The document discusses various aspects of software programming and development including:
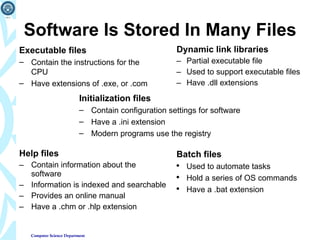
1) It describes different types of computer programs and how they are stored and executed, such as executable files, dynamic link libraries, and initialization files.
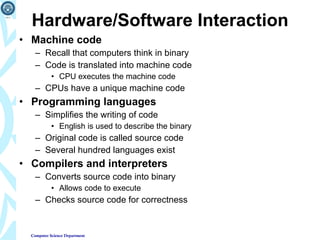
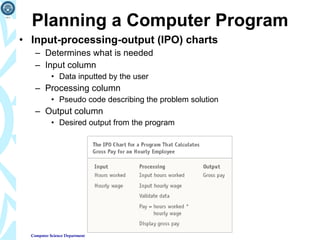
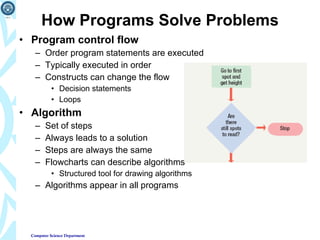
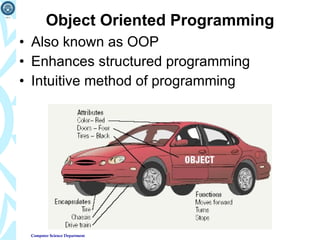
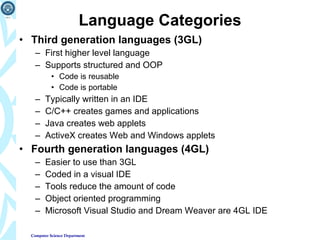
2) It explains how programs are planned, written in various programming languages, and solve problems through techniques like algorithms, structured programming, and object-oriented programming.
3) It provides an overview of the systems development life cycle which includes phases for needs analysis, design, development, implementation, and maintenance of software solutions.