1. Programming languages enable humans to communicate with computers by using words, symbols, and codes to direct a computer to perform tasks and control mechanical devices.
2. Early programming languages progressed from machine language and assembly language as first and second generation languages, to higher-level languages like FORTRAN, BASIC, and COBOL as third generation languages. Fourth and fifth generation languages provided more specialized and visual interfaces.
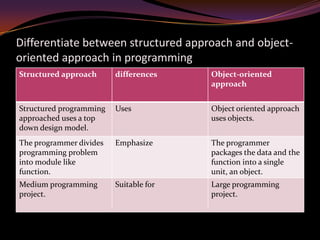
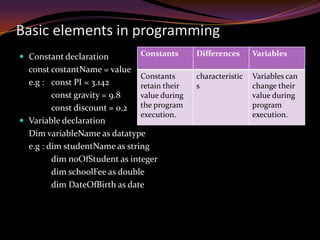
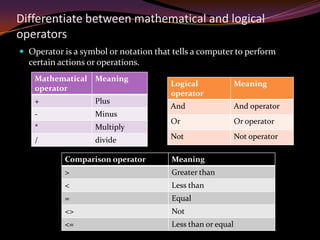
3. Key aspects of programming include structured and object-oriented design, variables and constants, operators, flow control, translation methods like compilers and interpreters, and the development process of problem analysis, design, coding, testing and documentation. Understanding different programming elements and techniques is essential for writing effective programs.