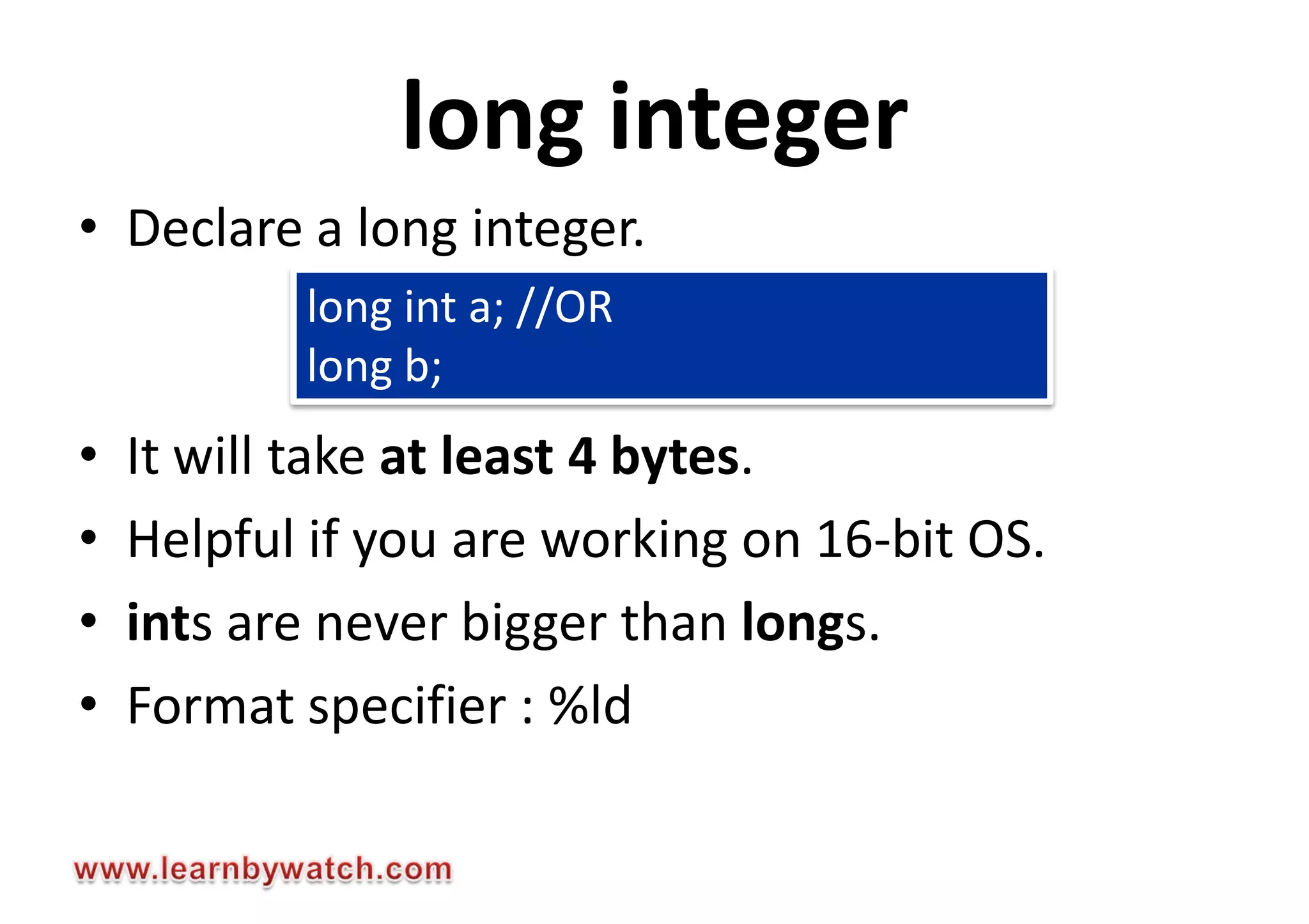
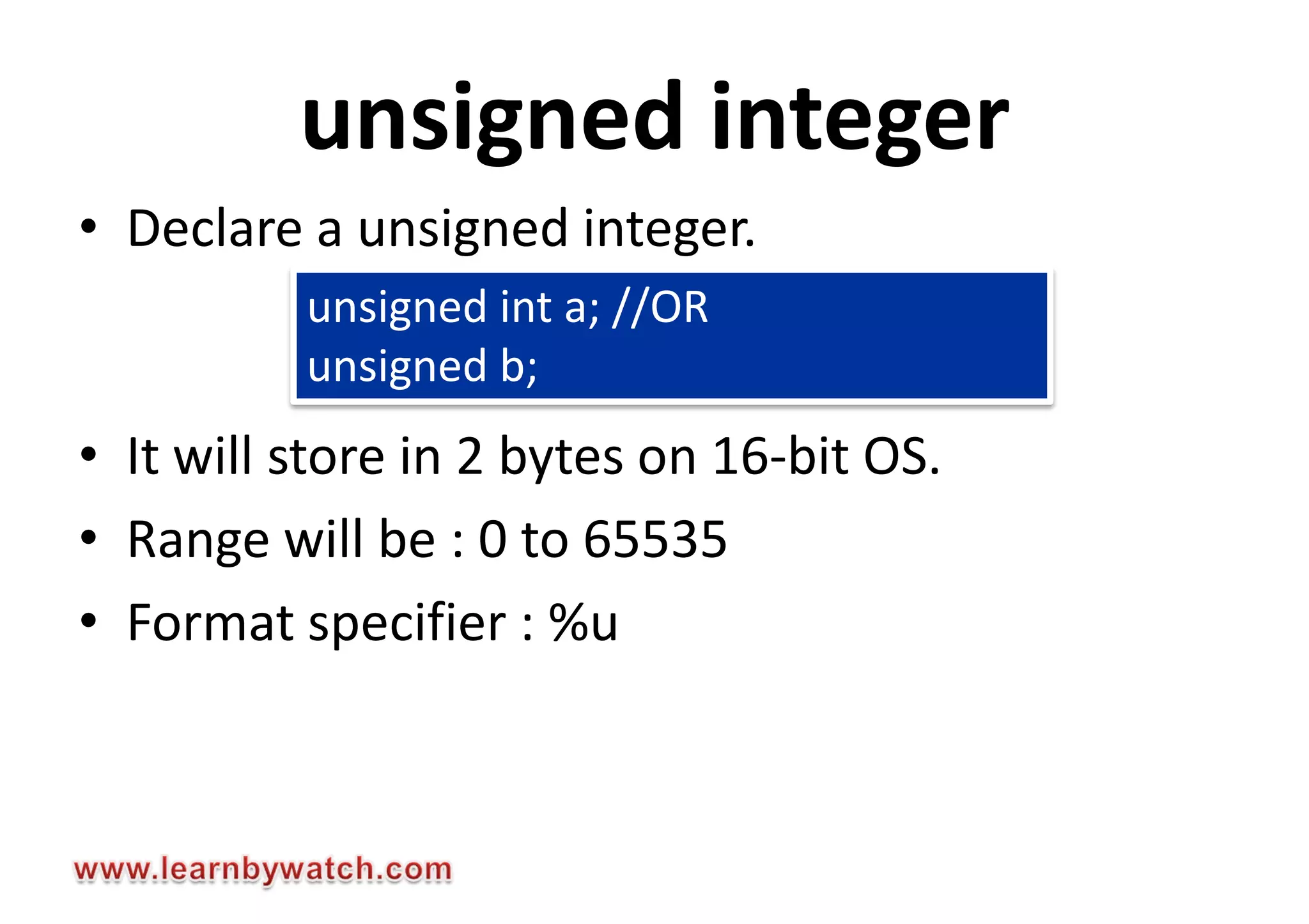
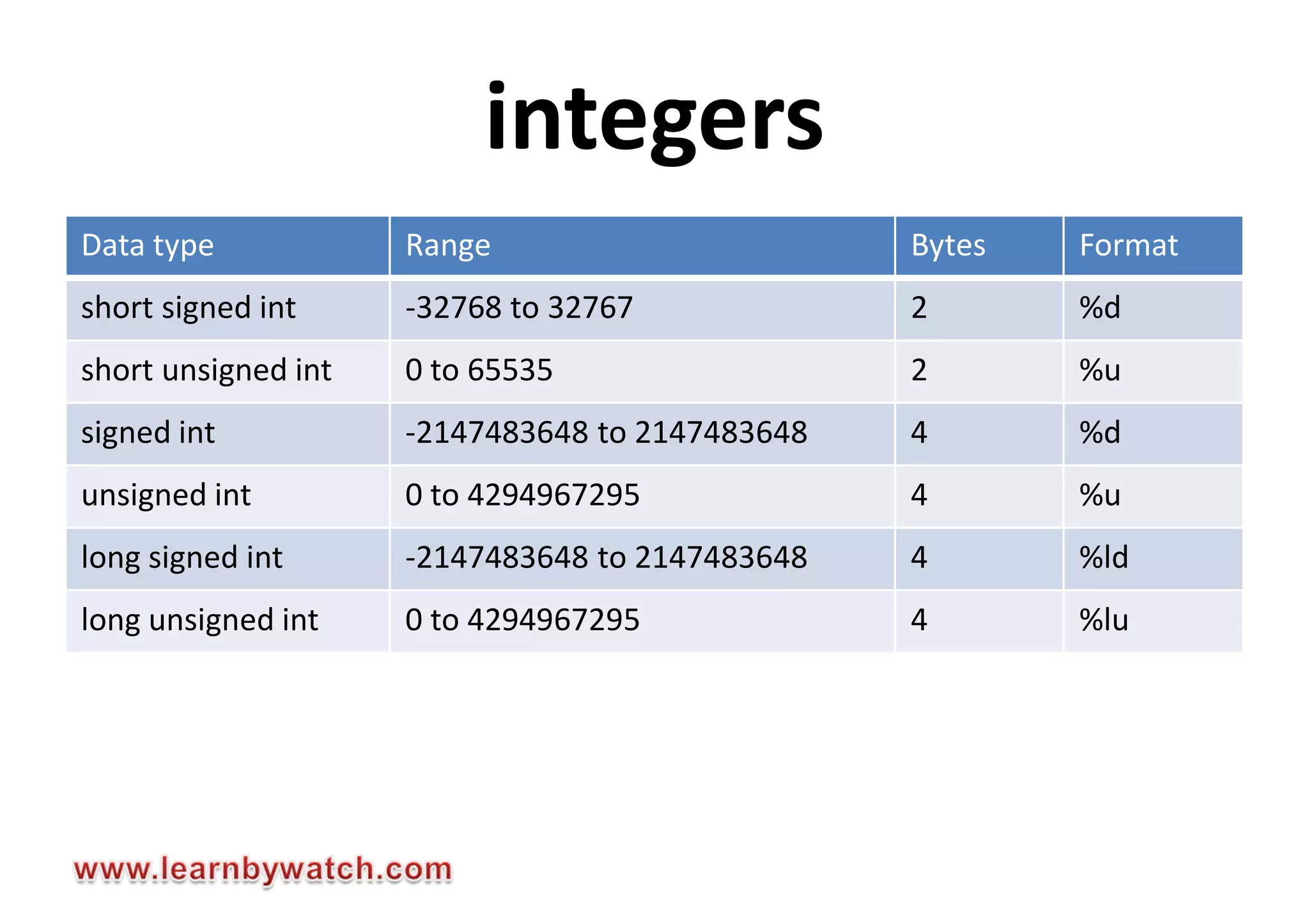
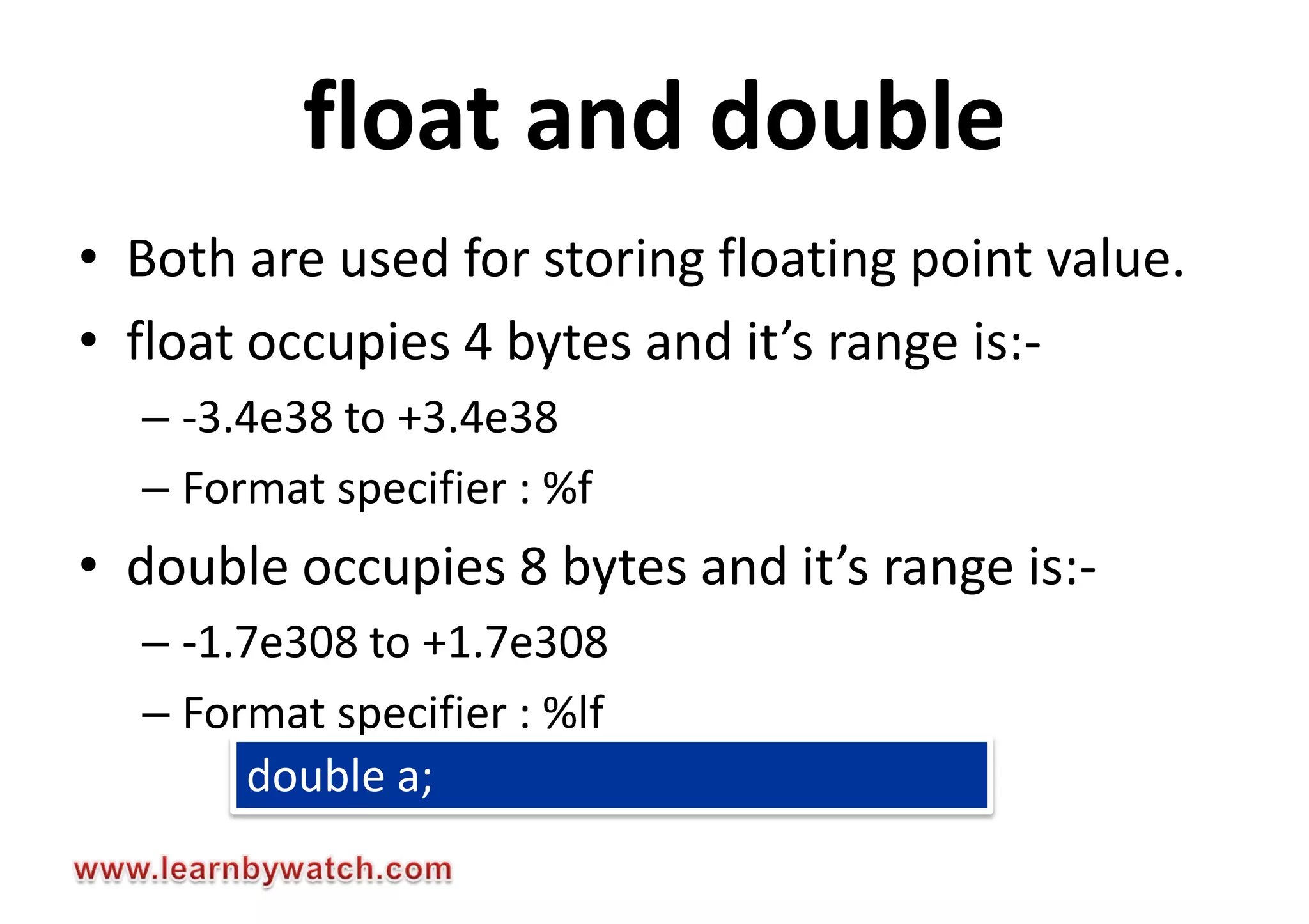
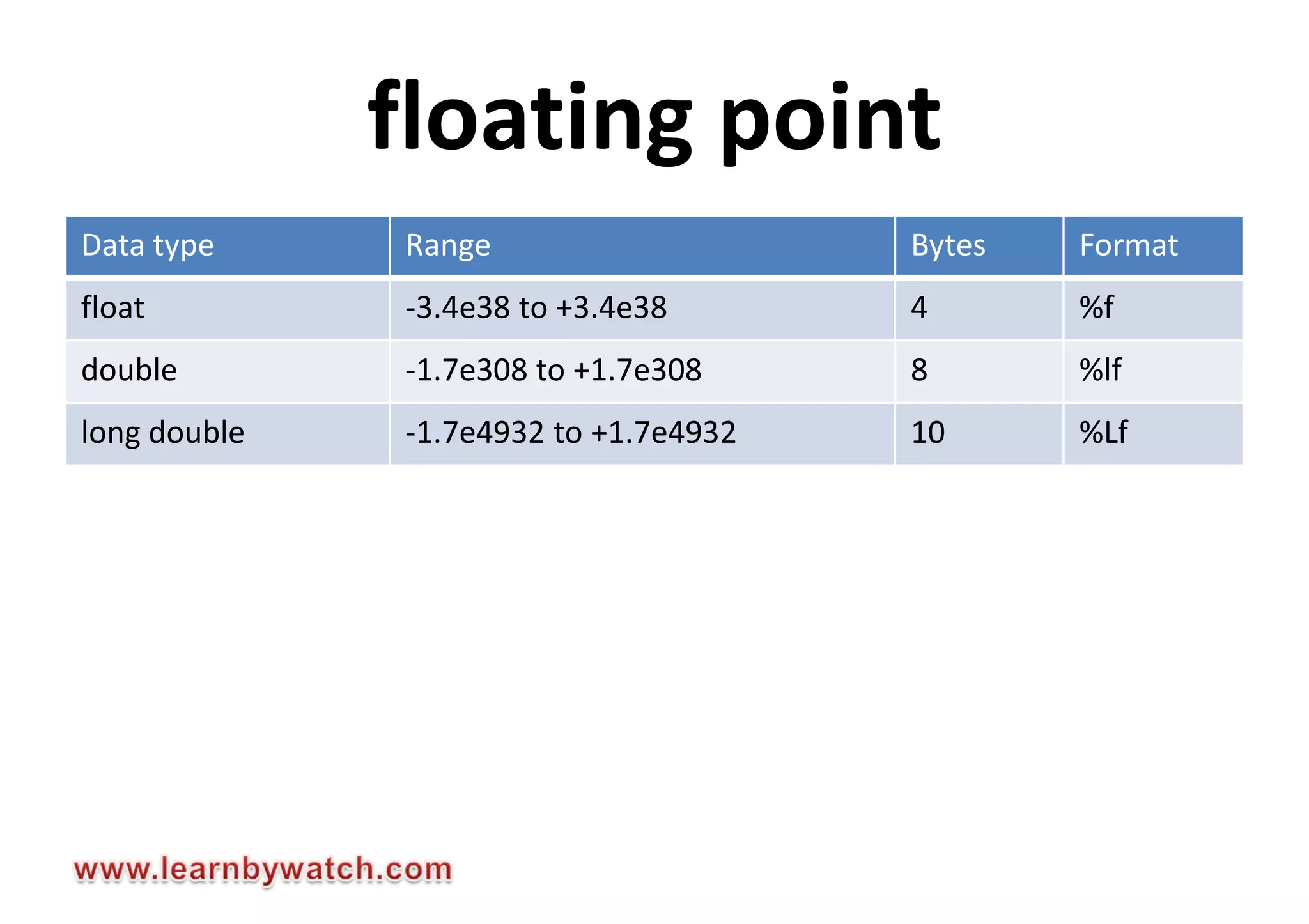
This document summarizes different data types in C programming language. It discusses integer data types like short, int, long and their signed and unsigned variants. It also covers character data type and floating point data types like float, double, long double. For each data type, it provides the storage size, value range and format specifier to print the values. The document encourages readers to solve quiz questions and contact the author in case of any doubts regarding the concepts covered.