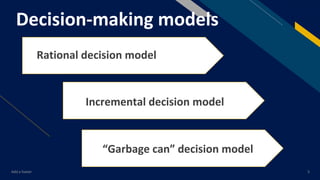
Chapter 4 focuses on decision-making in public policy and governance, defining it as the selection of policy options and discussing various actors involved. It outlines decision-making models, the decision-making process, and challenges faced, along with strategies for effective decision-making. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of sound decisions for improved implementation and outcomes in public policy.