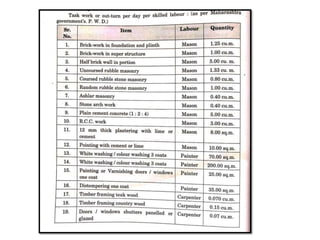
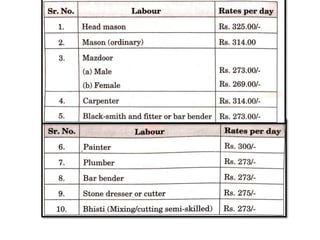
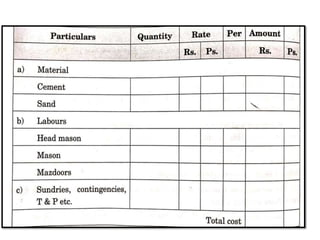
The analysis of rates is determining the cost per unit of an item of work based on materials, labor, and other expenses. It involves calculating the costs of materials and labor, which vary by location, and determining the actual cost per unit. This is used to calculate the costs of extra work, revise rates due to cost changes, and ensure economical use of materials and processes. Factors that influence the analysis include material and labor costs, equipment, work conditions, specifications, and contractor profit.