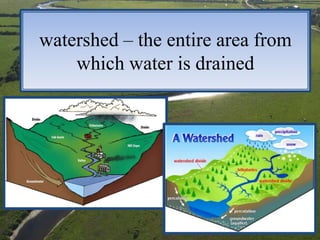
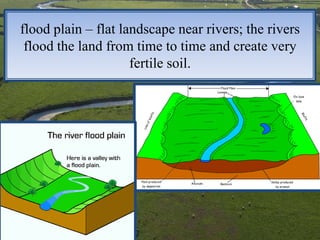
This document defines and describes various landforms created by water and erosion processes, including runoff, tributaries, watersheds, meanders, flood plains, deltas, water gaps, canyons, valleys, dunes, and landslides. It explains key terms like sediment, tributaries that feed into rivers, watershed areas, and landforms shaped by river currents, flooding, sediment deposition, and erosion from water and wind. The document provides definitions and brief descriptions of common landforms.