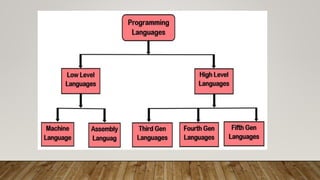
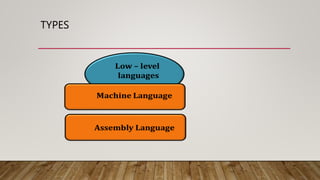
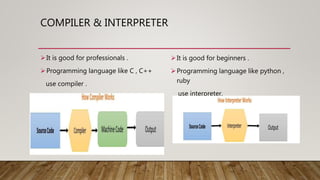
This document provides an overview of different computer languages. It begins by explaining that computer languages allow communication between humans and computers. It then distinguishes between low-level languages like machine language and assembly language, which are close to hardware, and high-level languages, which are closer to human languages. Popular high-level languages mentioned include Python, JavaScript, Java, C, and C++. Procedural languages require specifying how to solve a problem, while non-procedural languages only require specifying what problem to solve.