This document discusses the key elements of planning and decision making for organizations. It covers topics such as:
- The importance of decision making and how it drives the planning process.
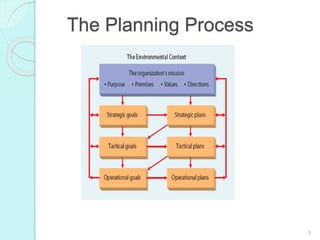
- The different types of goals organizations set, including mission statements, strategic goals, and operational goals. Goals provide guidance, promote planning, and serve as a motivation and evaluation tool.
- The various levels and timeframes of planning including strategic plans, tactical plans, operational plans, long-range plans, and short-range plans.
- Responsibilities for planning including planning staff, boards of directors, CEOs, line management, and contingency/crisis planning.
- Barriers to effective goal setting and planning