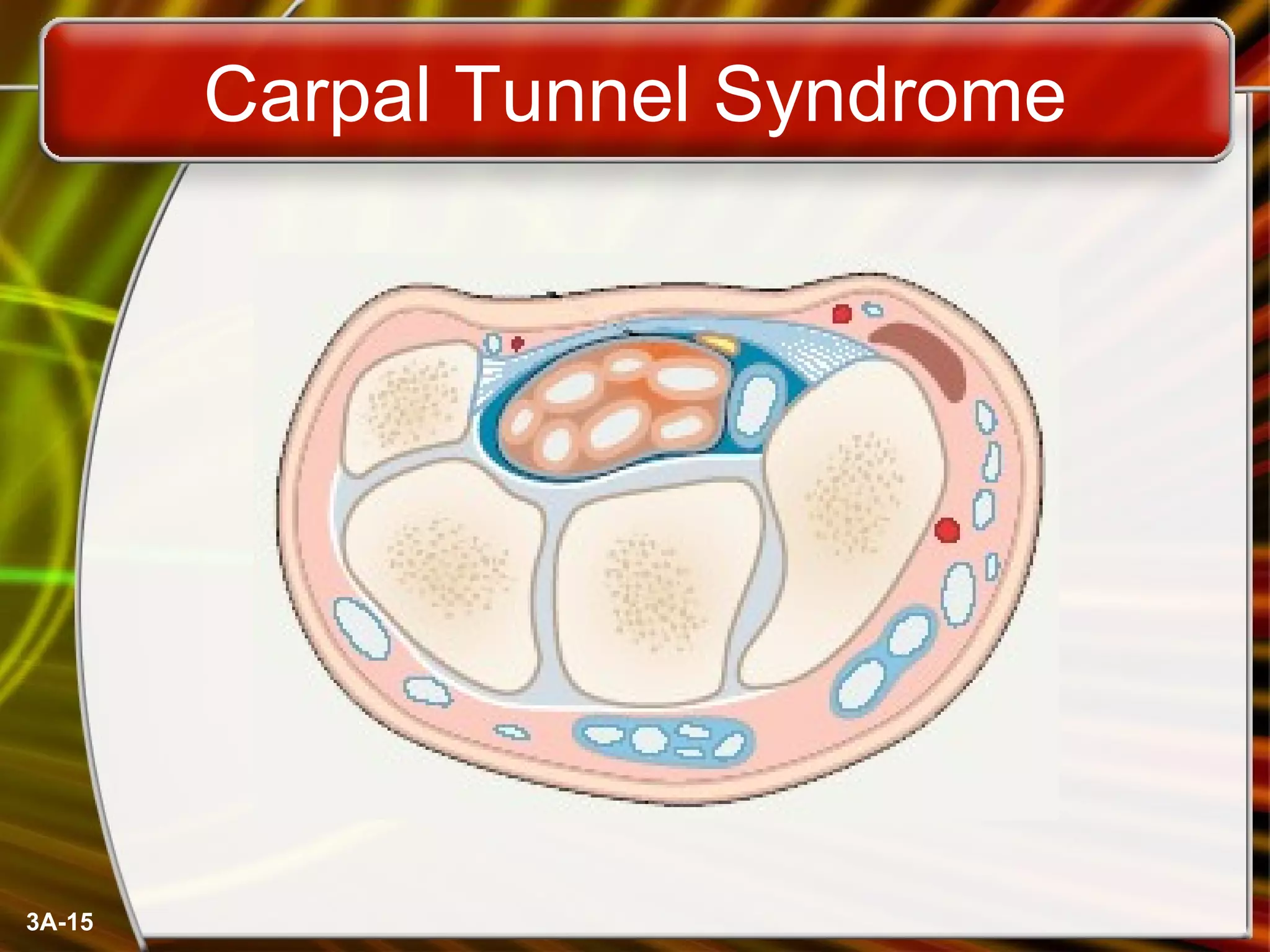
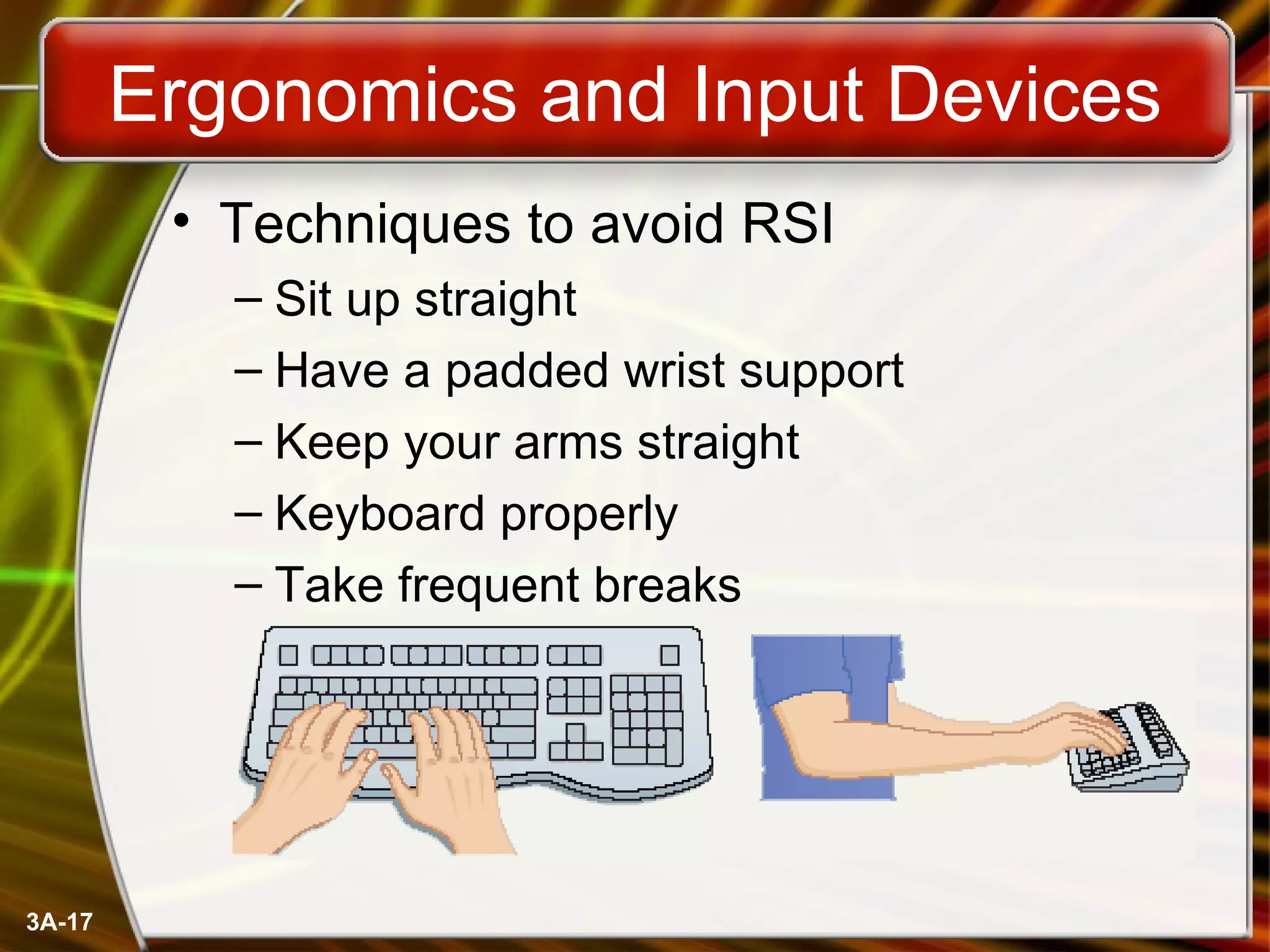
The document discusses different input devices used with computers including keyboards, mice, and variants. It covers how keyboards and mice work, common actions used with mice like clicking and dragging, and different types of mice like trackballs and trackpads. The document also discusses ergonomics as it relates to input devices and repetitive strain injuries that can result from prolonged use of keyboards and mice without proper posture and technique.