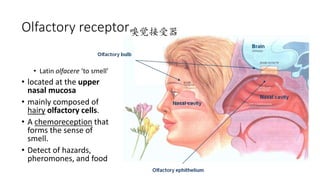
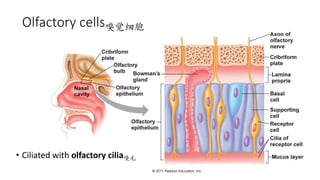
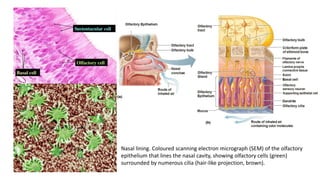
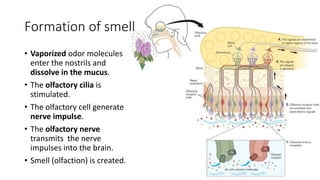
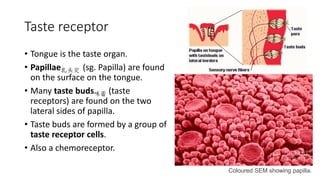
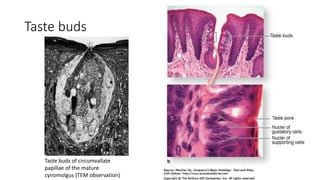
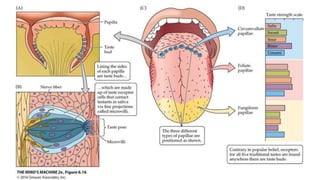
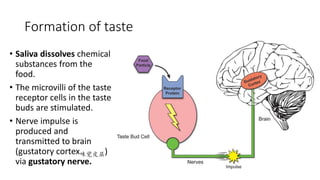
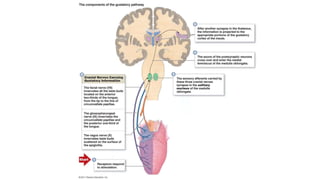
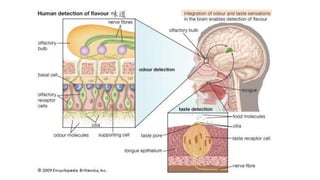
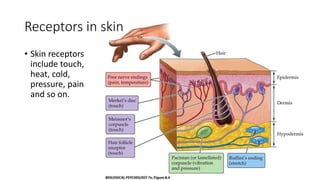
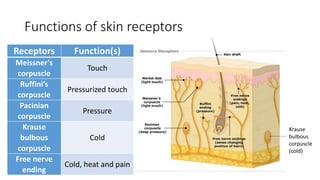
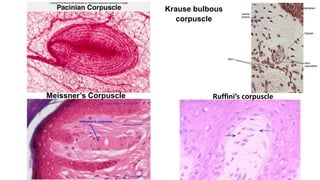
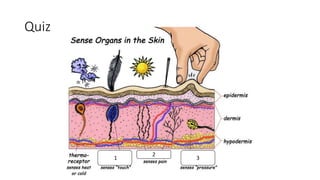
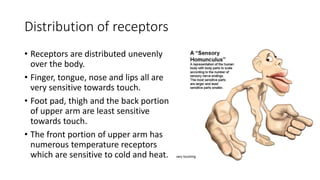
This document discusses the senses of smell, taste, and touch. It describes how smell is detected by olfactory receptors in the nasal cavity. Taste is detected by taste receptor cells in taste buds located on papillae on the tongue. The skin contains several types of receptors, including Meissner's corpuscles for touch, Ruffini's corpuscles for pressure, and free nerve endings for pain, cold and heat. Quizzes are also included to test understanding.