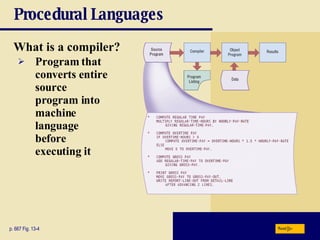
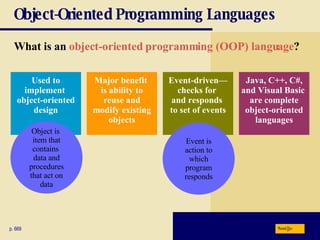
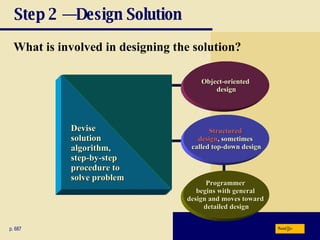
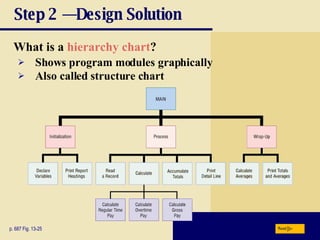
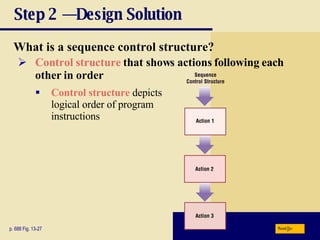
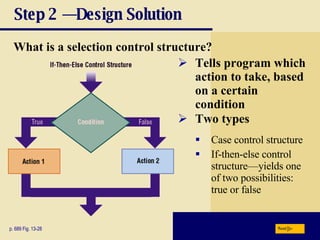
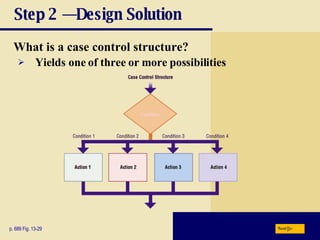
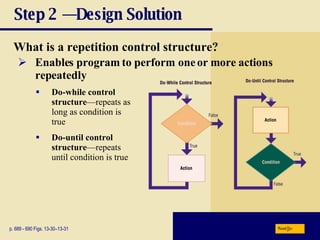
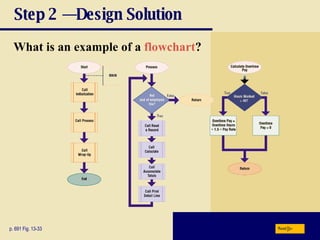
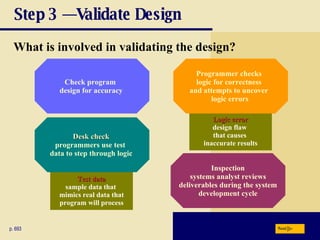
The document discusses various programming languages and program development tools. It describes low-level languages like machine language and assembly language, procedural languages like COBOL and C, and object-oriented languages like Java, C++, C#, and Visual Basic. It also discusses scripting languages, dynamic HTML, XML, and tools for web page authoring.