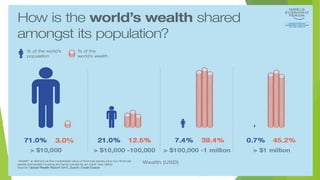
This document discusses the concepts of redistribution and economic growth, and the relationship between the two. It defines redistribution as the transfer of economic resources from wealthier to poorer individuals through policies like taxation and welfare. Economic growth is defined as the increase in production of goods and services over time, often measured by GDP. The document explores the debate around whether redistribution promotes or hinders growth, noting arguments on both sides. It also outlines different forms redistribution can take, such as progressive taxation, education/health investments, land reform, and public goods provision. The conclusion is that while scholars disagree on the impact, certain types of redistributive policies like education spending and public finance can potentially increase both social justice and economic growth.