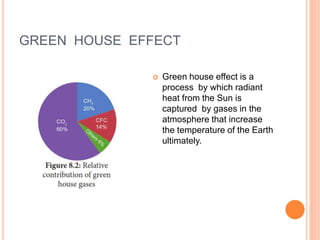
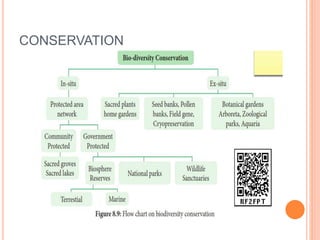
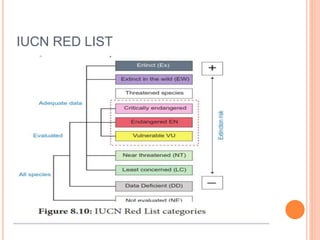
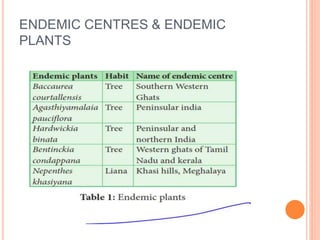
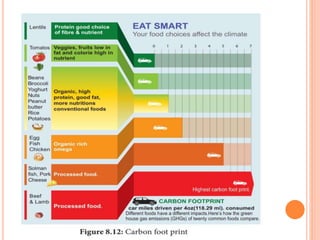
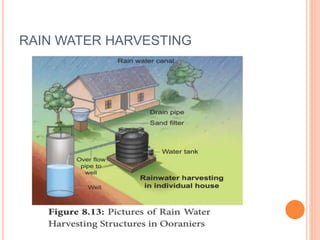
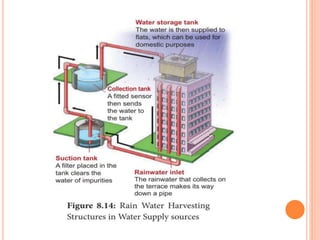
The document discusses key environmental issues such as the greenhouse effect, global warming, ozone depletion, and deforestation, highlighting their causes and impacts. It also covers environmental management practices like agroforestry, social forestry, carbon capture, and rainwater harvesting, which aim to mitigate these issues. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of biodiversity conservation through different strategies and technologies, including GIS and GPS for data management.