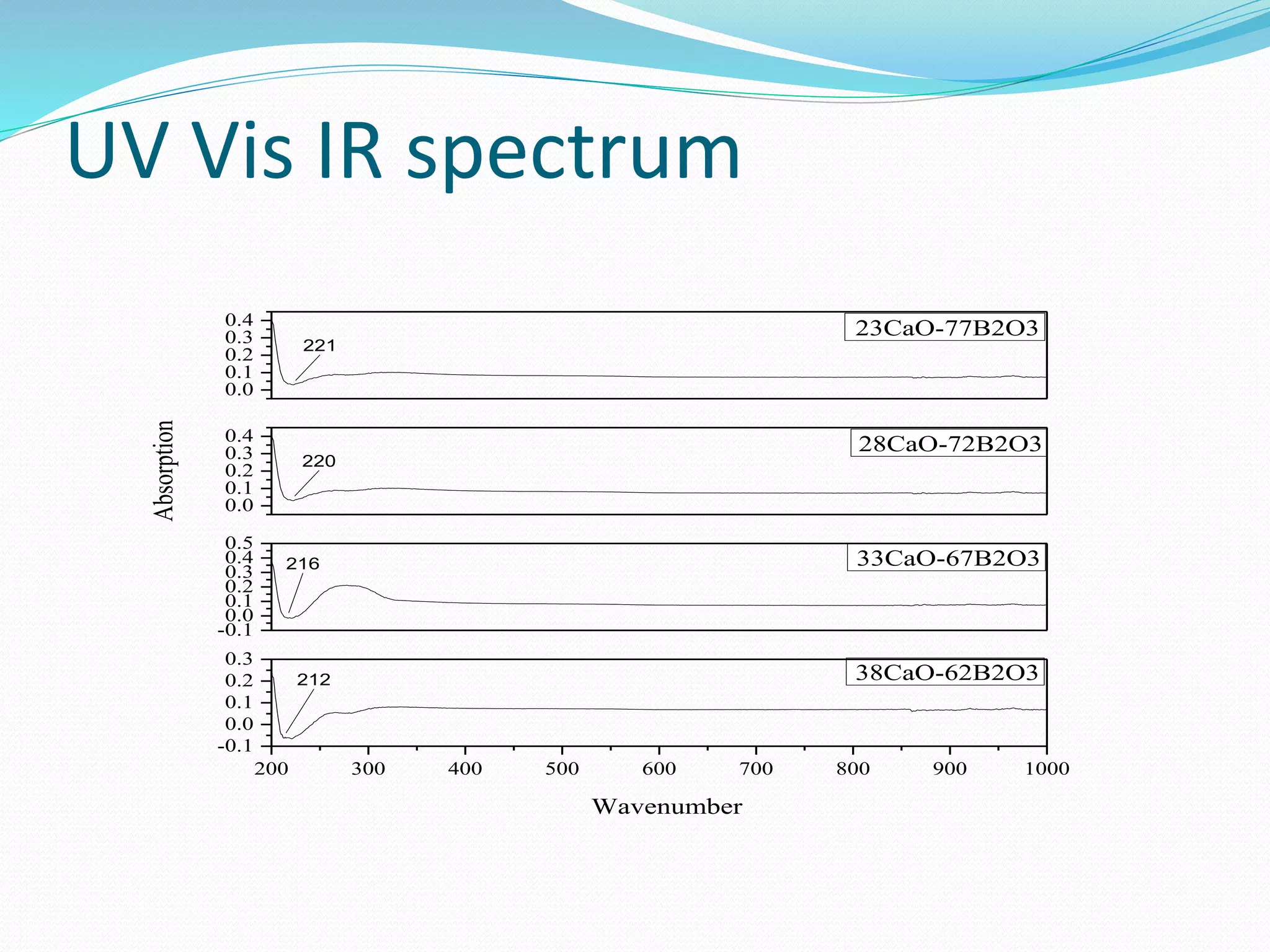
![UV Vis IR analysis
Main peak show at 221 cm-1 for 23% CaO-77% B2O3,
220 cm-1 for 28% CaO-72% B2O3, 216 cm-1 for 33% CaO-
67% B2O3 and 212 cm-1 for 38% CaO-62%
B2O3.[3][4][27]
UV Vis IR spectra shows peak at 216±5 cm-1. Its value
decreases with increase in weight percentage of
calcium oxide. Four sample made are 23%,28%,33%
and 38%.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-190513090021/75/Characterization-of-simulant-material-in-nuclear-reactor-61-2048.jpg)
