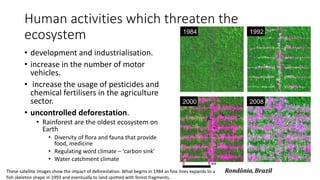
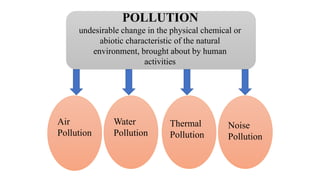
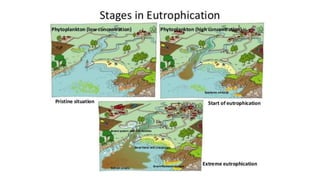
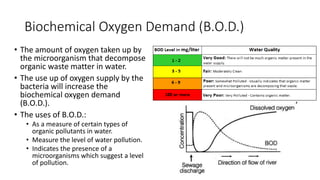
This document discusses human activities that endanger ecosystems and proper management of development. It outlines how uncontrolled deforestation, pollution from industry and vehicles, and pesticide/fertilizer usage threaten biodiversity and cause problems like soil erosion, flooding and global warming. The greenhouse effect and thinning ozone layer from chlorofluorocarbons also disrupt ecosystems by raising temperatures and increasing UV radiation, harming health and crop yields. Proper management is needed through laws, technology, education and renewable resources to preserve ecosystems while allowing responsible development.