This document provides an overview of several theories about brain structure and function:
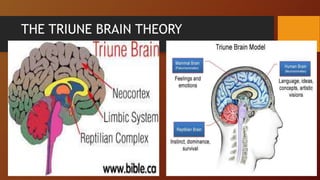
1. It summarizes Paul Broca's 1861 study on language lateralization, Roger Sperry's split-brain research which earned him a Nobel Prize, and Paul MacLean's triune brain theory identifying three brain structures.
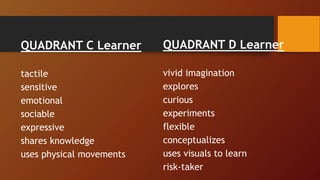
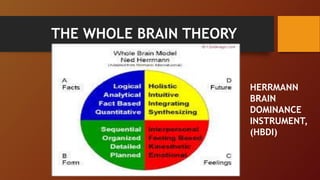
2. It describes Ned Herrmann's whole brain theory and the Herrmann Brain Dominance Instrument which measures preference strengths across four quadrants related to logic, organization, imagination, and social skills.
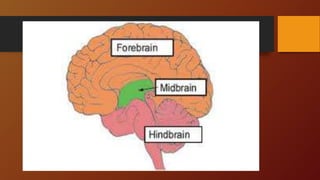
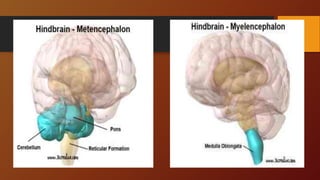
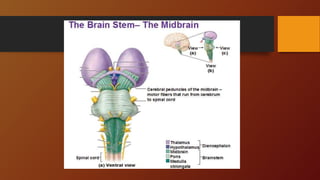
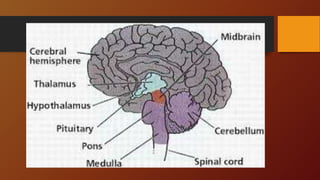
3. The document outlines functions of the hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain. It also explains how the left and right hemispheres are specialized for different cognitive tasks according to the split-brain theory