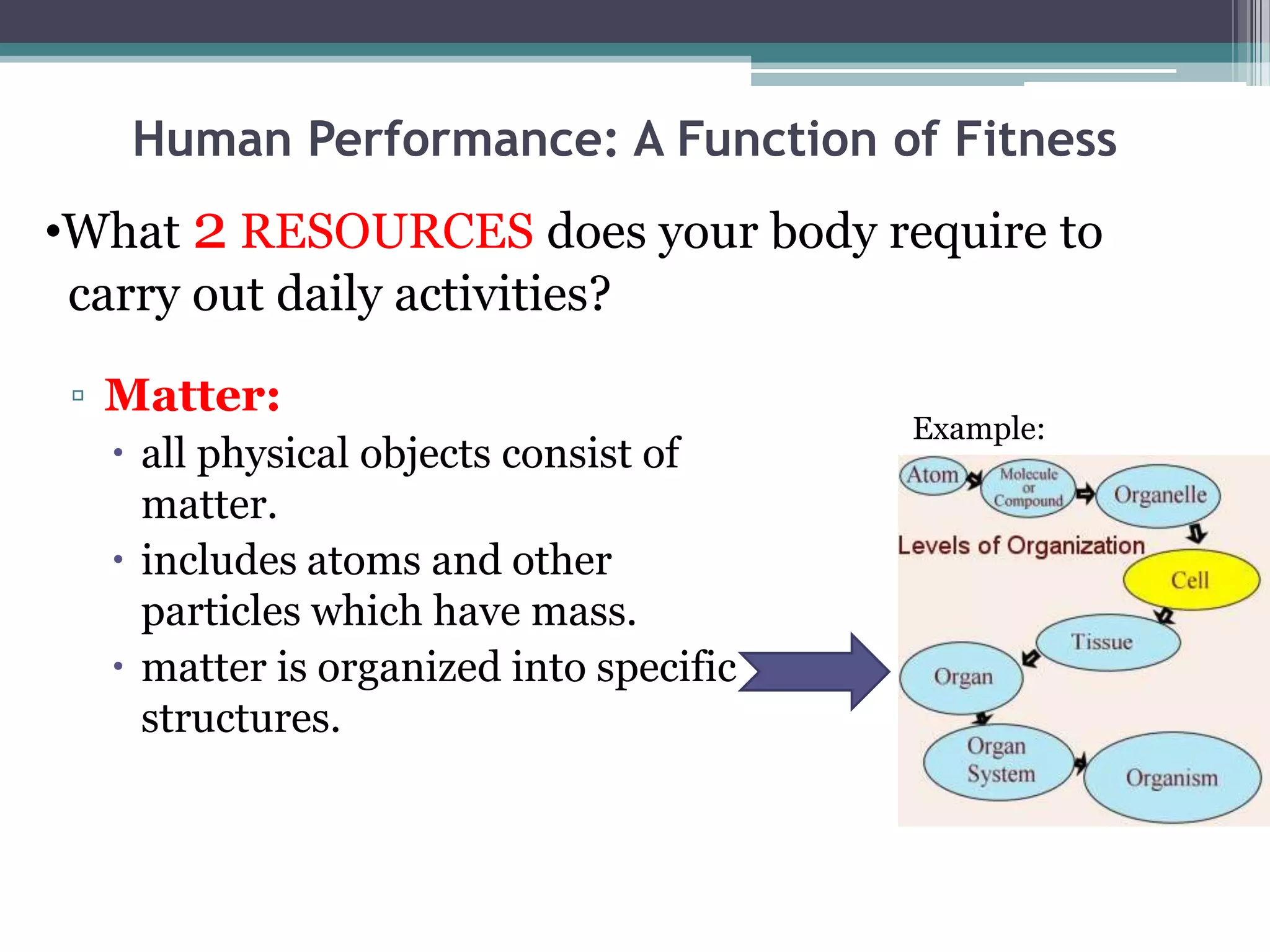
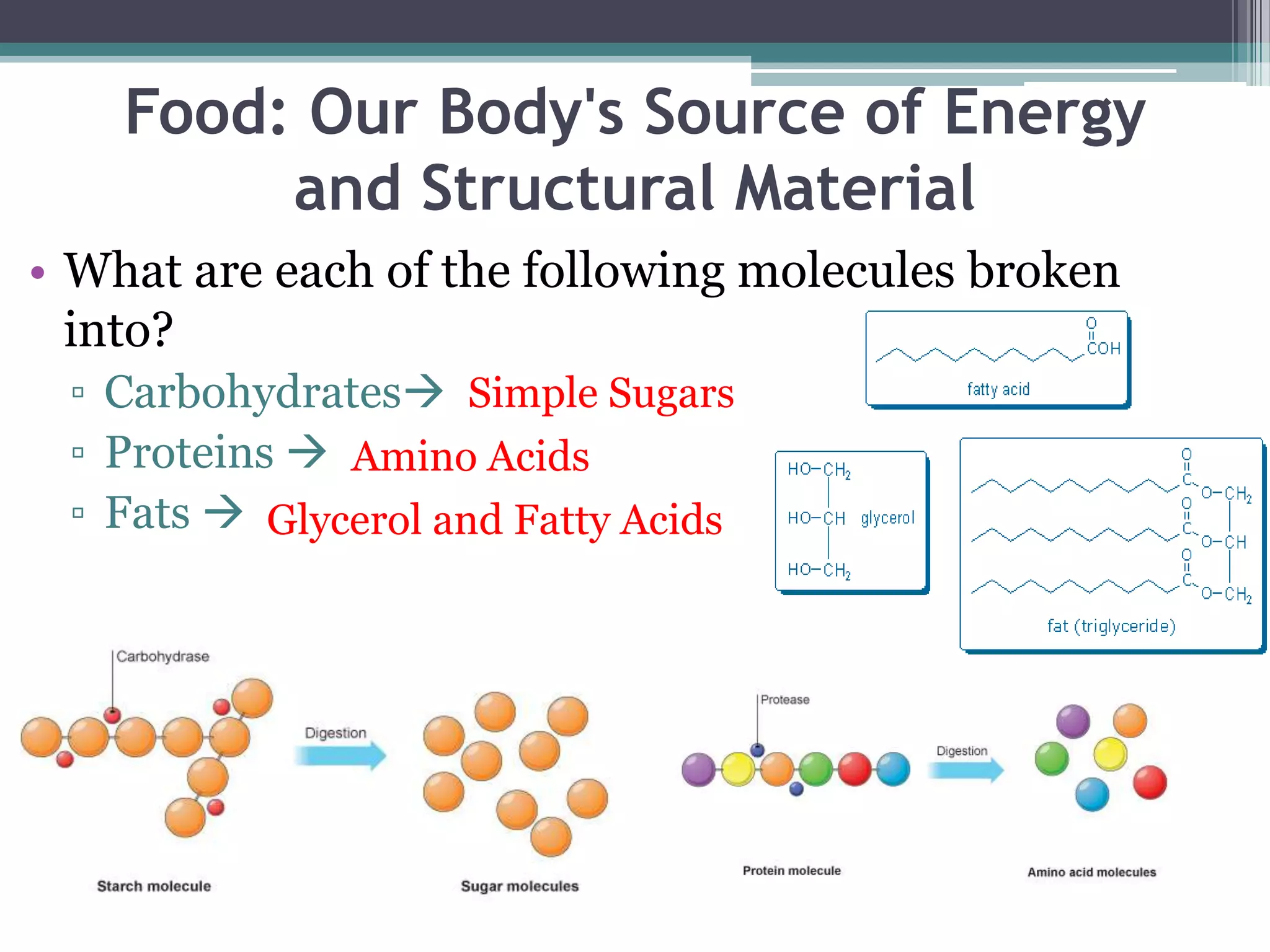
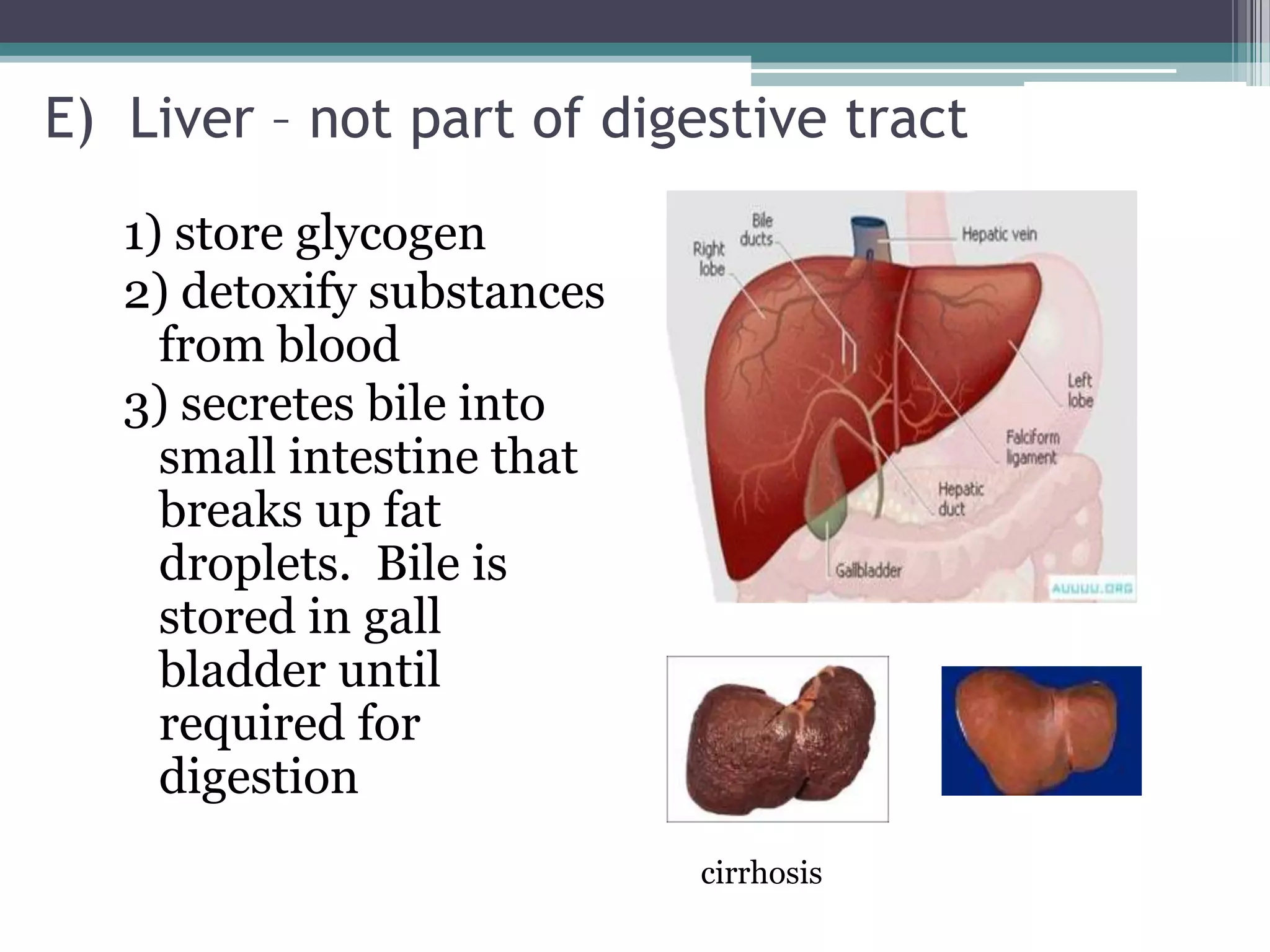
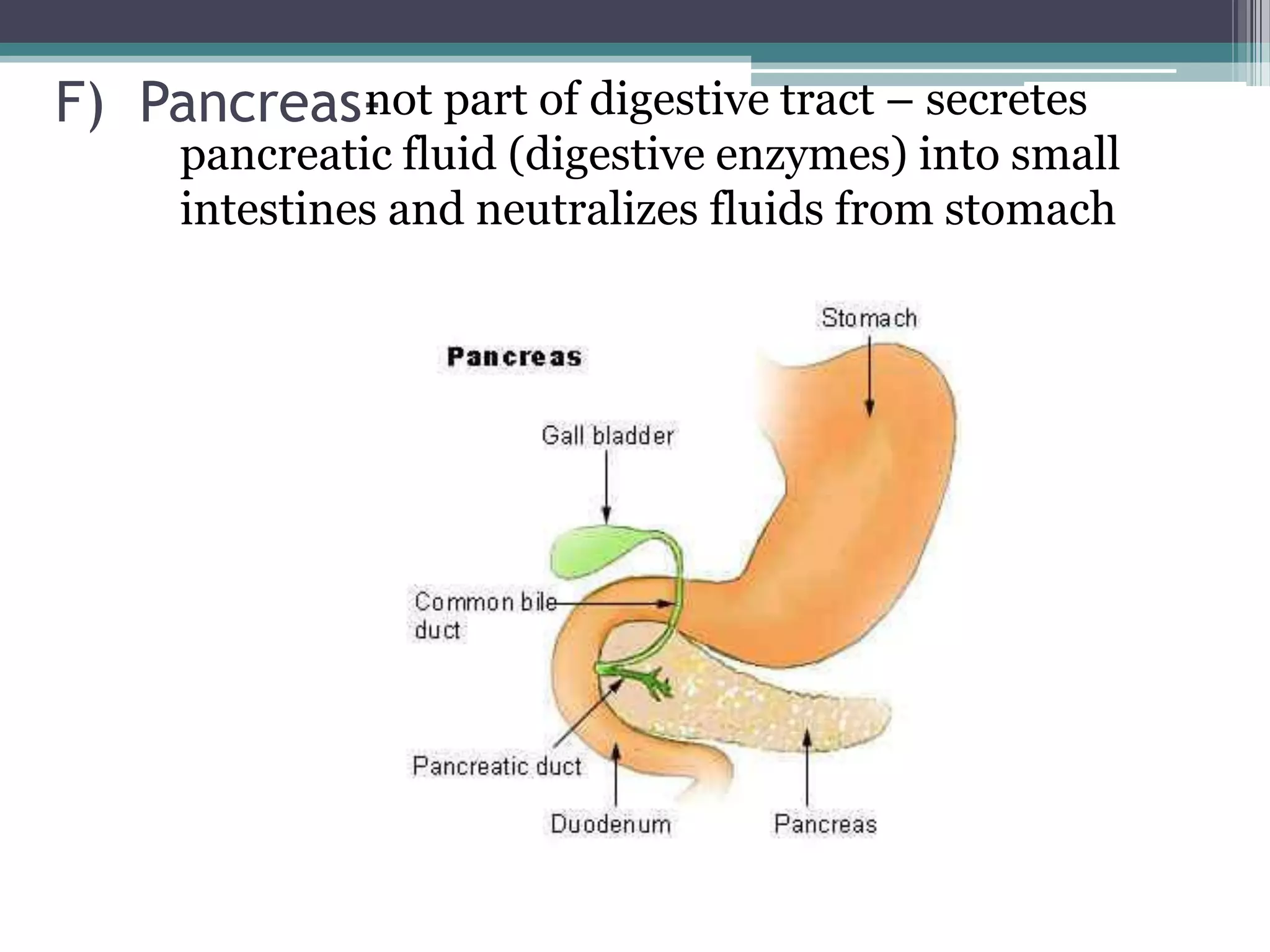
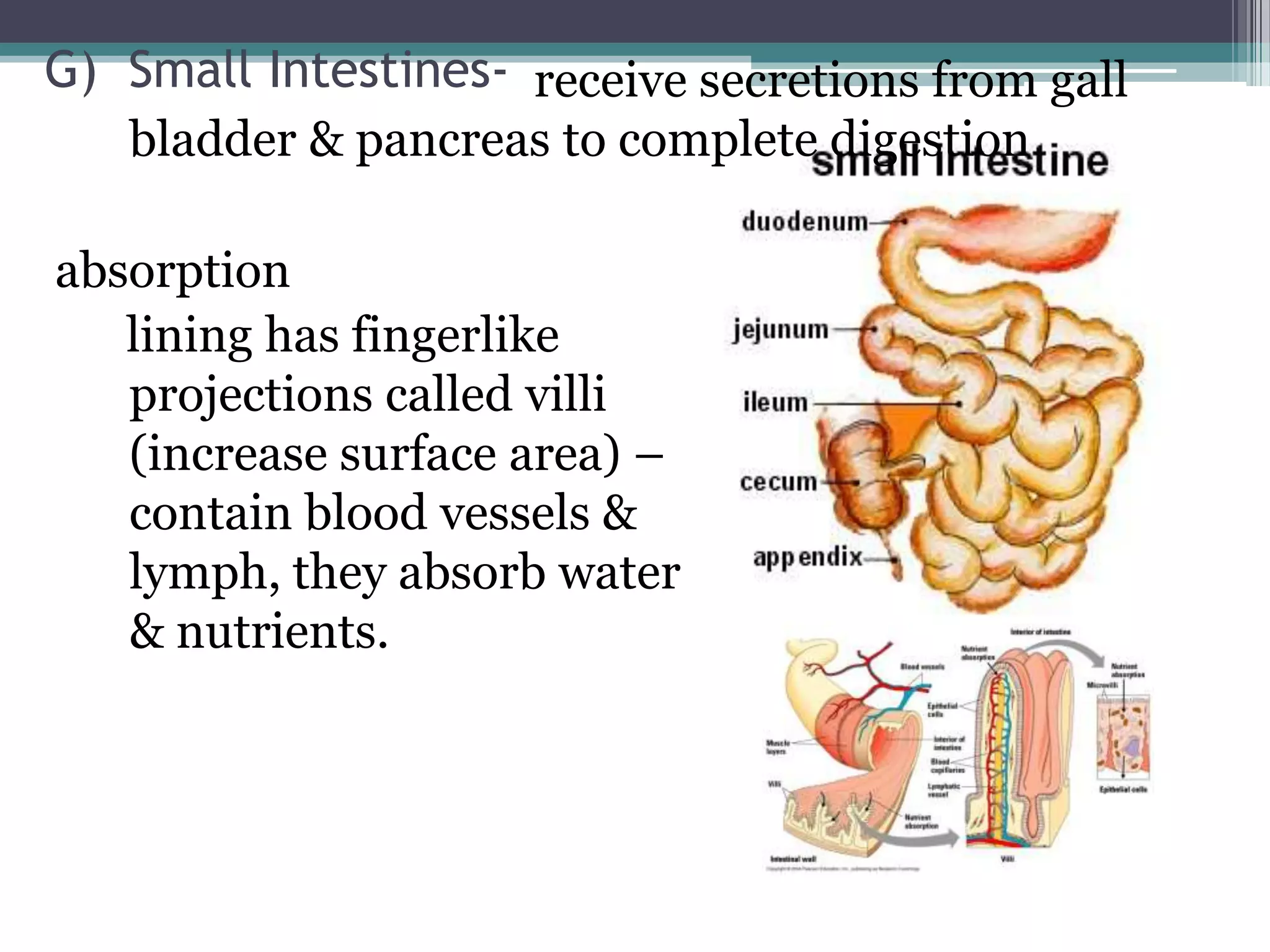
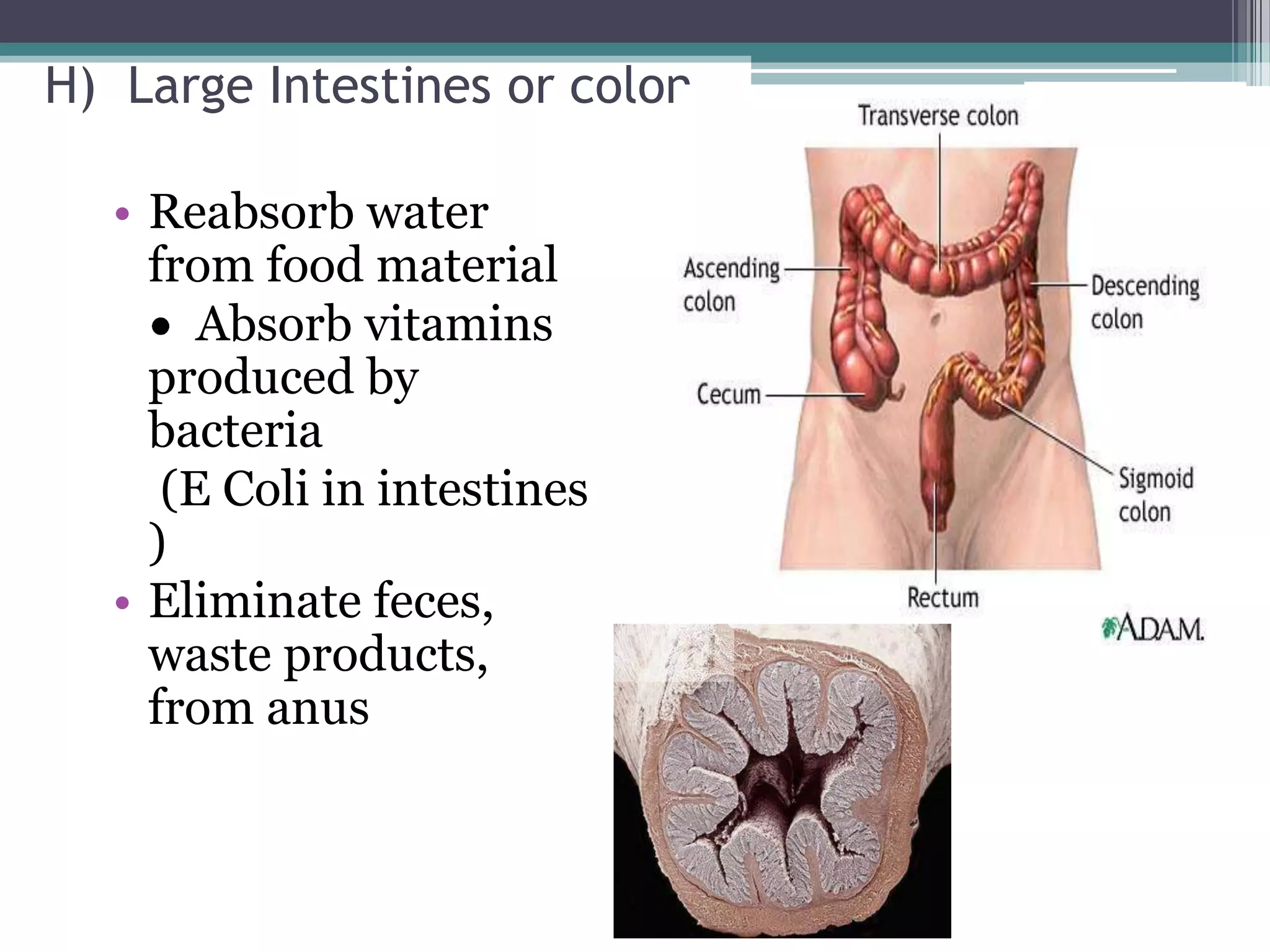
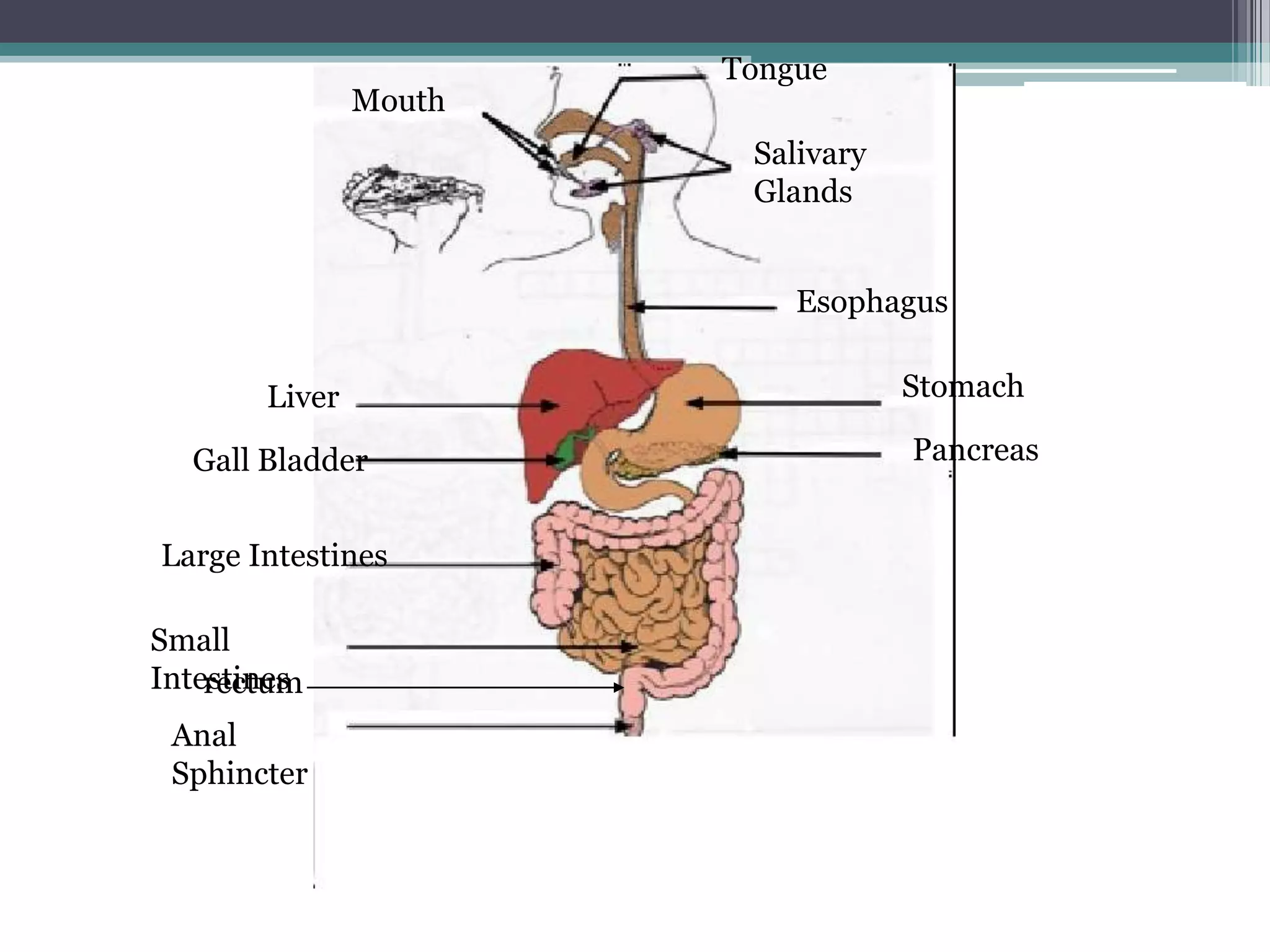
The document discusses human performance and fitness, explaining that the body requires matter and energy to carry out daily activities, and that fitness relates to how effectively the body organizes matter and supplies energy. It also covers the digestive system and the role of food as the body's source of energy and structural material, noting that carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals make up nutrients and must be broken down for absorption. Finally, it briefly describes the eating disorder anorexia nervosa and some of its potential health consequences if left untreated.