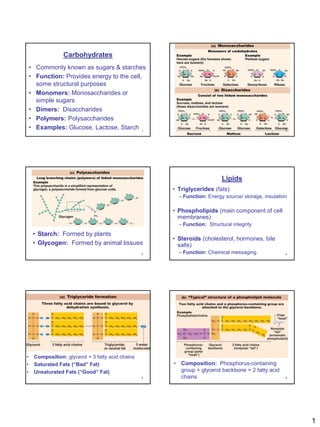
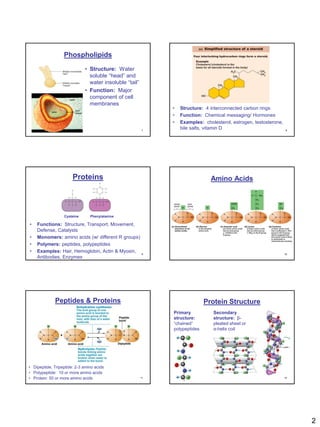
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are the four major macromolecules in living things. Carbohydrates function to provide energy and have monosaccharides like glucose as building blocks. Lipids serve as energy storage and include triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids. Proteins perform many roles like structure, transport, movement, and catalysis, with amino acids as monomers. Nucleic acids DNA and RNA contain genetic information and direct protein synthesis, using nucleotides as subunits. These macromolecules are essential to sustaining and reproducing life.