This document provides an introduction to PHP, including:
- What scripting languages and PHP are, and how PHP works as a server-side scripting language
- The history and origins of PHP
- How to set up a PHP development environment using XAMPP
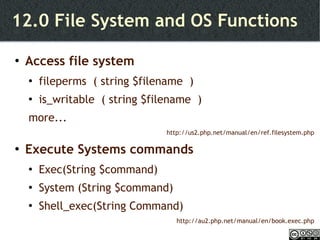
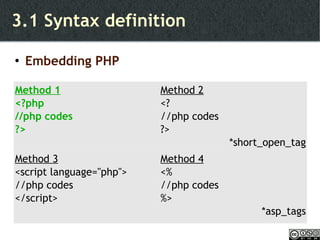
- PHP programming fundamentals like syntax, operators, and control structures
- How to handle forms and files in PHP
- How to connect to and manipulate databases like MySQL from PHP
- Several tasks as examples of working with forms, files, and databases in PHP
![PHP :\Introduction> Powered by www.RedOffice.com K.Sarveswaran Department of Computer Science, University of Jaffna [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-111117100641-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-PHP-1-2048.jpg)




























![3.5 Arrays Method 1 $person[0] = "Saman"; $person[1] = "Ravi"; $person[2] = "Kamal"; Method 2 $method2['Country'] = "Sri Lanka"; $method2['Location'] = "Indian Ocean";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-111117100641-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-PHP-34-320.jpg)




![4.2 Handling form data POST $variable=$_POST['variable']; GET $variable=$_GET['variable']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-111117100641-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-PHP-39-320.jpg)












![6.4 File uploads Useful functions : Set proper enctype in the input form $_FILES["file"]["name"] - the name of the uploaded file $_FILES["file"]["type"] - the type of the uploaded file $_FILES["file"]["size"] - the size in bytes of the uploaded file $_FILES["file"]["tmp_name"] - the name of the temporary copy of the file stored on the server $_FILES["file"]["error"] - the error code resulting from the file upload move_uploaded_file($_FILES["file"]["tmp_name"], "uploads/" . $_FILES["file"]["name"])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-111117100641-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-PHP-52-320.jpg)









![7.3 Database handing basics -2 Tabular data manipulation Retrieve data Inside the SQL queries, all strings values must be single quoted. Insert data Returns true / false $result = mysql_query ("SELECT * FROM table"); while($row = mysql_fetch_array ($result)) { echo $row['field1'] . " " . $row['field2']; } mysql_query ("INSERT INTO Table (Field1, Field2) VALUES ('Value1', 'Value2')");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-111117100641-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-PHP-62-320.jpg)






![8.2 Cookie Create Cookie Prototype : setcookie(name, value, expire) Eg : setcookie("id", "123", time()+3600); This should be before the <HTML> Access Cookie $_COOKIE['name'] Delete Cookie Set the expiration time is passed setcookie("id", "", time()-1000)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-111117100641-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-PHP-71-320.jpg)
![8.3 Session Start session session_start(); This must be the very 1 st statement of a script Access session $_SESSION['sessionName'] Destroy a session variable unset($_SESSION['sessionName']) Destroy whole session session_destroy();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-111117100641-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-PHP-72-320.jpg)





![9.1 PHP- OOP basics - 4 Constructor - Destructor Class Employee { function _construct([arg1, arg2...]) { } Function _destruct() { } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-111117100641-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-PHP-79-320.jpg)