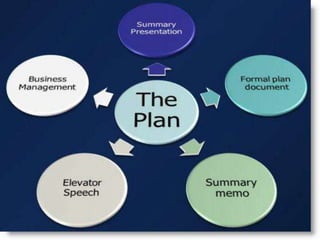
The document discusses various types of business plans including strategic plans, tactical plans, operational plans, and other types of plans. A strategic plan focuses on high-level goals and defines actions to achieve those goals. Tactical plans help execute strategic plans and cover shorter time periods. Operational plans define how strategic and tactical plans will be implemented through engagement of resources and management of risks and sustainability. Other plan types include single-use plans for one-time objectives and standing plans that provide ongoing guidance.