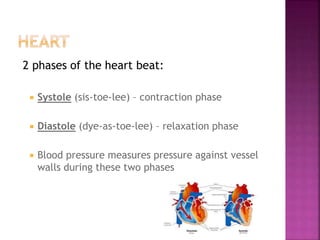
This document provides an overview of the major body systems, including their structures, functions, and common age-related changes. It discusses the skin, skeletal, muscular, nervous, circulatory, respiratory, urinary, digestive, endocrine, and immune systems. For each system, it lists key components, functions, normal aging changes to watch for, and nursing considerations for care.