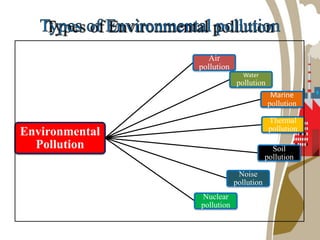
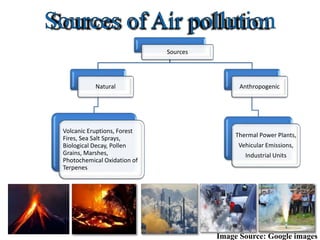
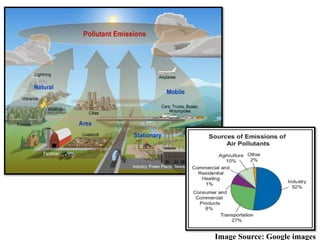
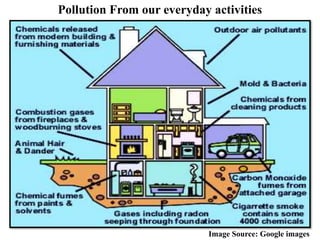
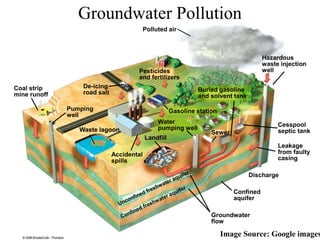
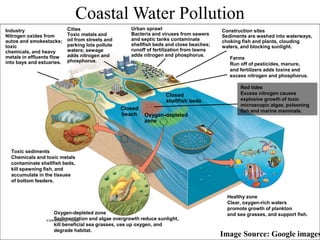
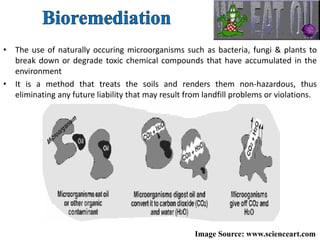
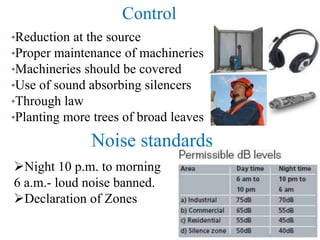
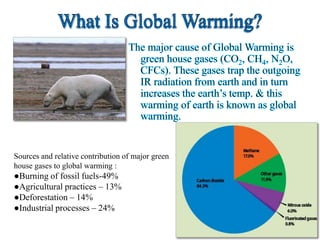
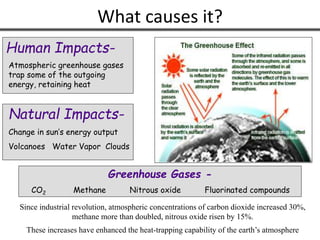
The document discusses various forms of environmental pollution including air, soil, water, noise, and thermal pollution, outlining their sources, effects on human health, flora, fauna, and the environment, along with prevention and control measures. It highlights the impacts of pollutants such as respiratory diseases in humans, damage to vegetation, and harm to aquatic life, while stressing the urgency of addressing these issues to mitigate global warming and ecological degradation. The text emphasizes individual responsibility in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and implementing sustainable practices to preserve the environment.