1. The document discusses rate analysis and costing for construction projects. It covers collecting standard data on labor and machinery hours, analyzing market and schedule rates, and preparing cost estimates using computer software.
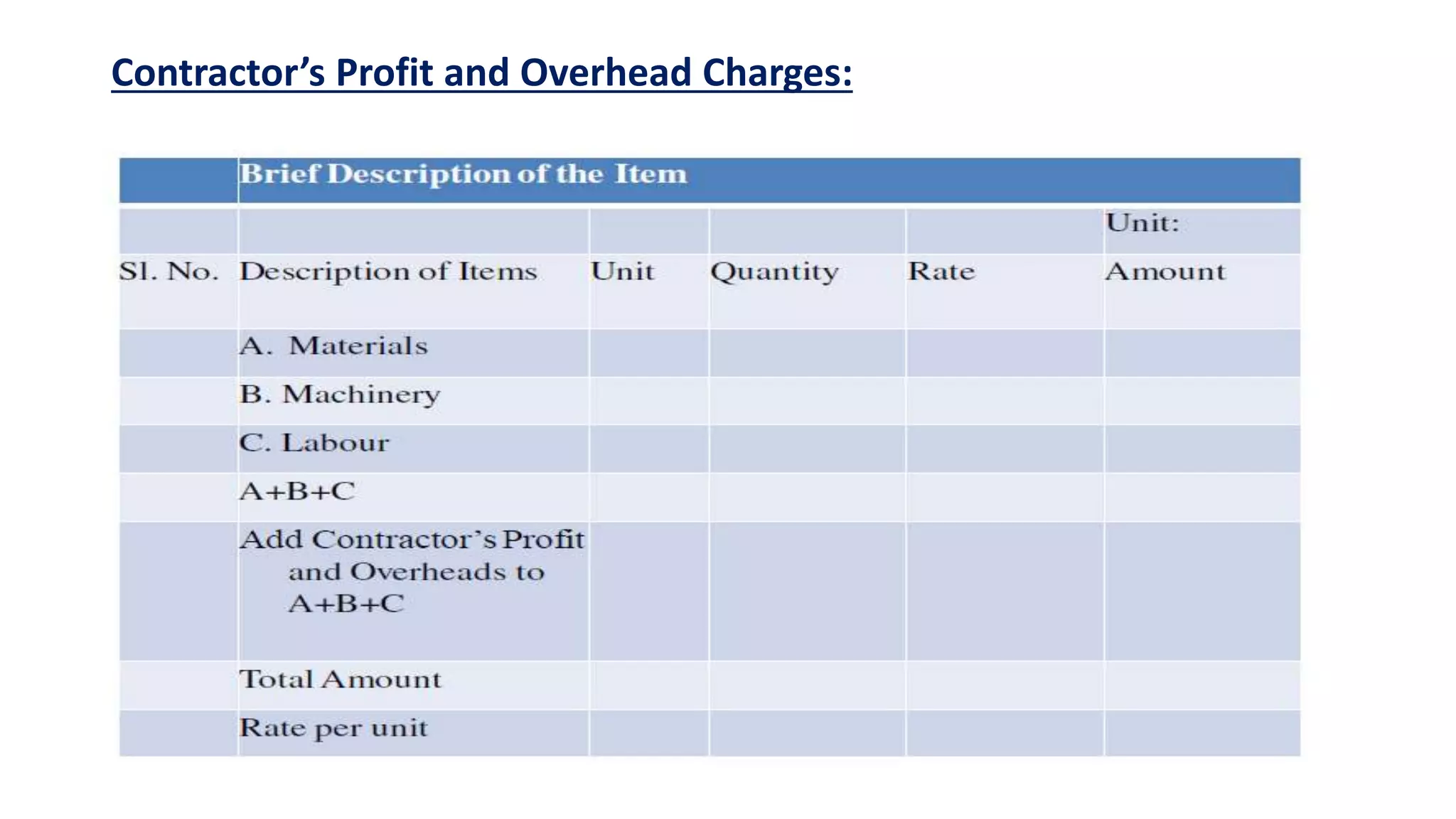
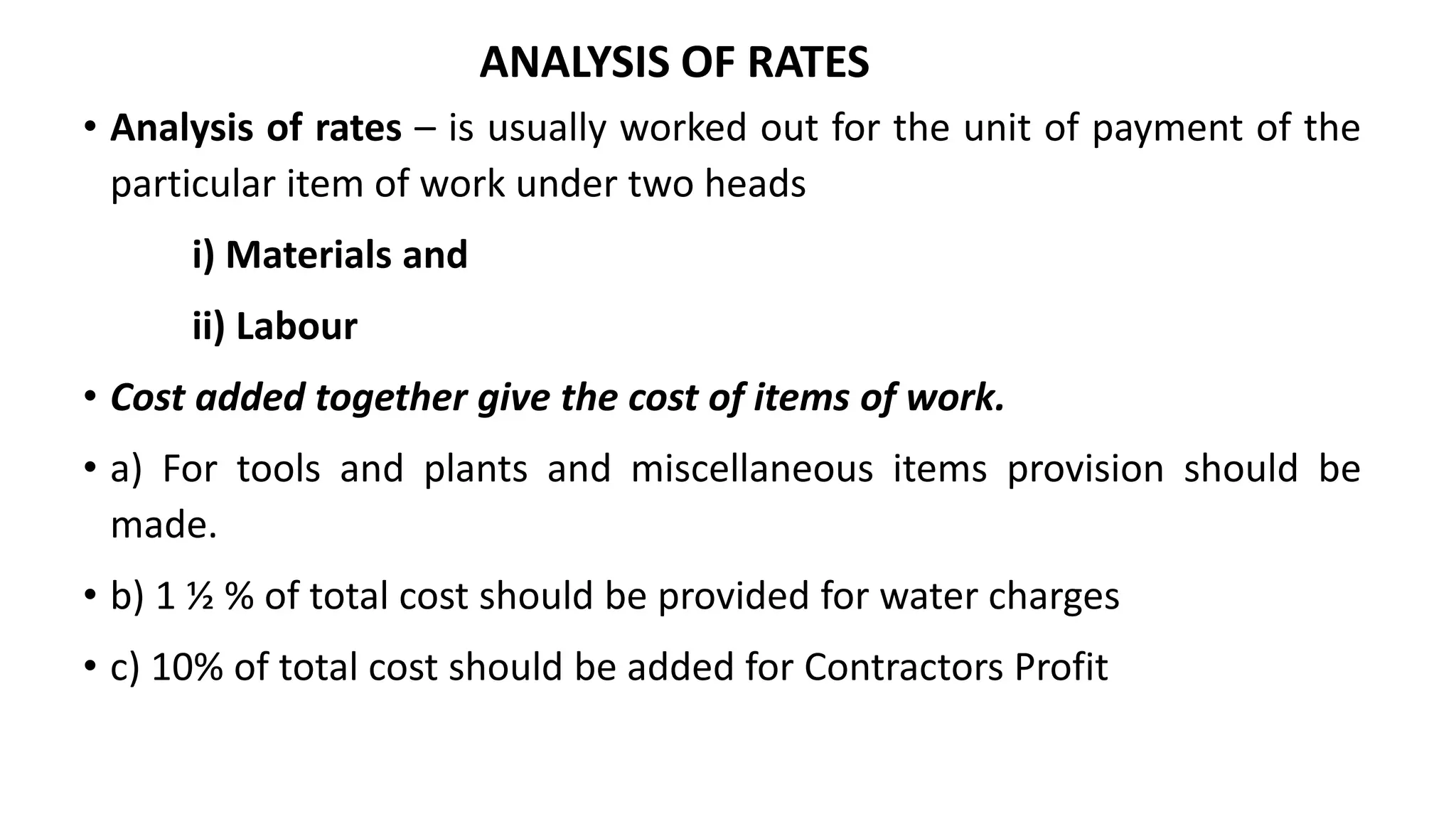
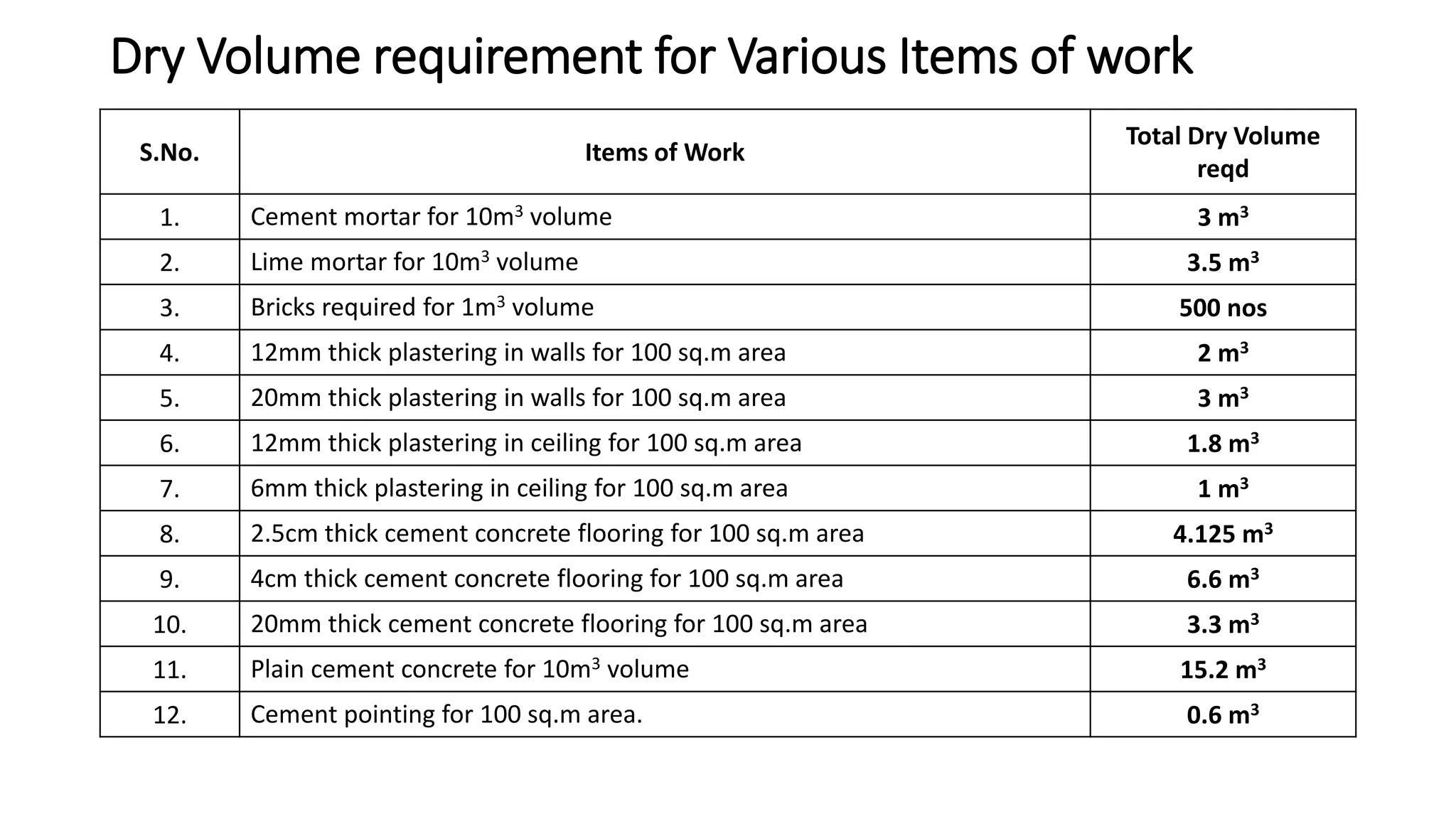
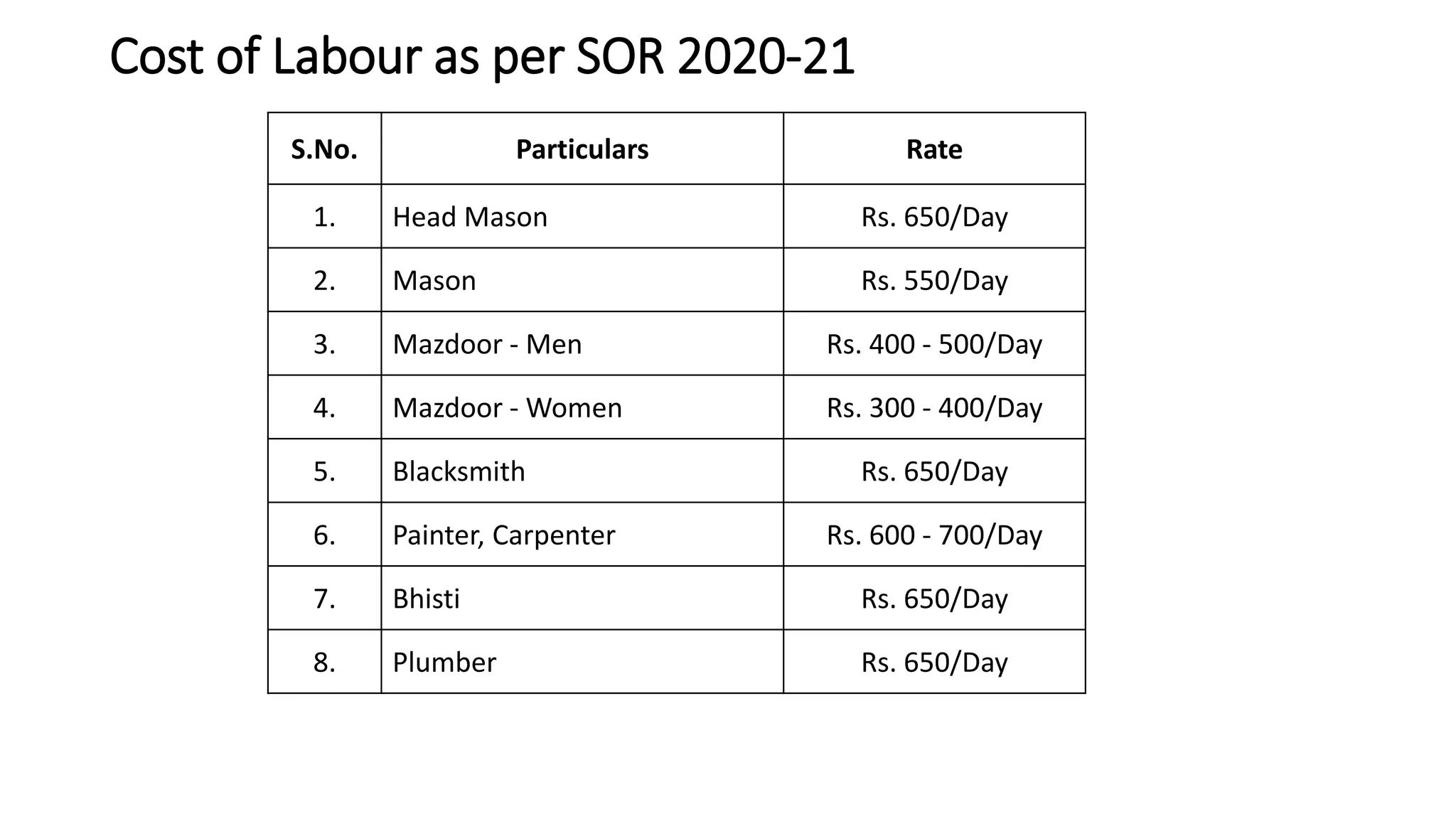
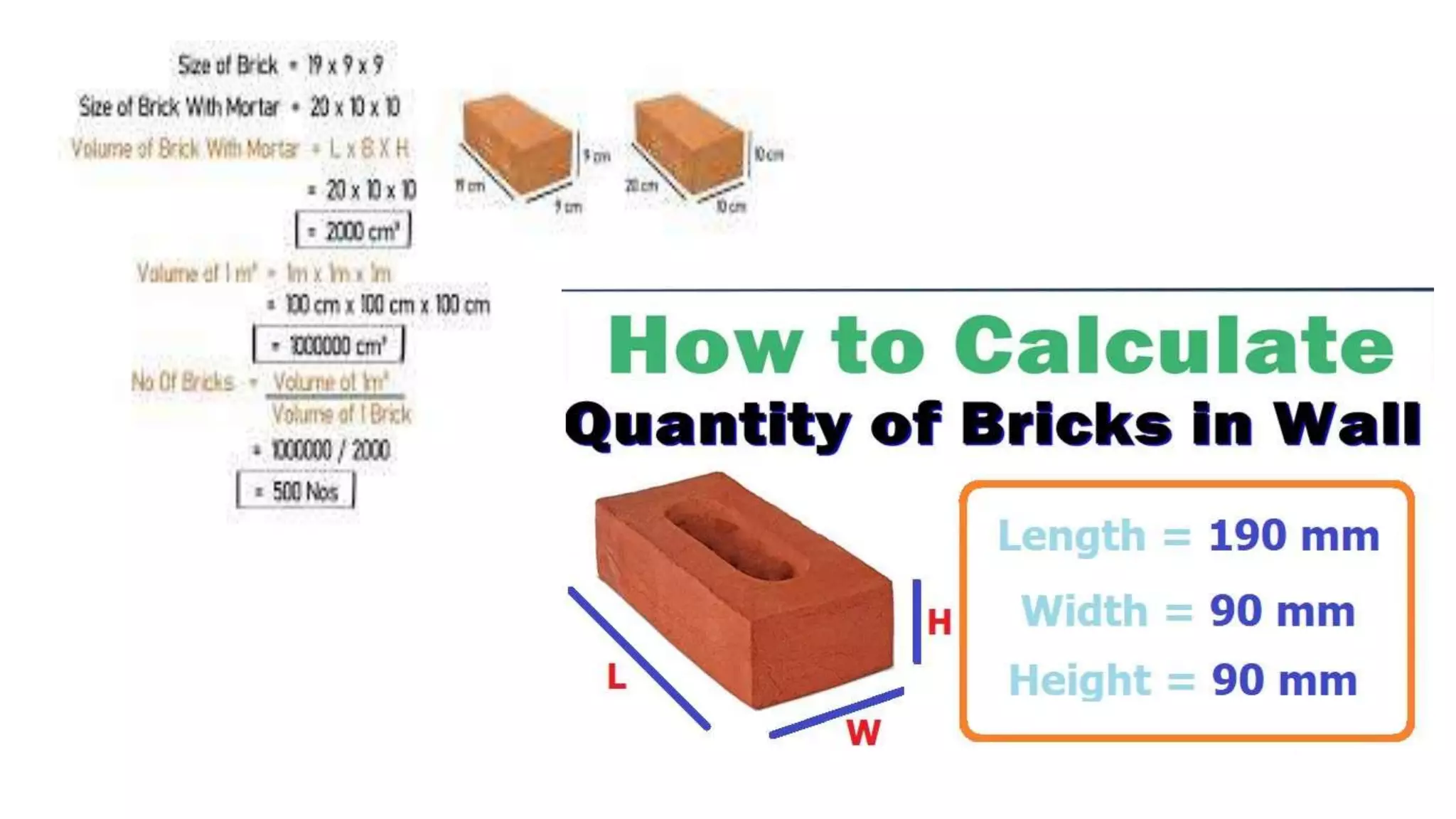
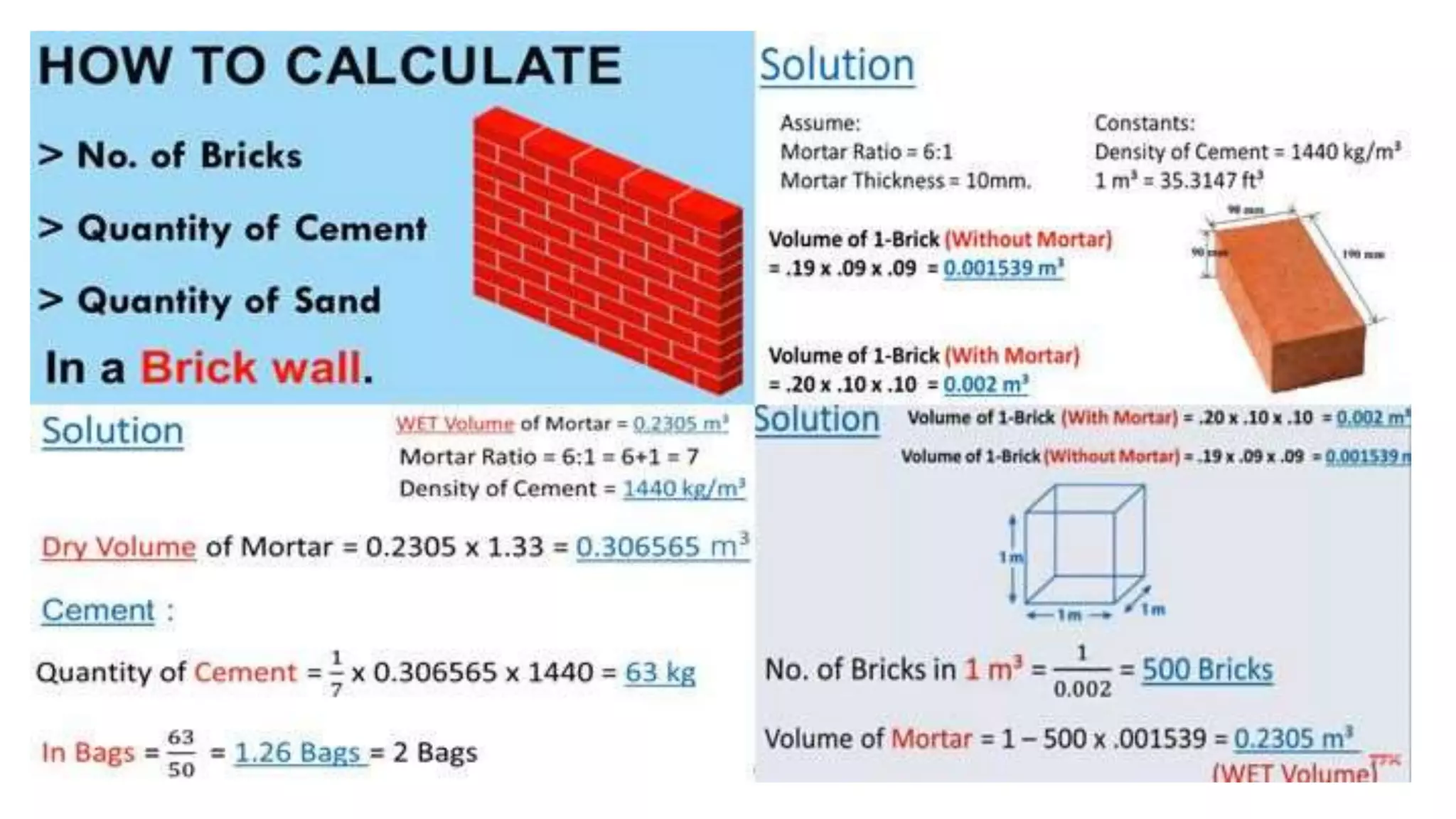
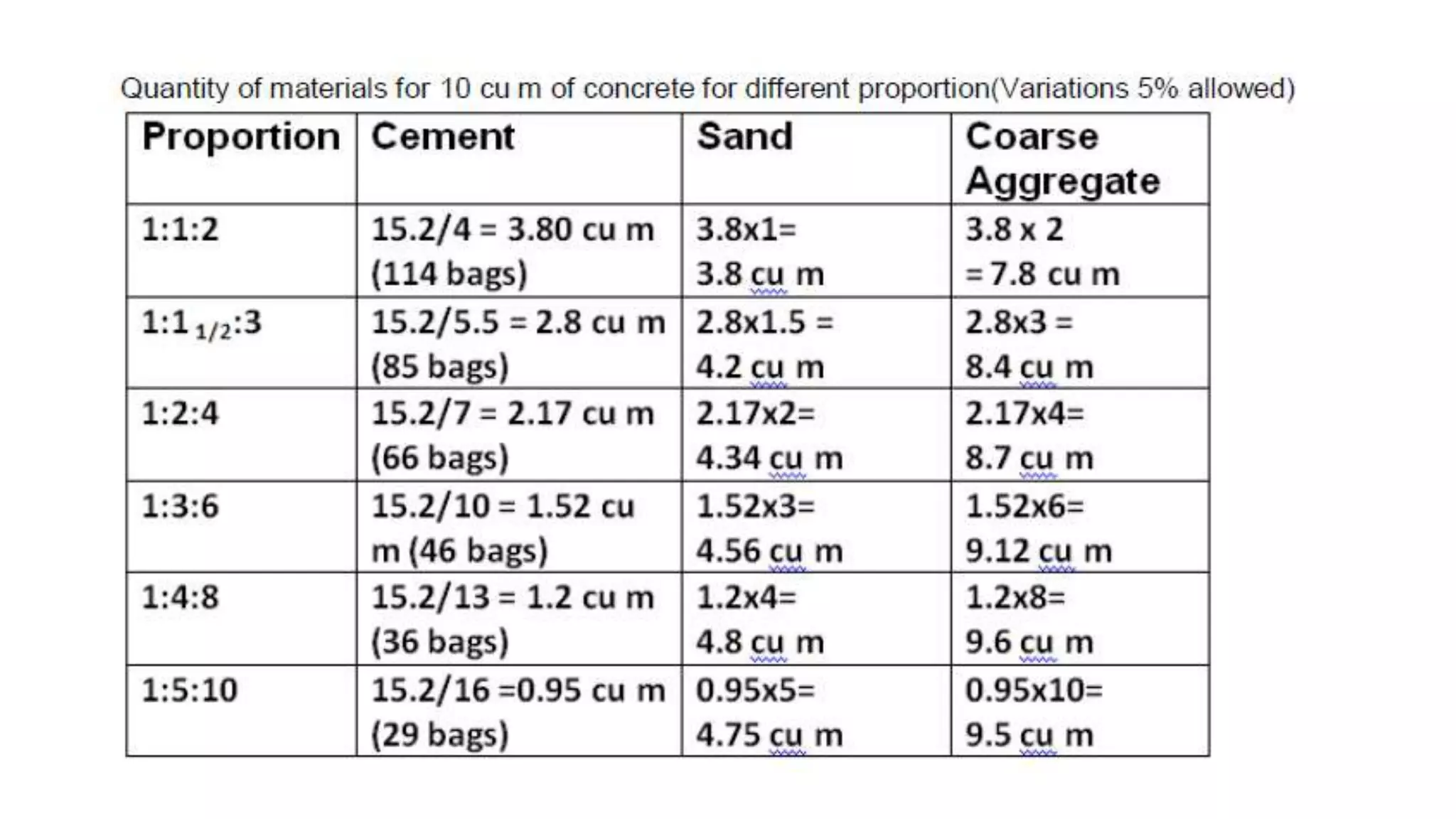
2. Key steps in rate analysis are collecting data on labor and material rates, quantities from standard data books, calculating costs, and adding overhead and profit to determine the unit rate.
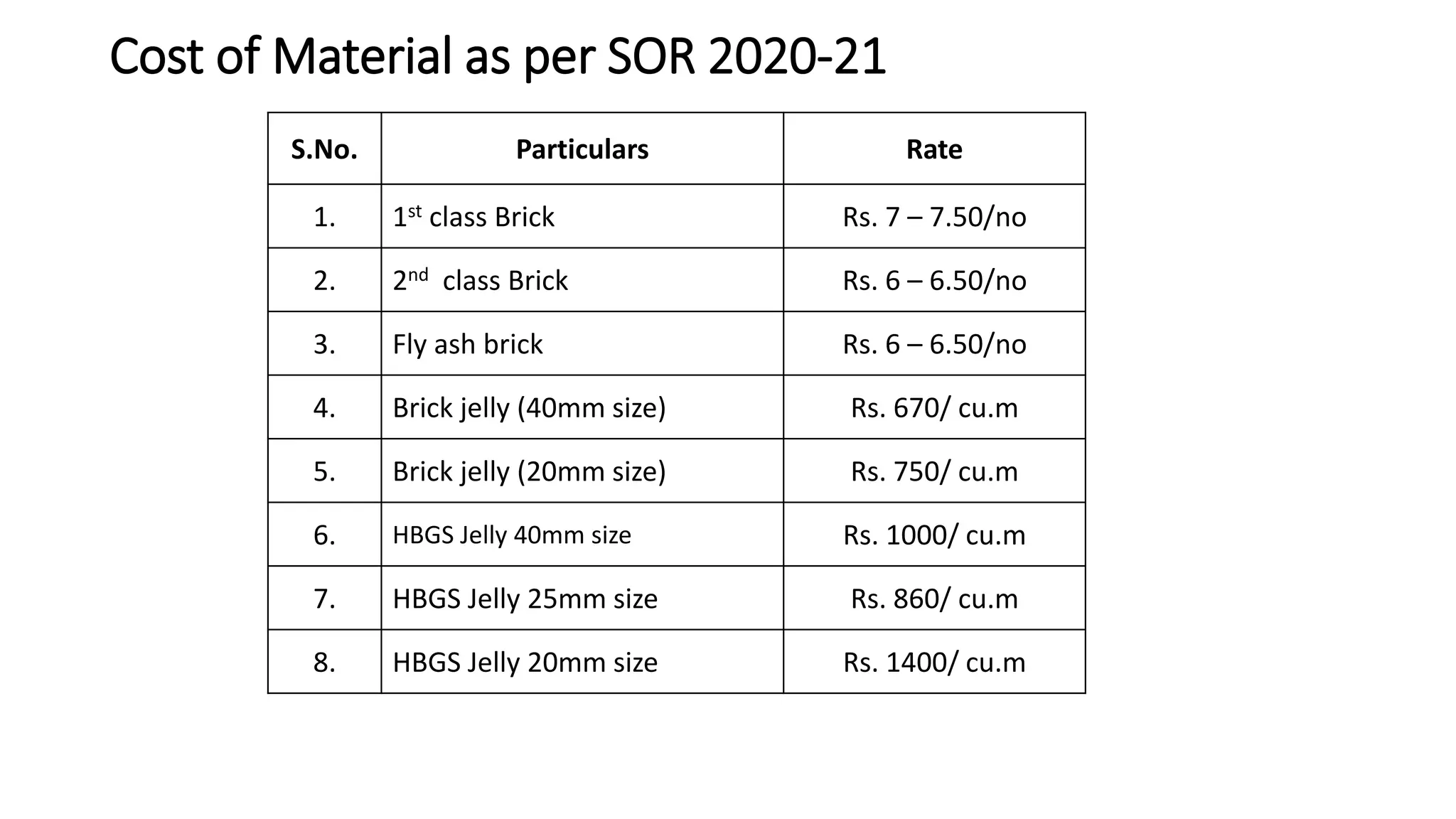
3. Important considerations for rate analysis include drawings, specifications, labor costs, material costs and transportation, tools and plants, overhead charges, and contractors' profit. The analysis is done to accurately estimate costs.