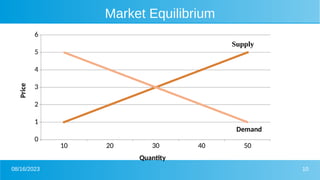
The document discusses the principles of supply and demand within economic theory and their applications in policy contexts, highlighting key concepts such as market characteristics, demand and supply determinants, and market equilibrium. It also addresses the critiques of traditional supply and demand models, their relevance to global issues such as water and electricity demand, and the implications on sectors like healthcare and food security. Furthermore, case studies are referenced to illustrate the complexities within these markets and the failures of supply and demand systems to meet theoretical expectations.