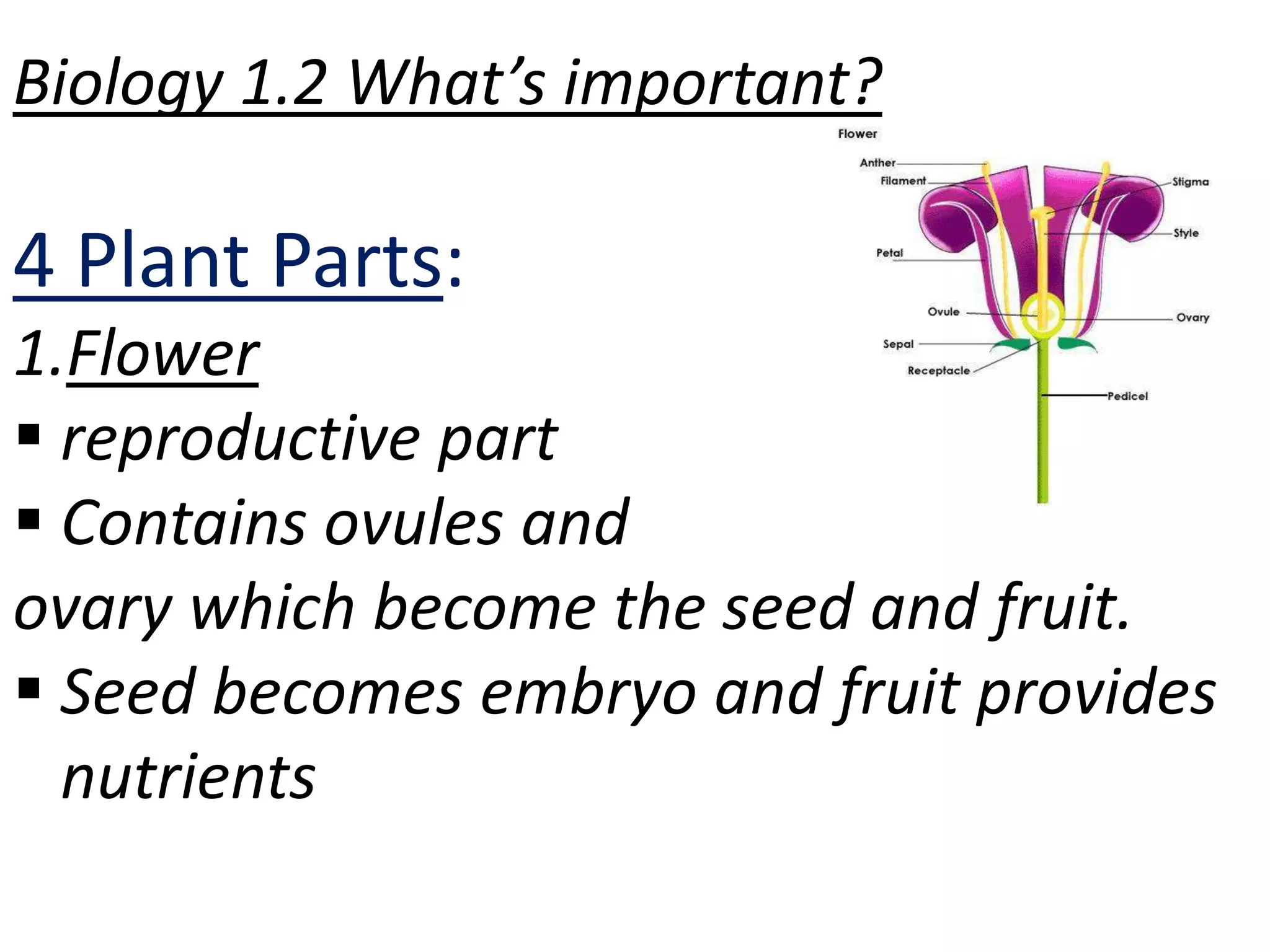
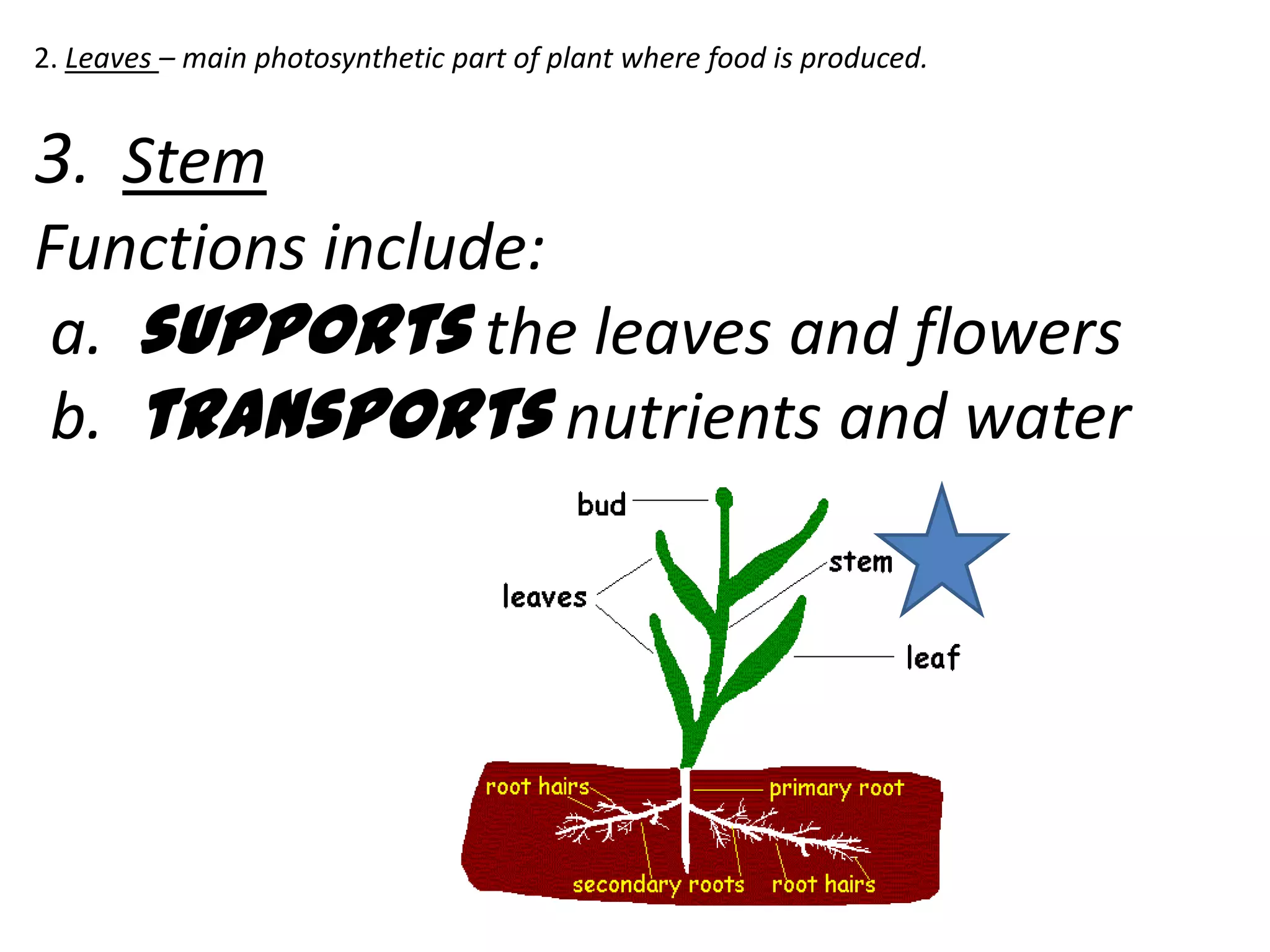
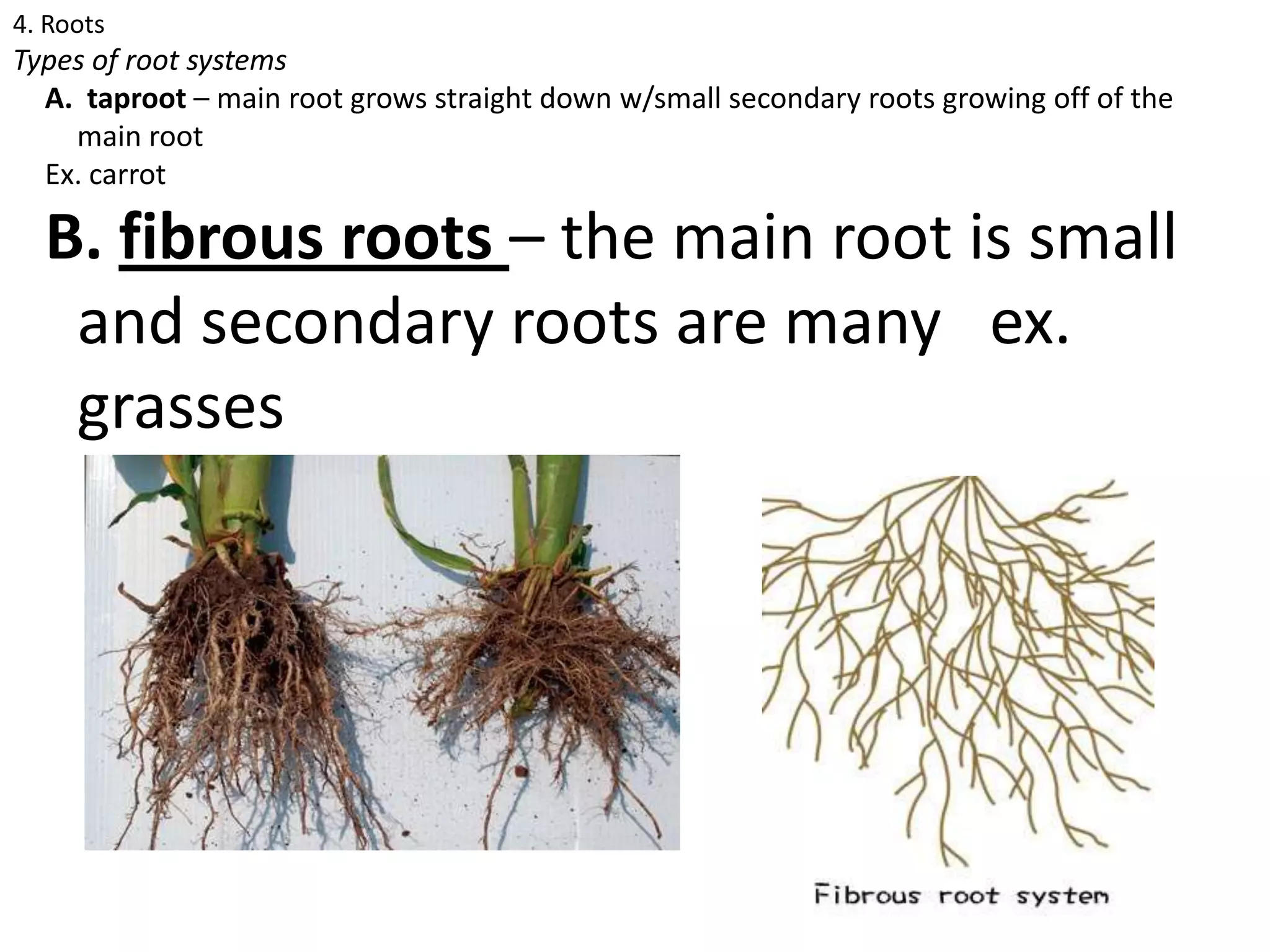
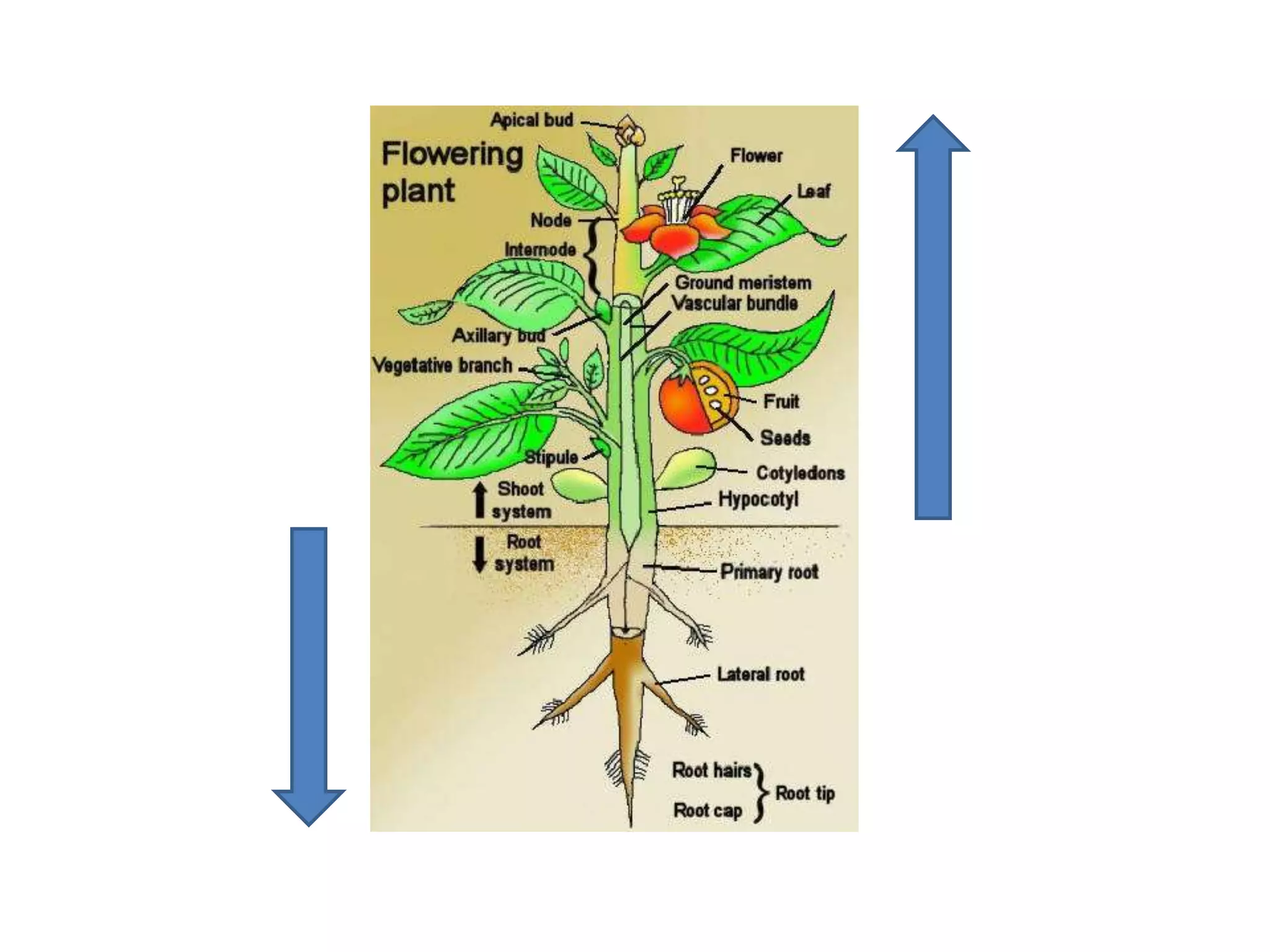
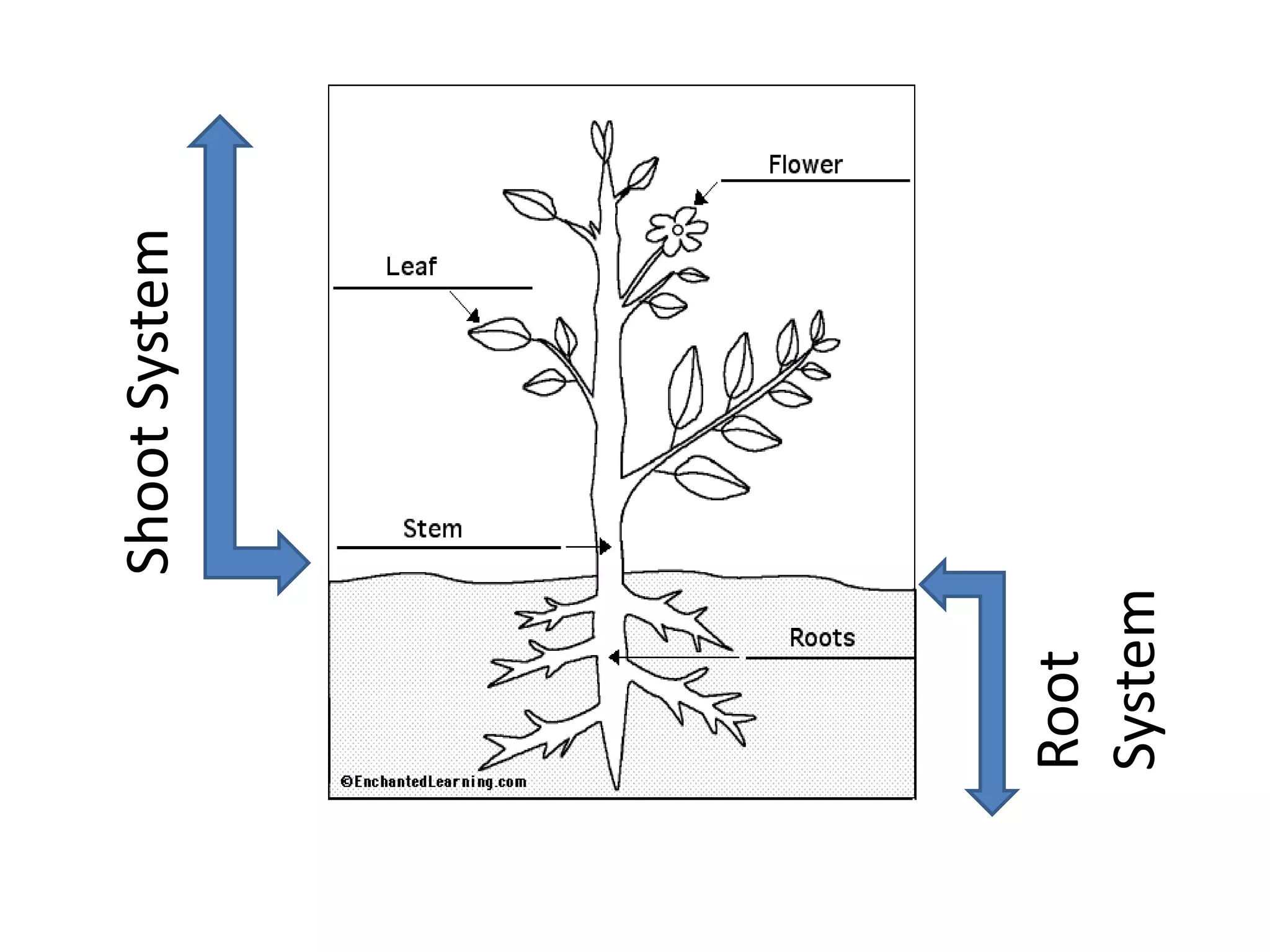
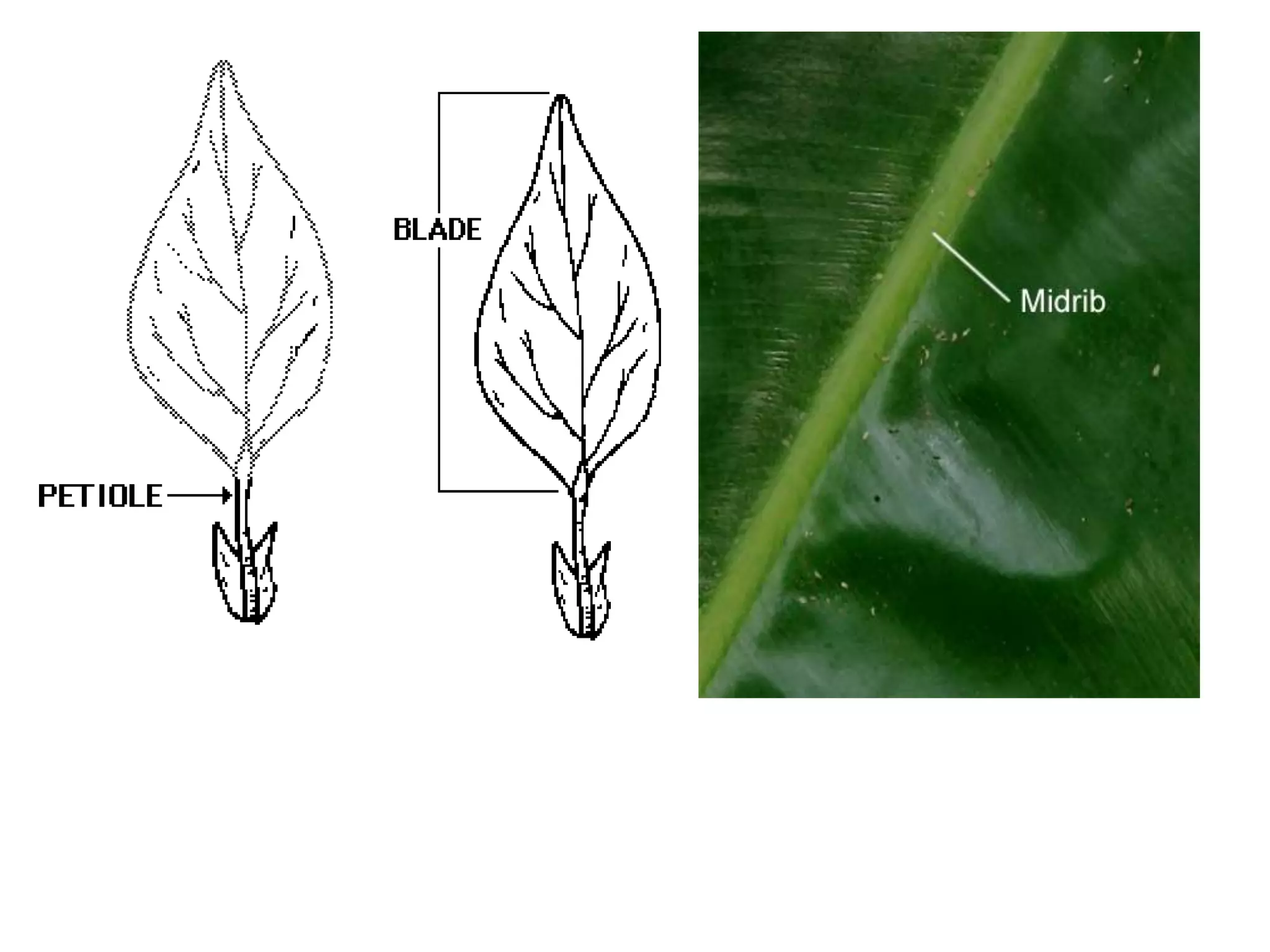
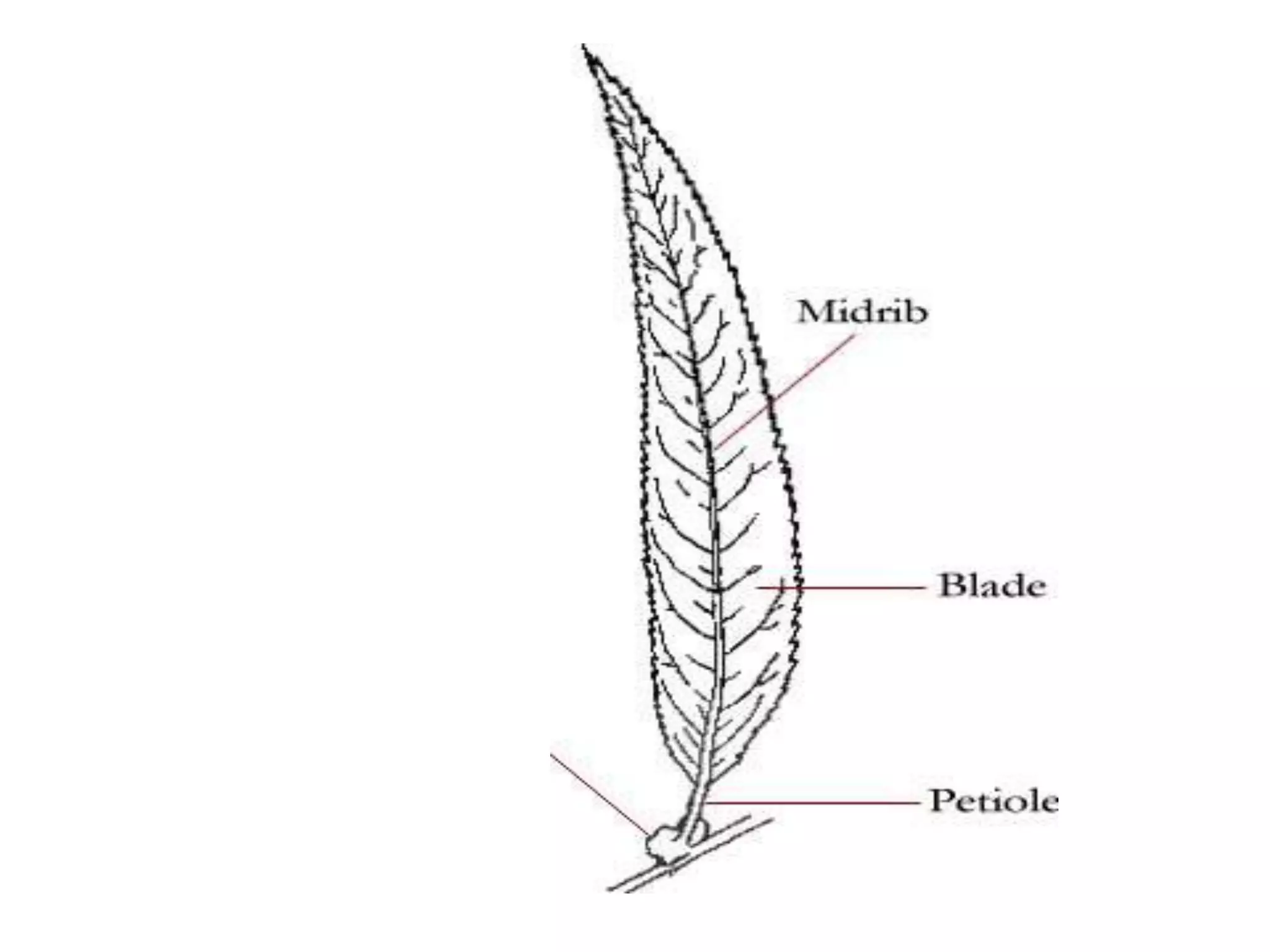
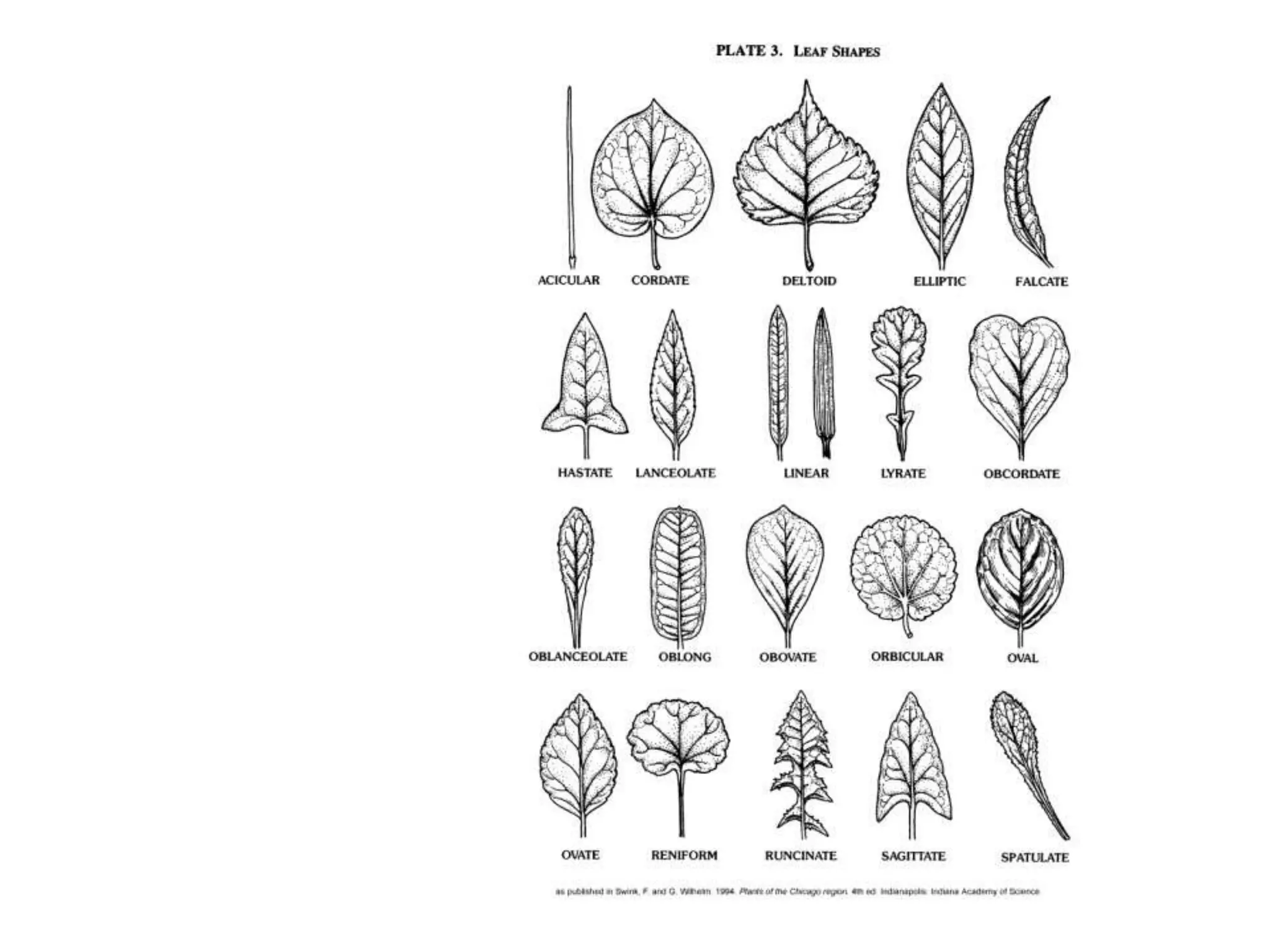
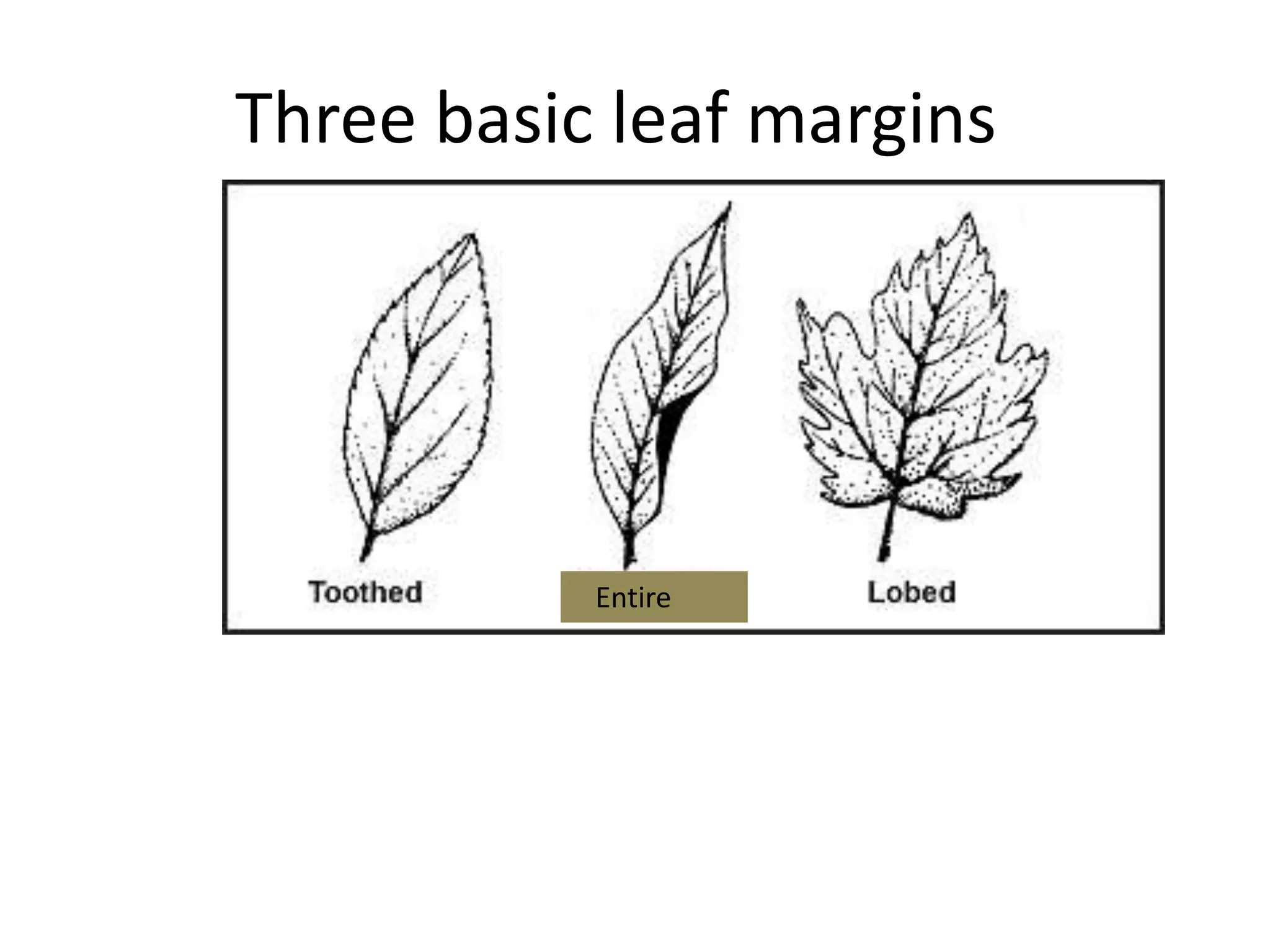
The document discusses the four main plant parts: flowers, leaves, stems, and roots. It describes their key functions, such as flowers being the reproductive part that contains seeds, leaves producing food through photosynthesis, stems supporting leaves/flowers and transporting water/nutrients, and roots anchoring plants and absorbing water/nutrients. It also defines different types of each part, such as the four types of plants based on their stems (trees, shrubs, herbs, vines), and two main root systems (taproot and fibrous roots).