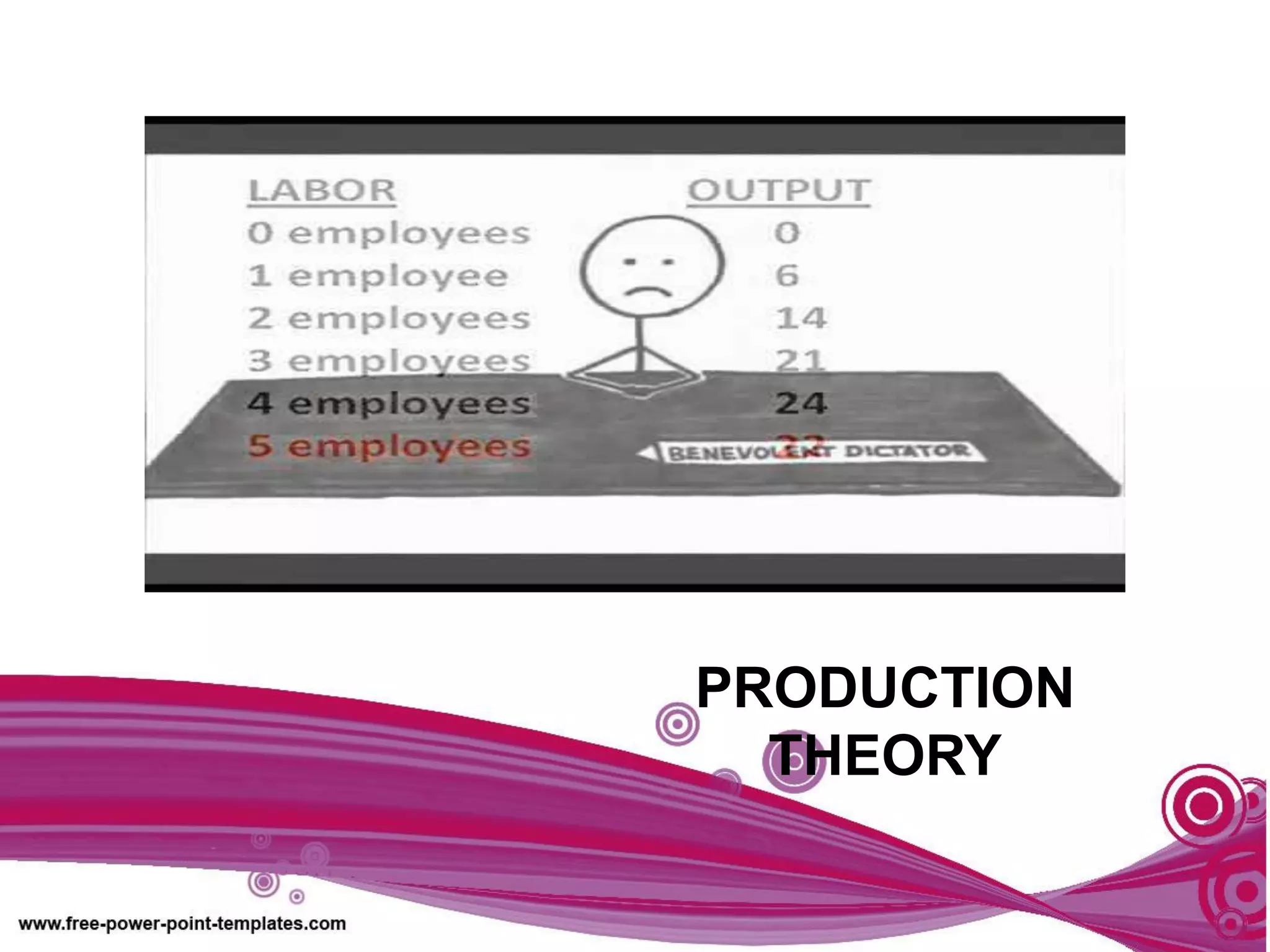
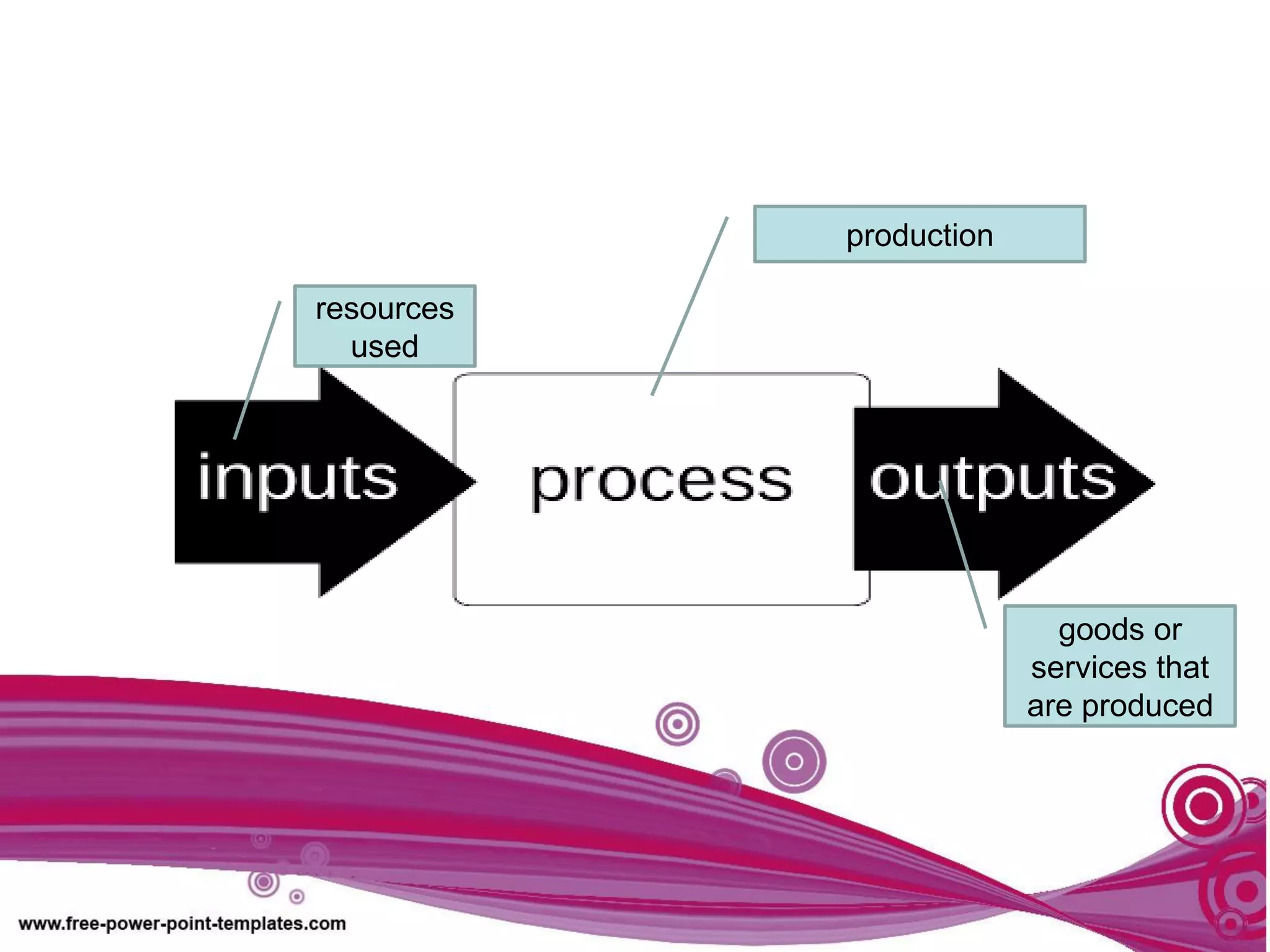
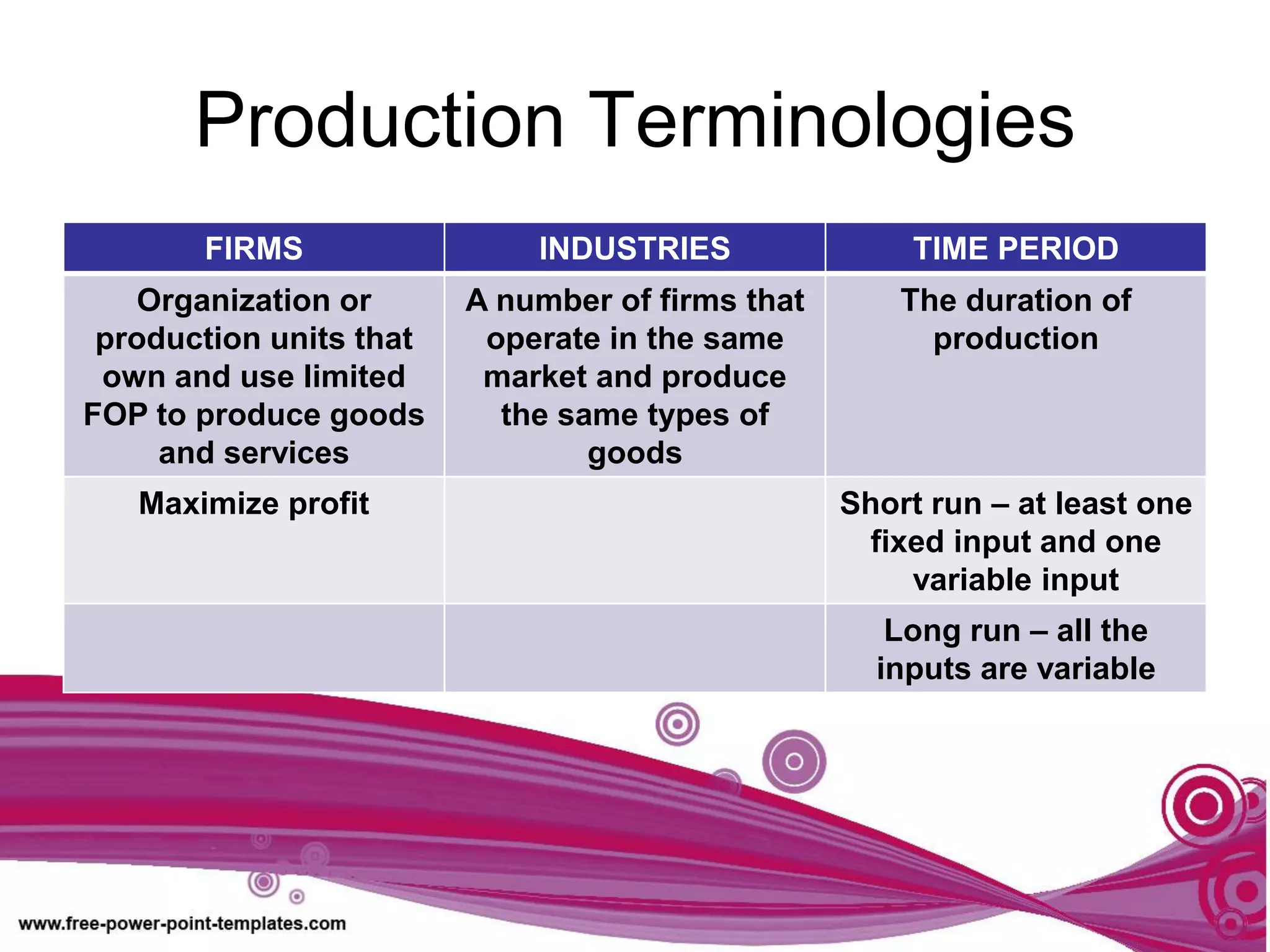
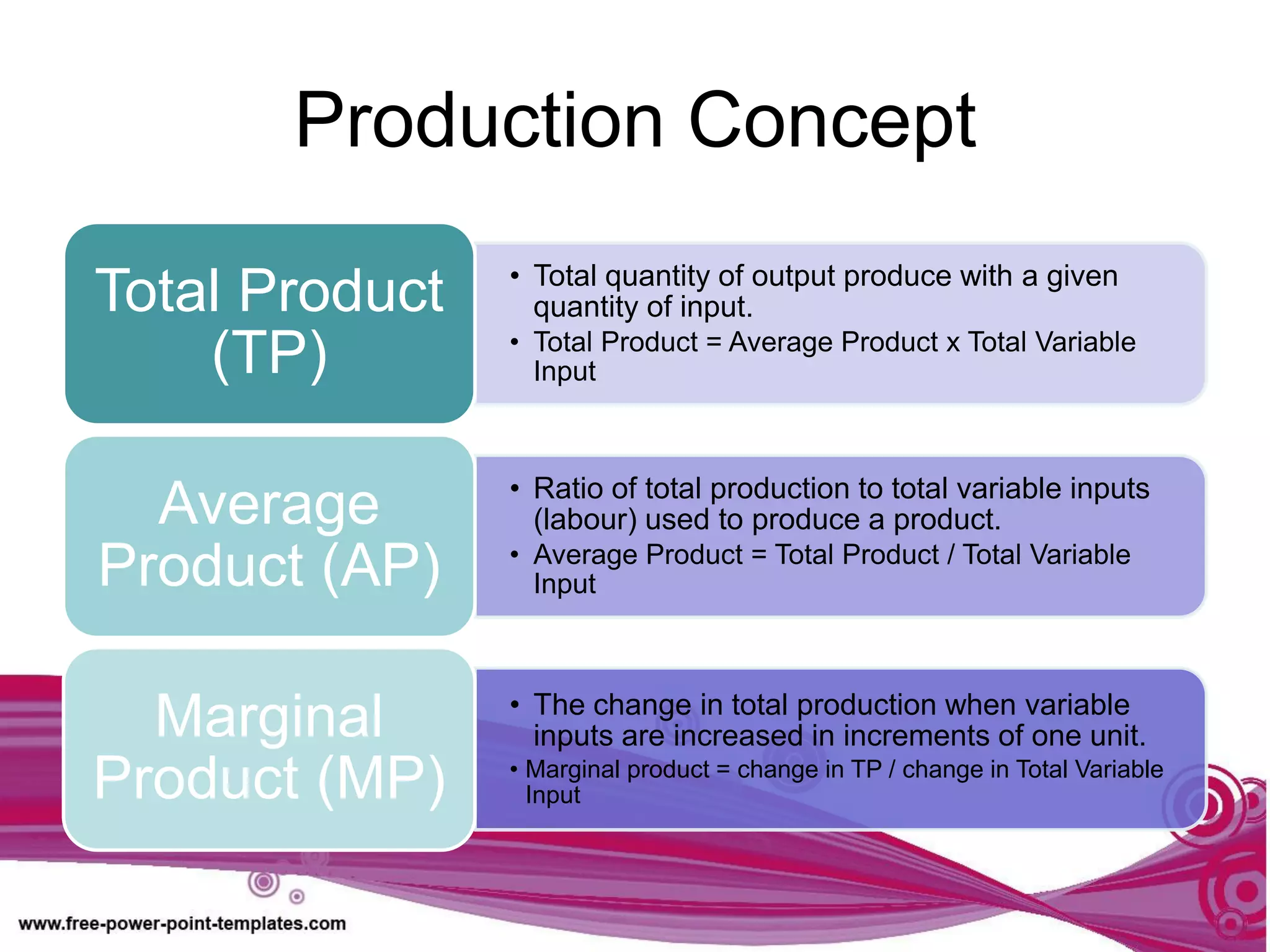
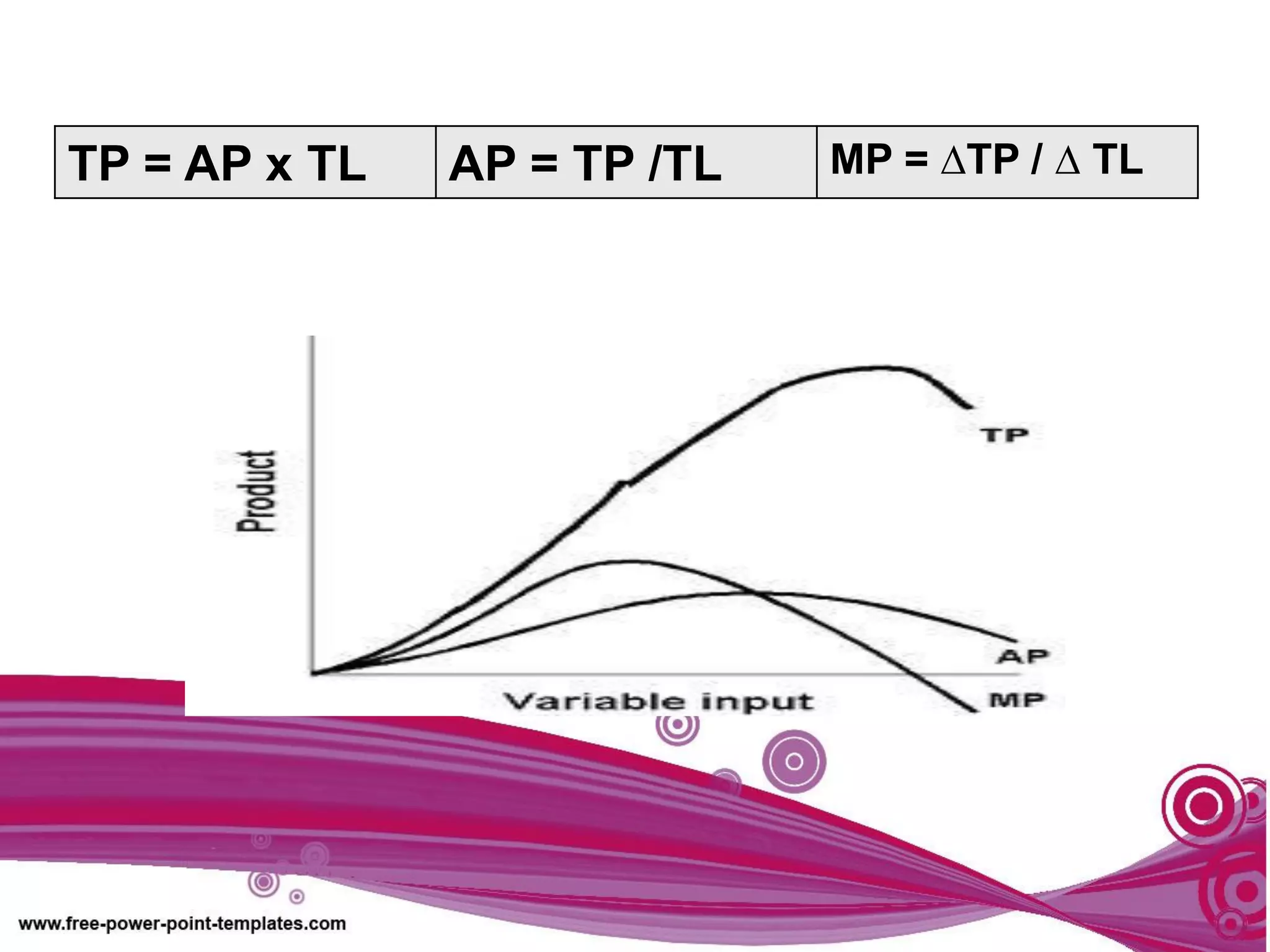
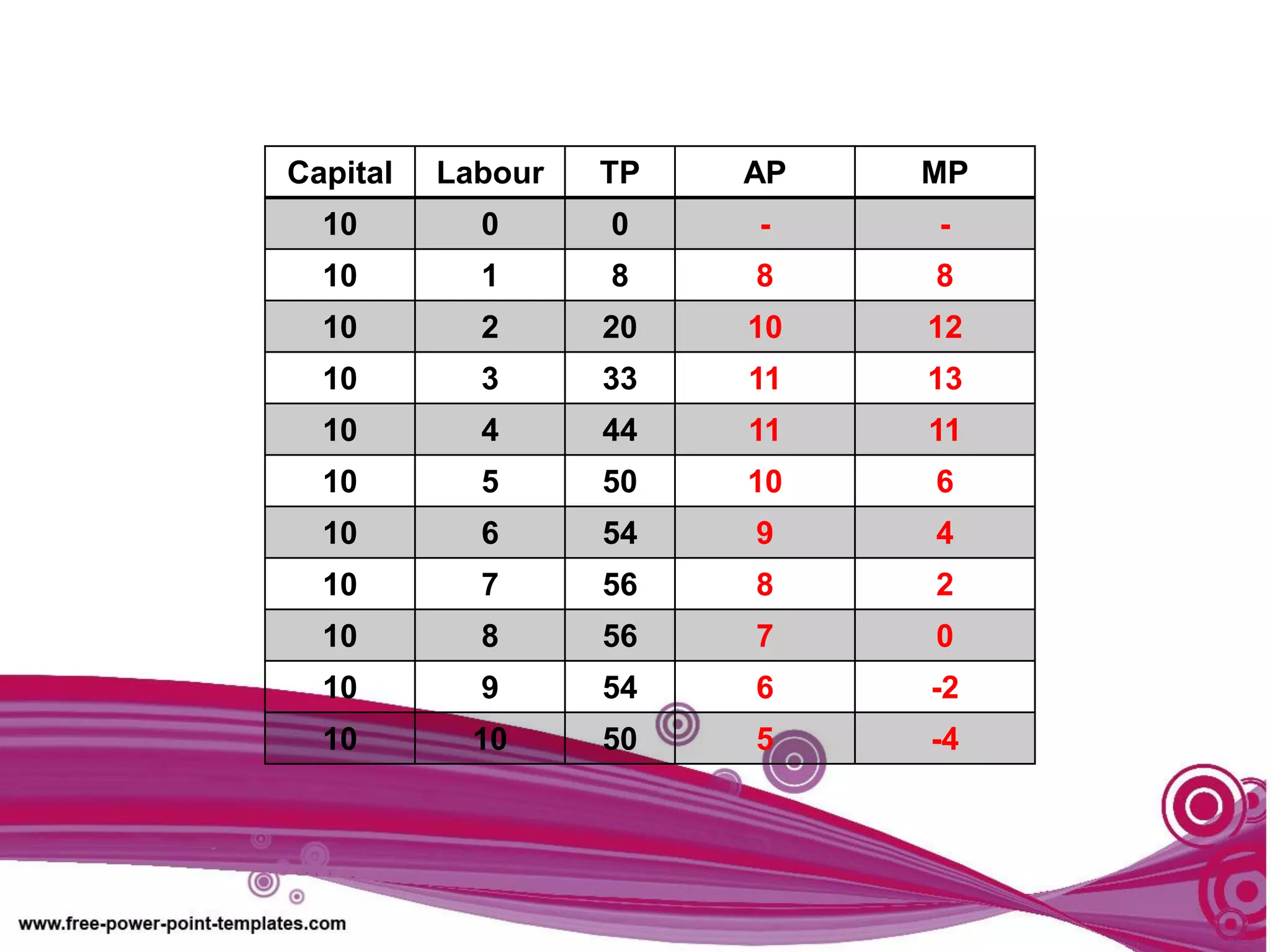
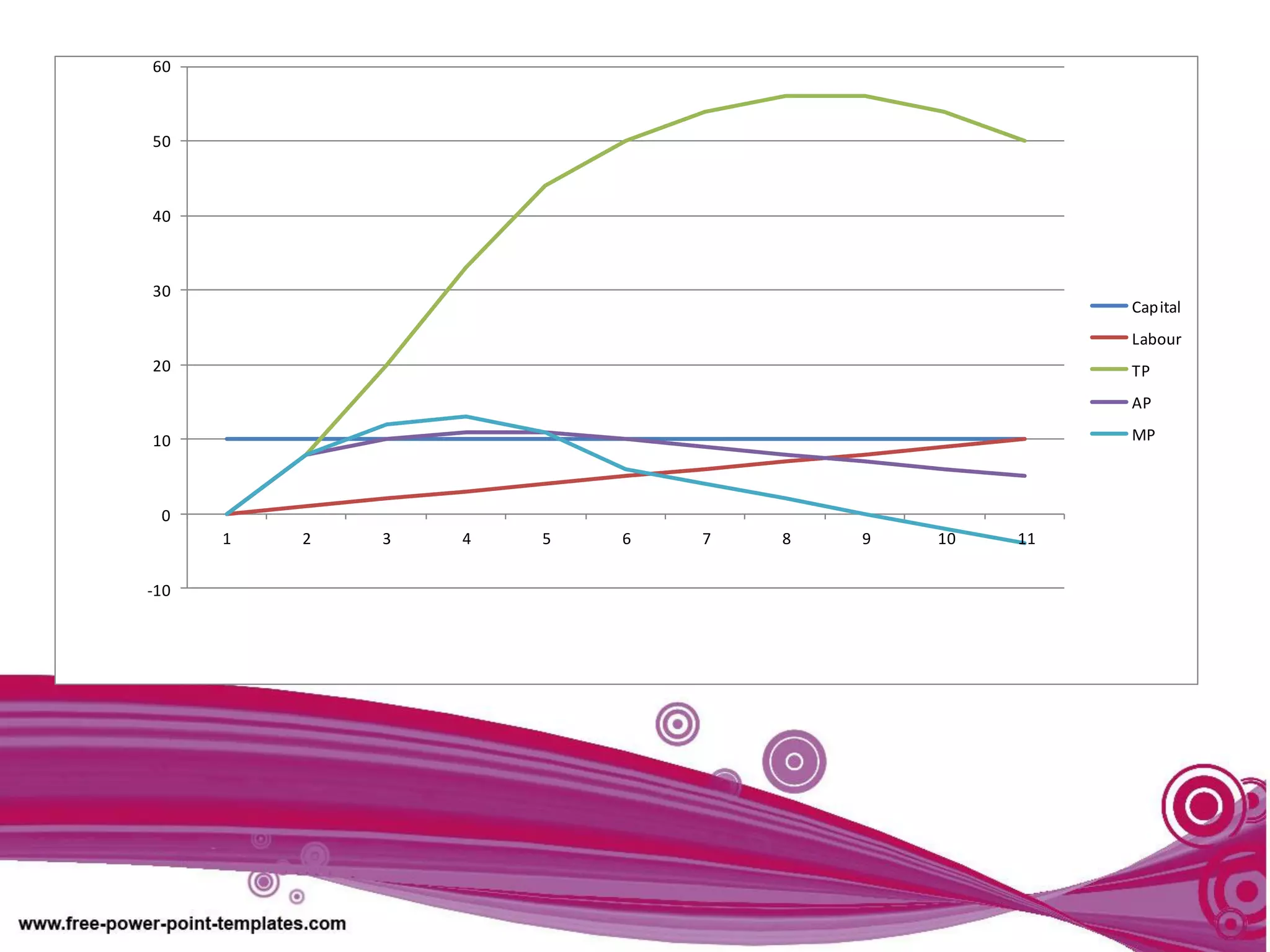
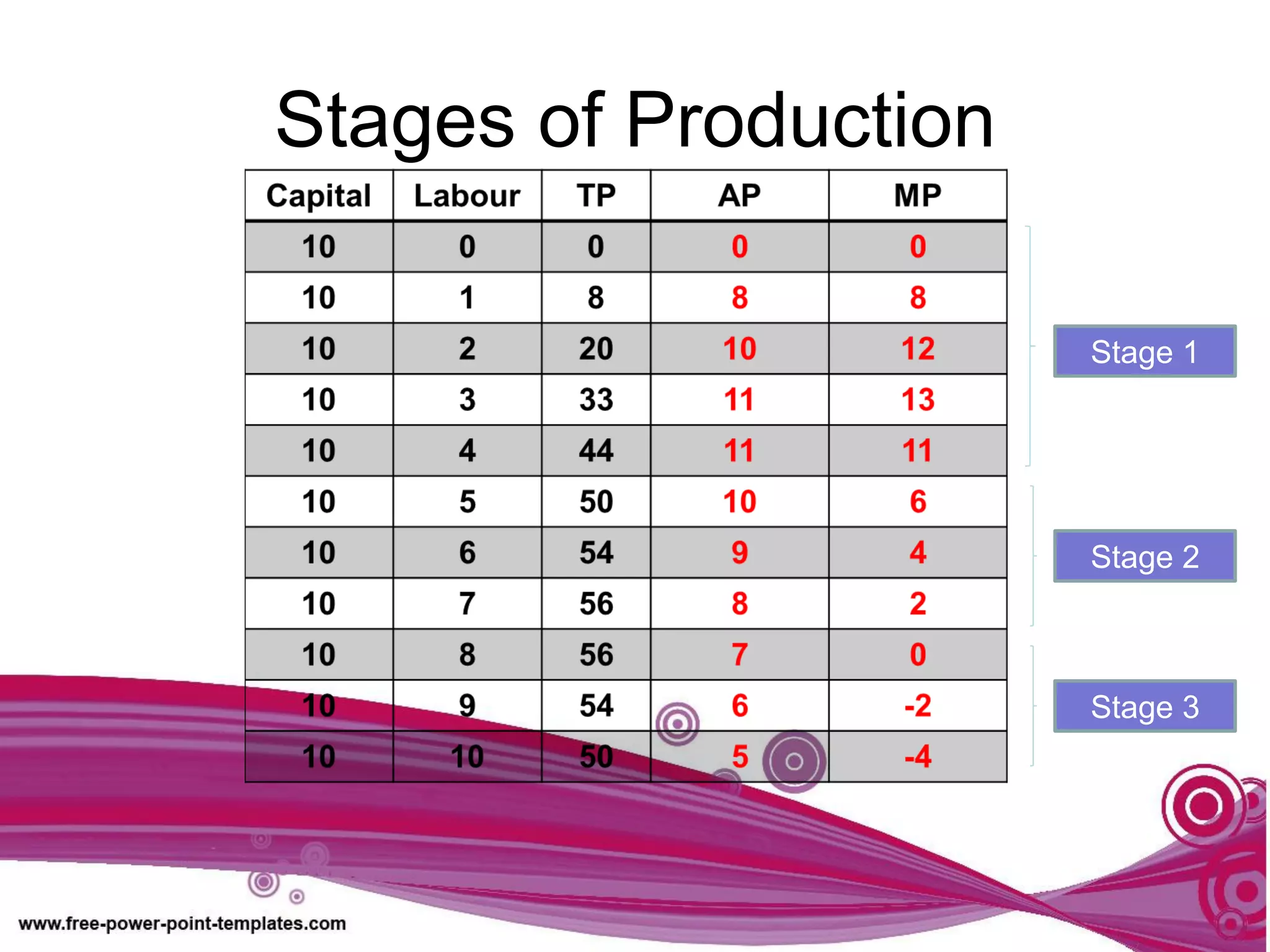
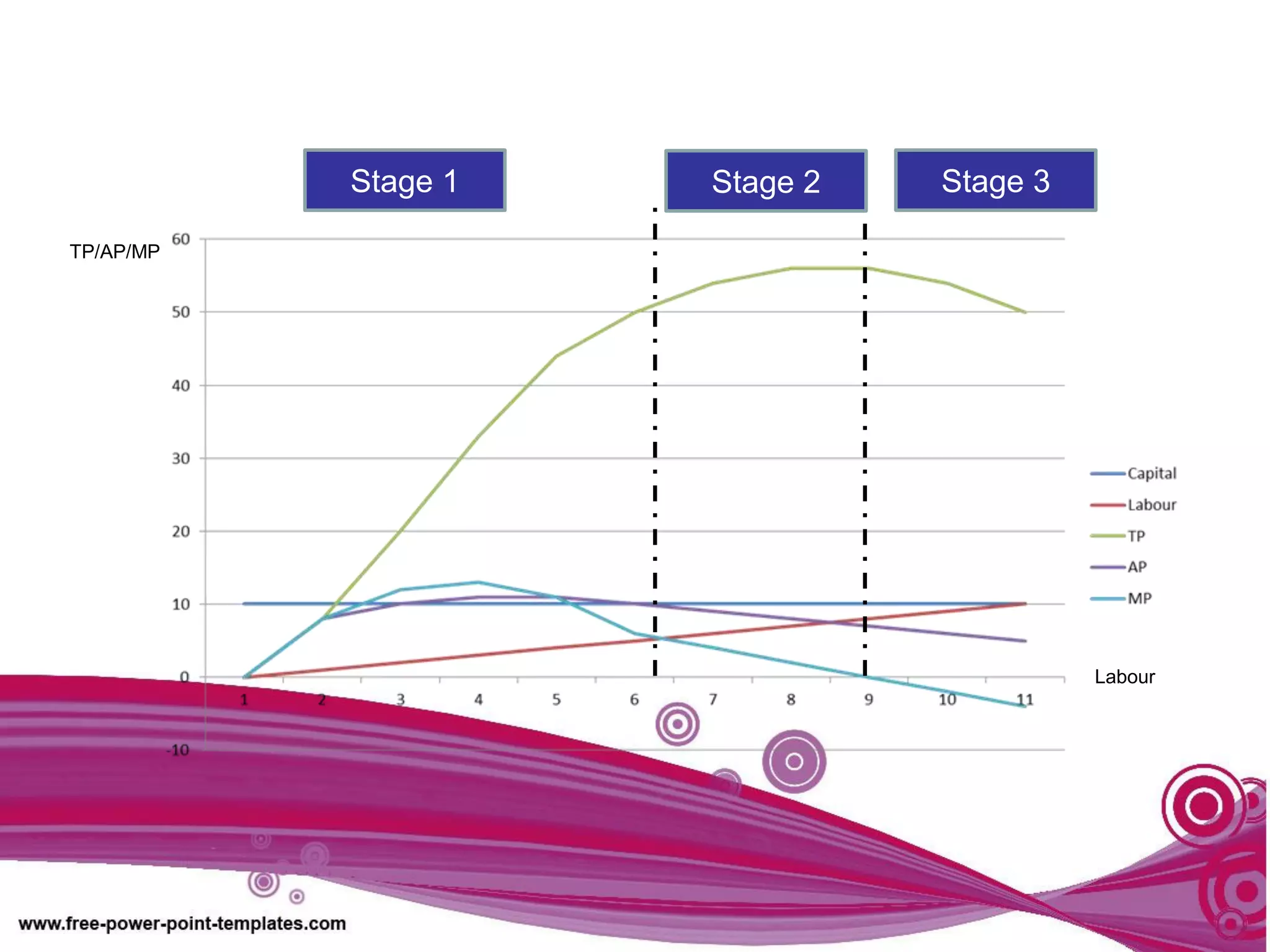
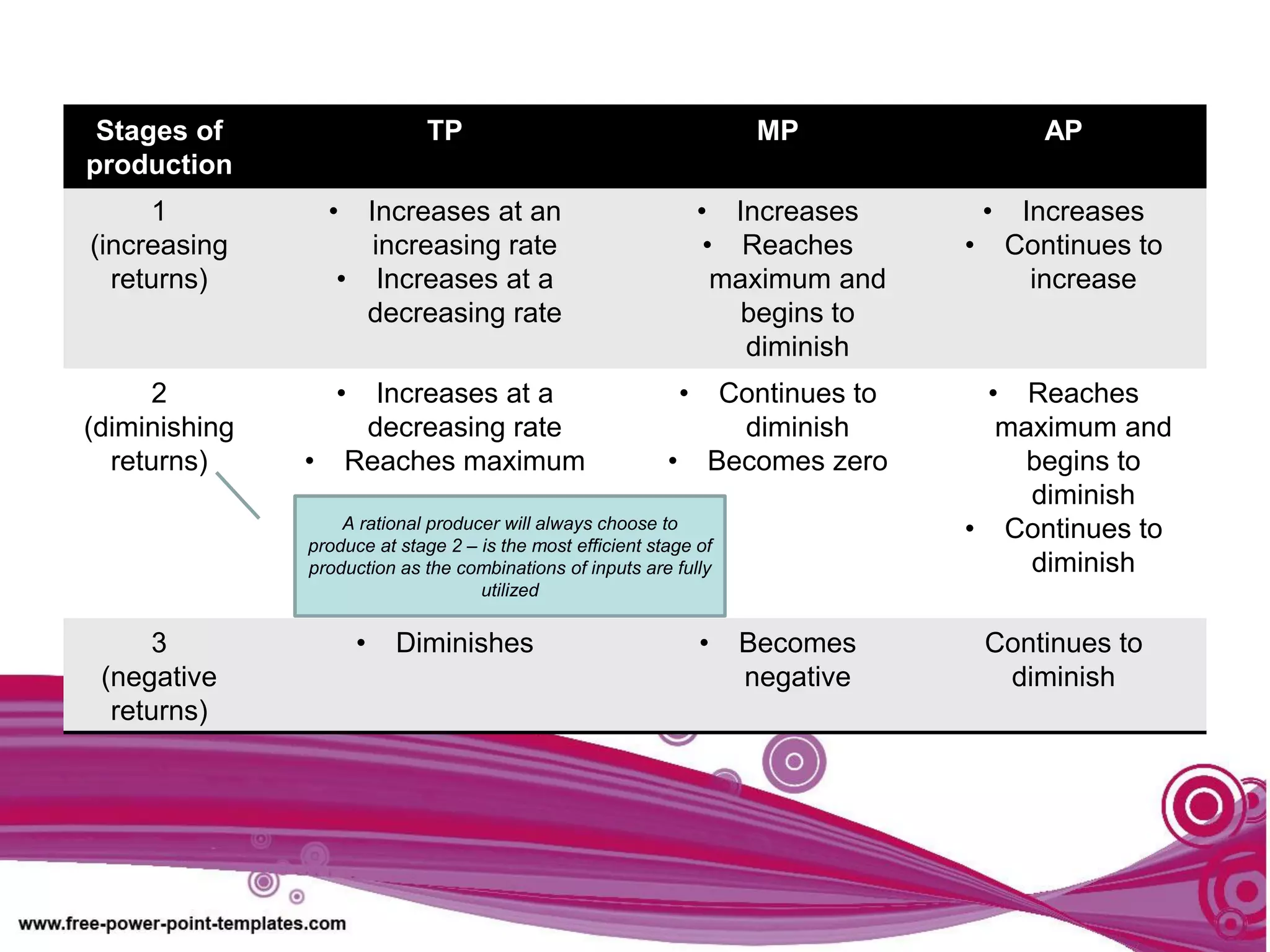
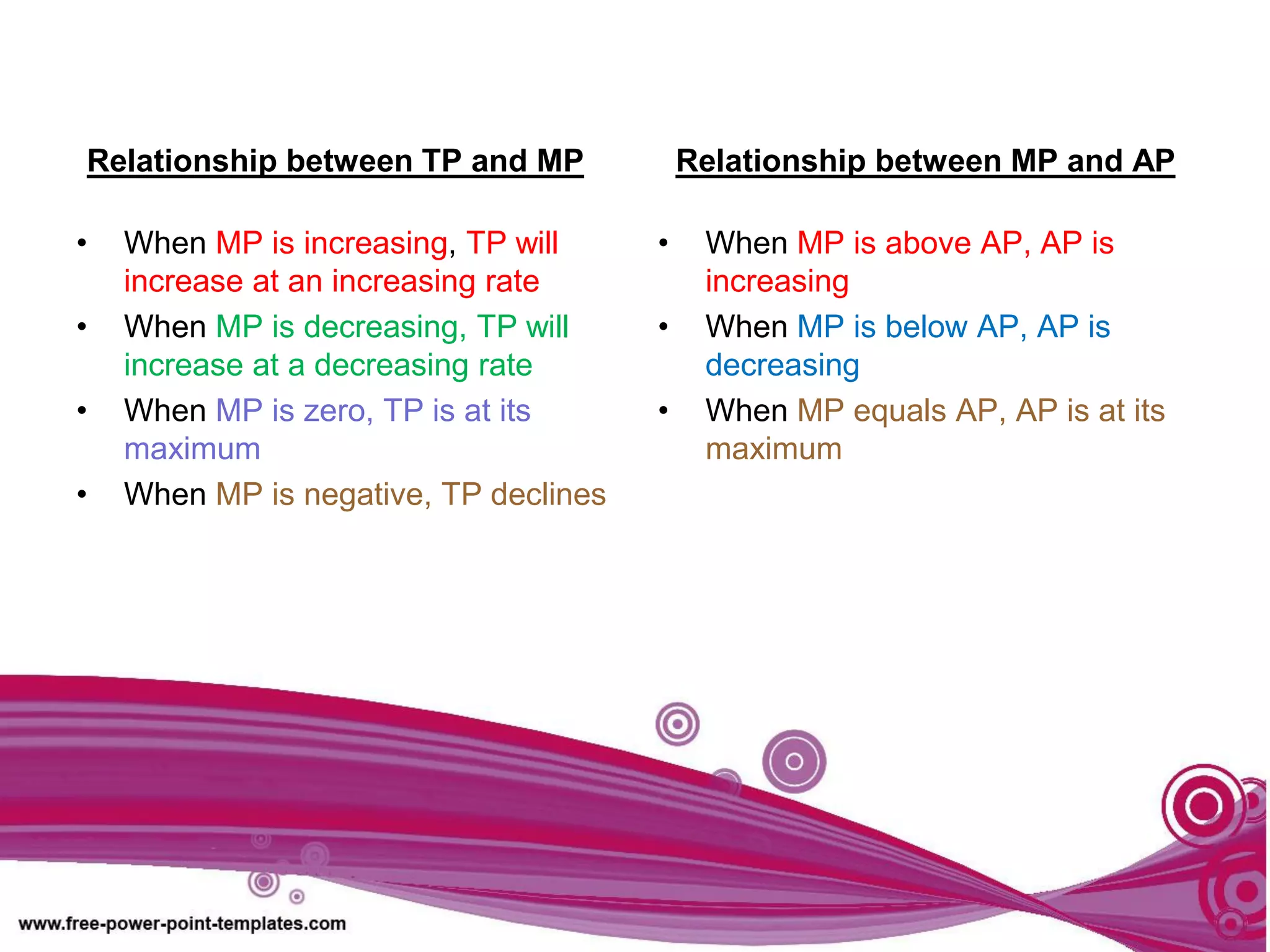
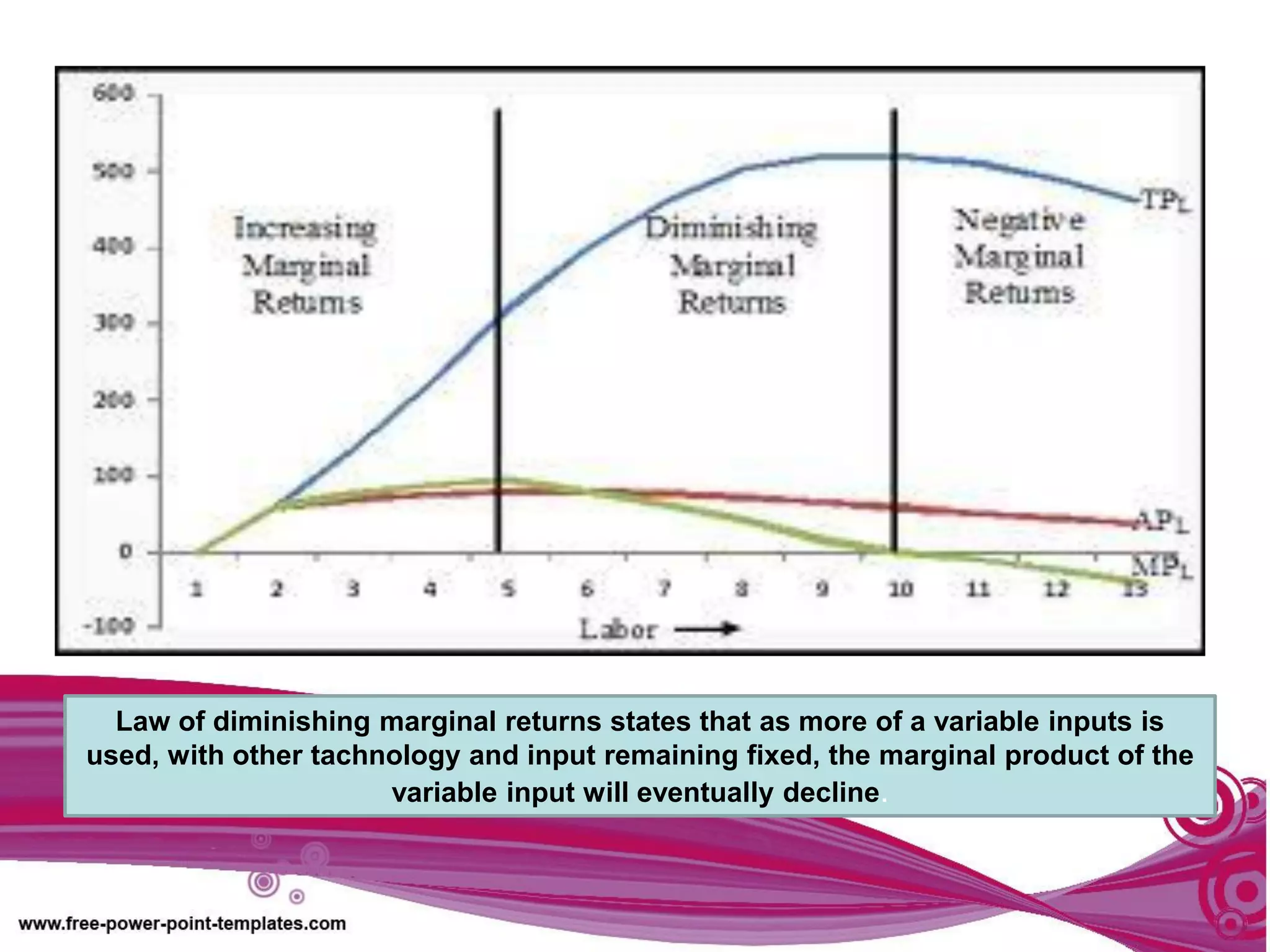
The document discusses production theory concepts including factors of production, production terminologies, production functions, stages of production, and the law of diminishing marginal returns. It defines key terms like firms, industries, time periods, total product, average product, and marginal product. Tables show how total product, average product, and marginal product change as capital is held constant and labor is increased. Graphs plot the relationships between these production concepts. Stages of production are outlined showing how total product, average product, and marginal product behave at different levels of input.