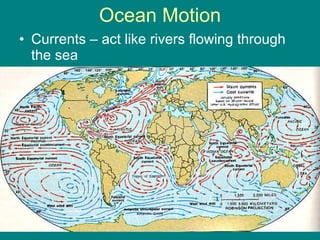
This document provides an overview of bodies of water and various landforms. It describes the four main oceans, ocean motion including currents, waves and tides, and the hydrologic cycle of water circulation. It also discusses groundwater, lakes, rivers and streams, drainage basins, the continental shelf, continental landforms including relief and topography, and major landforms such as islands, swamps, straits, deltas, oases, plateaus, prairies, steppes, mountains, valleys, glaciers, cataracts and cliffs.