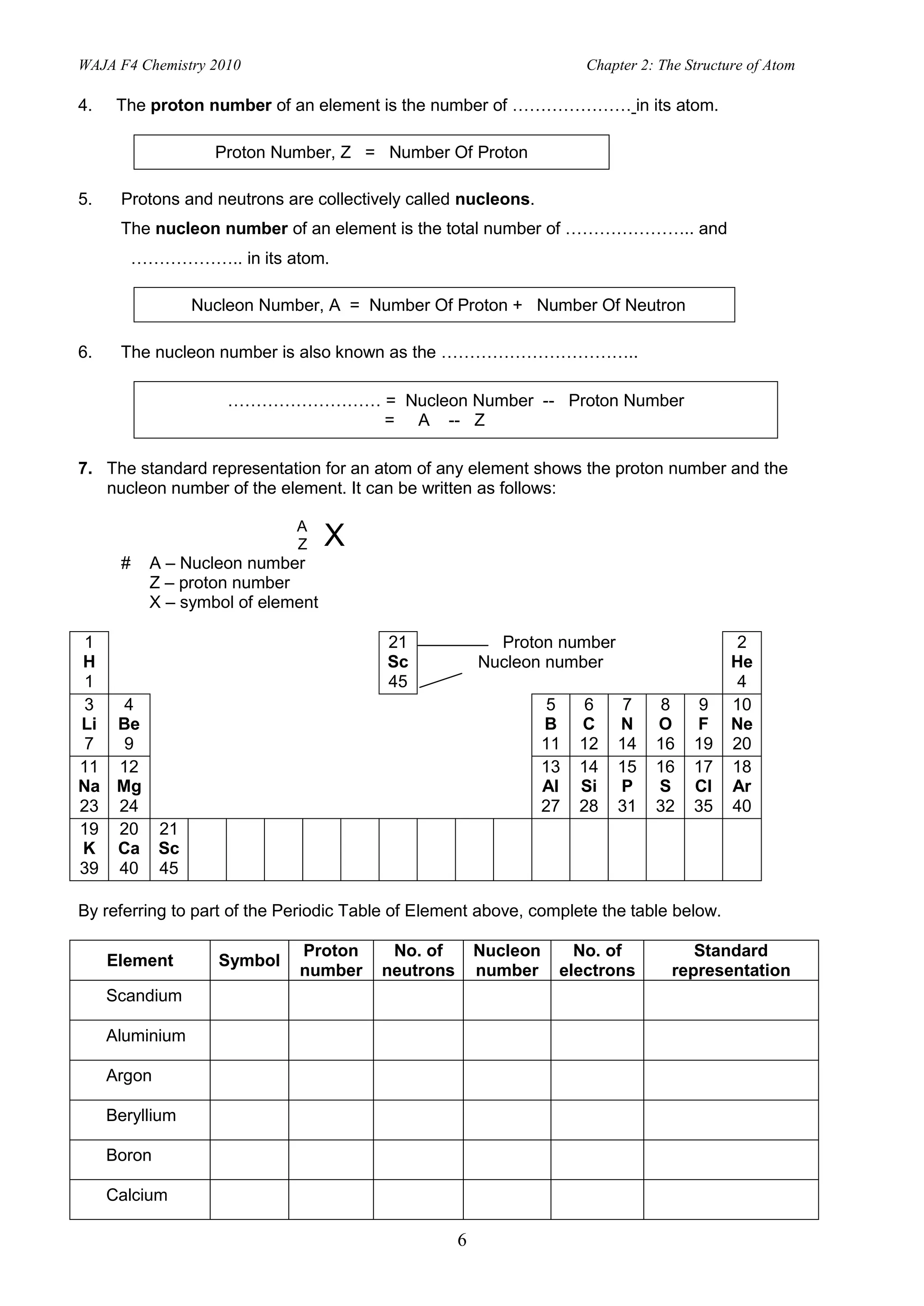
1. The document discusses the structure of atoms, including the development of atomic models from Dalton to Chadwick. It describes the subatomic particles that make up atoms - protons, neutrons, and electrons - and how they are arranged.
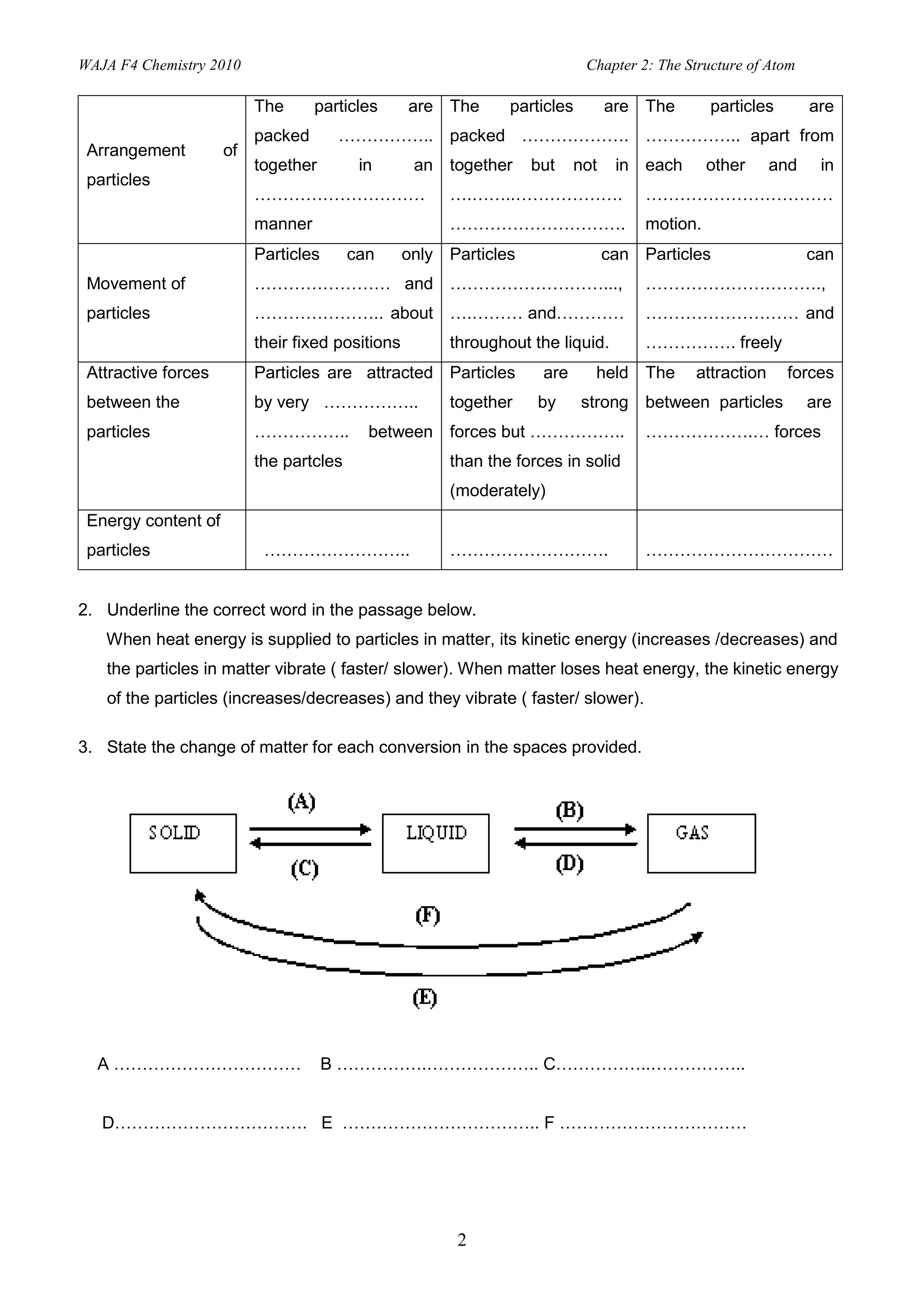
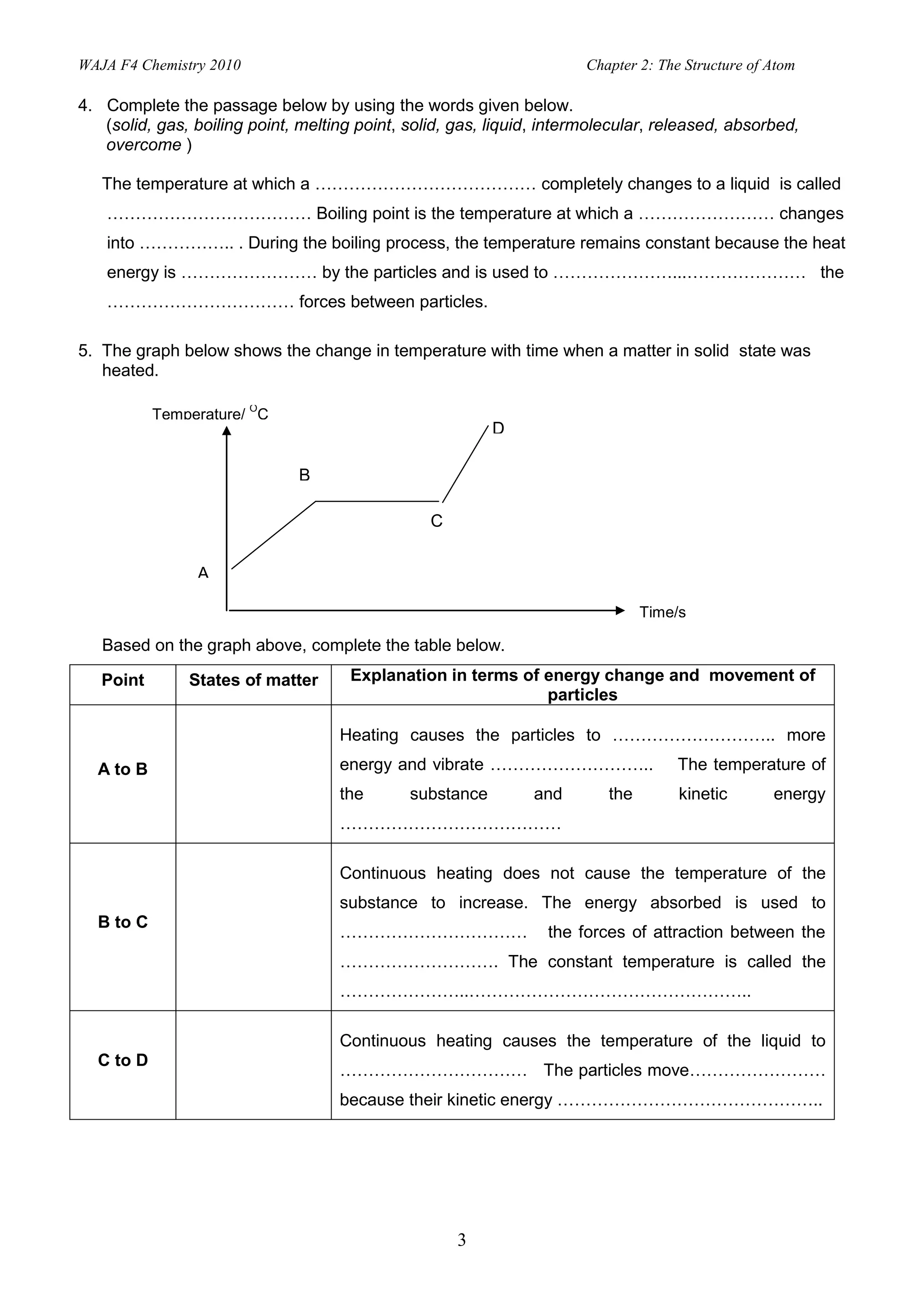
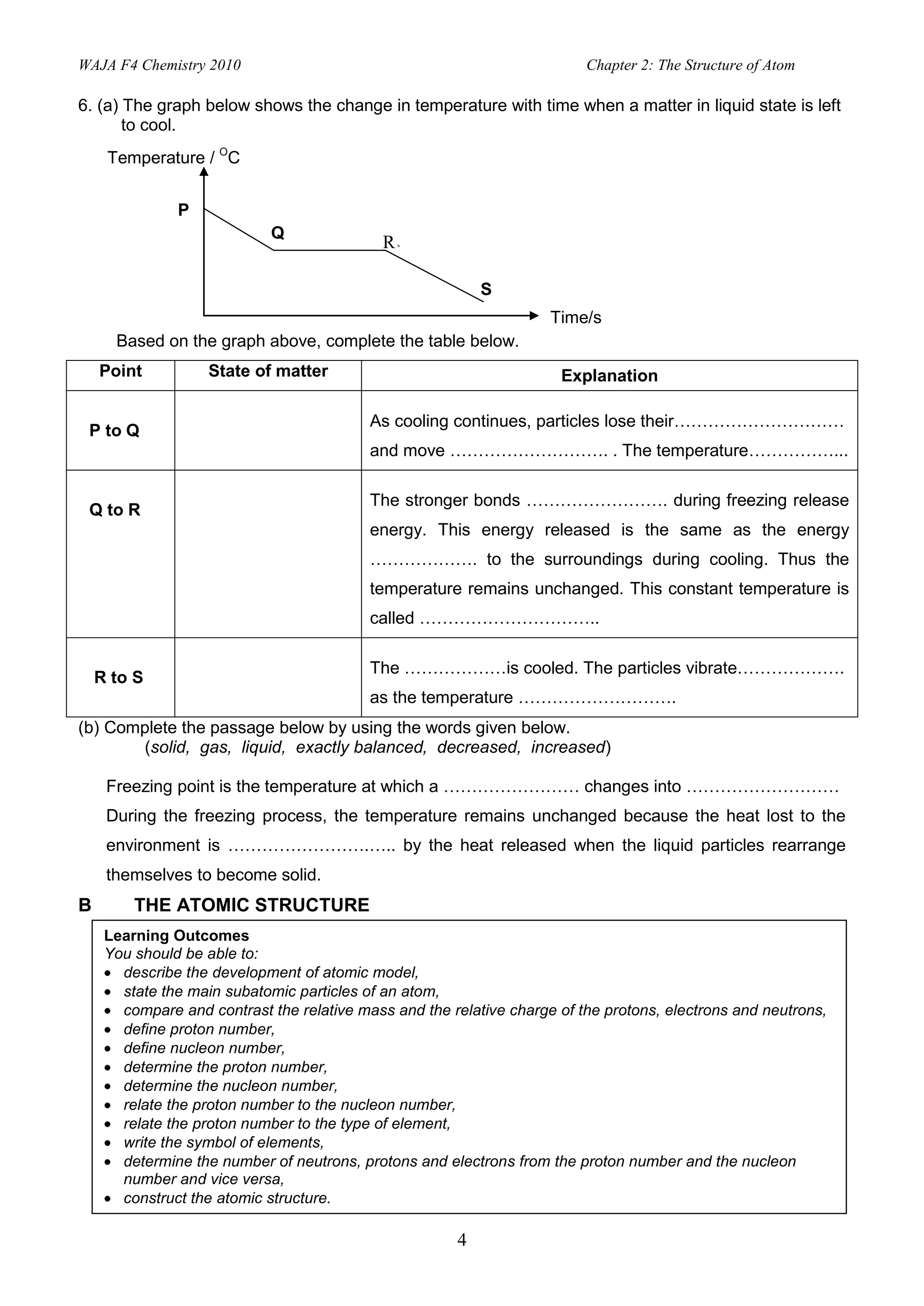
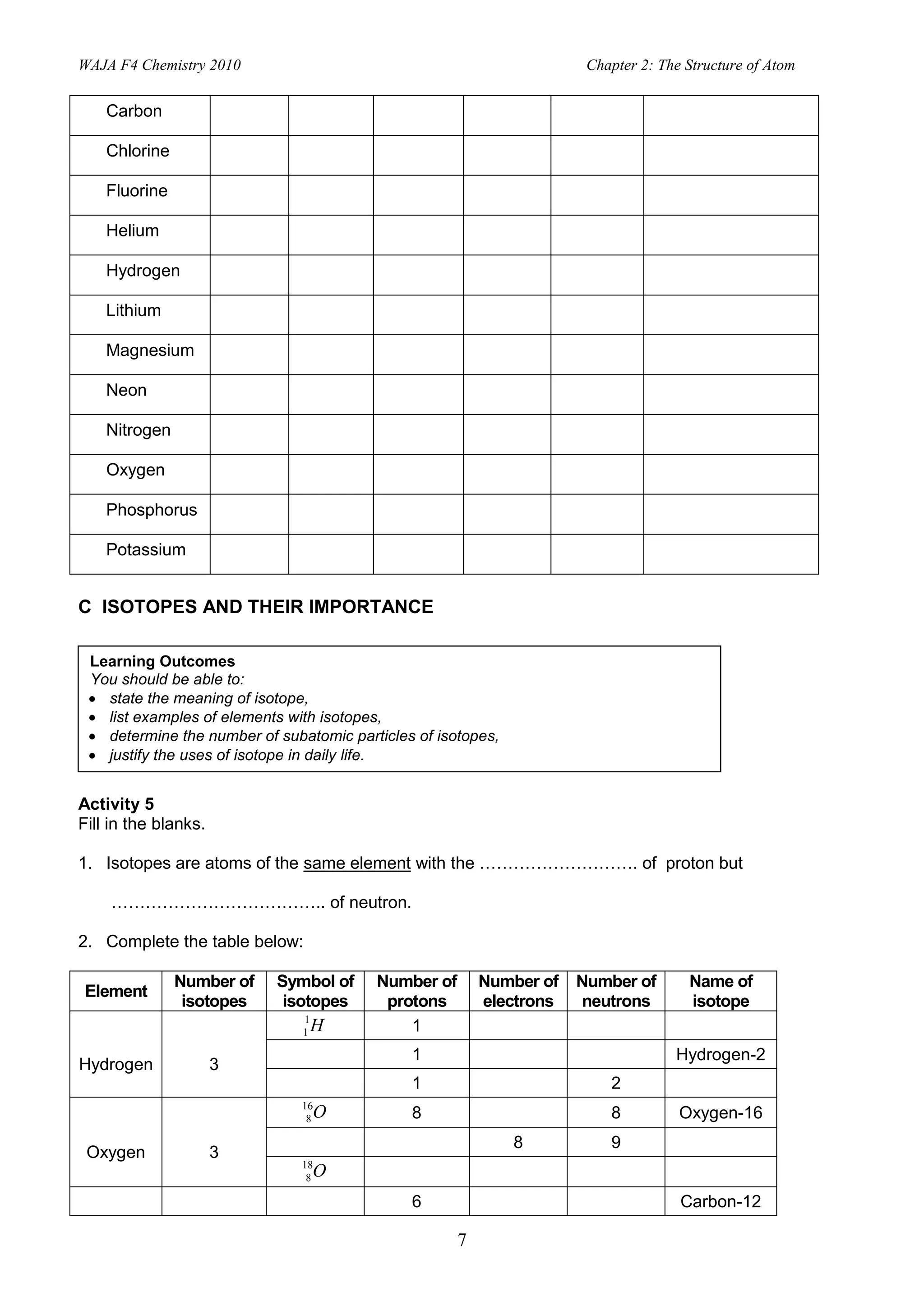
2. Activities include identifying states of matter based on particle arrangement and movement, writing atomic representations, determining numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons, and describing isotopes and their uses.
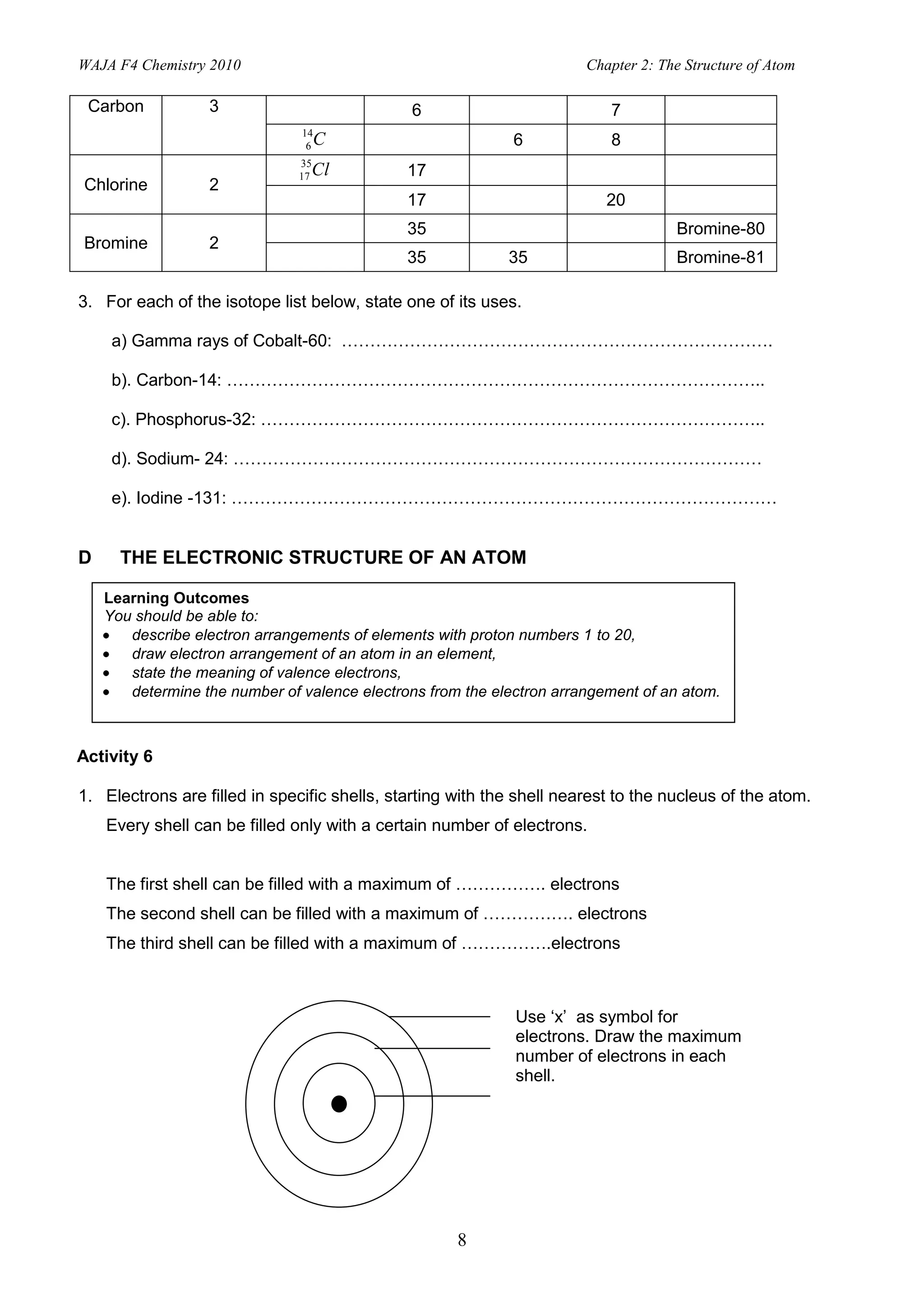
3. Electrons fill specific electron shells around the nucleus, with the first shell holding up to 2 electrons and subsequent shells filling with increasing numbers of electrons up to a maximum. Valence electrons are in the outermost shell.