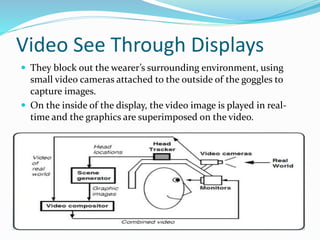
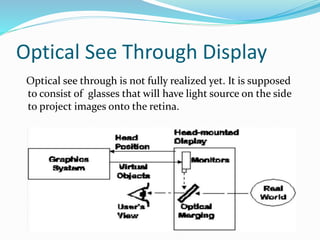
This document discusses augmented reality and virtual reality. It begins by defining augmented reality and virtual reality, noting that while virtual reality was attempted in the 1990s with devices like the Virtual Boy, the technologies are now improving. It then provides details on the key components of an augmented reality system, including head-mounted displays, tracking systems, and mobile computing power. Examples are given of how augmented reality could be used for education, medicine, tourism, and gaming. Limitations including accuracy of tracking systems and high hardware costs are also outlined. Major companies developing virtual reality technologies are mentioned, such as Oculus VR, Microsoft, Sony, Samsung, and Google.