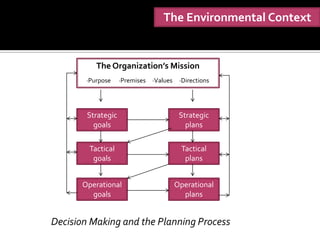
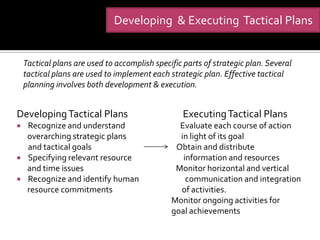
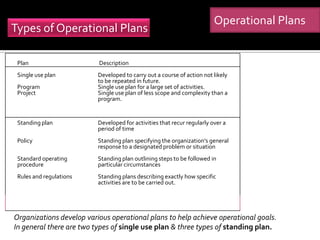
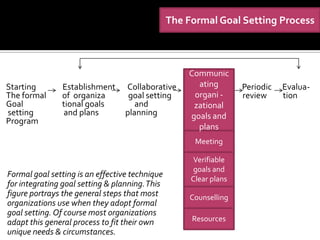
The document discusses decision making and the planning process. It describes how decision making drives the planning process and establishes organizational goals. There are strategic, tactical, and operational goals and plans. Strategic plans outline priorities to achieve strategic goals, tactical plans implement strategic plans to achieve tactical goals, and operational plans focus on carrying out tactical plans to achieve operational goals. Effective planning requires managing barriers like inappropriate goals, improper reward systems, and reluctance to establish goals. Formal goal setting through management by objectives can help integrate planning by involving collaboration between managers and subordinates.