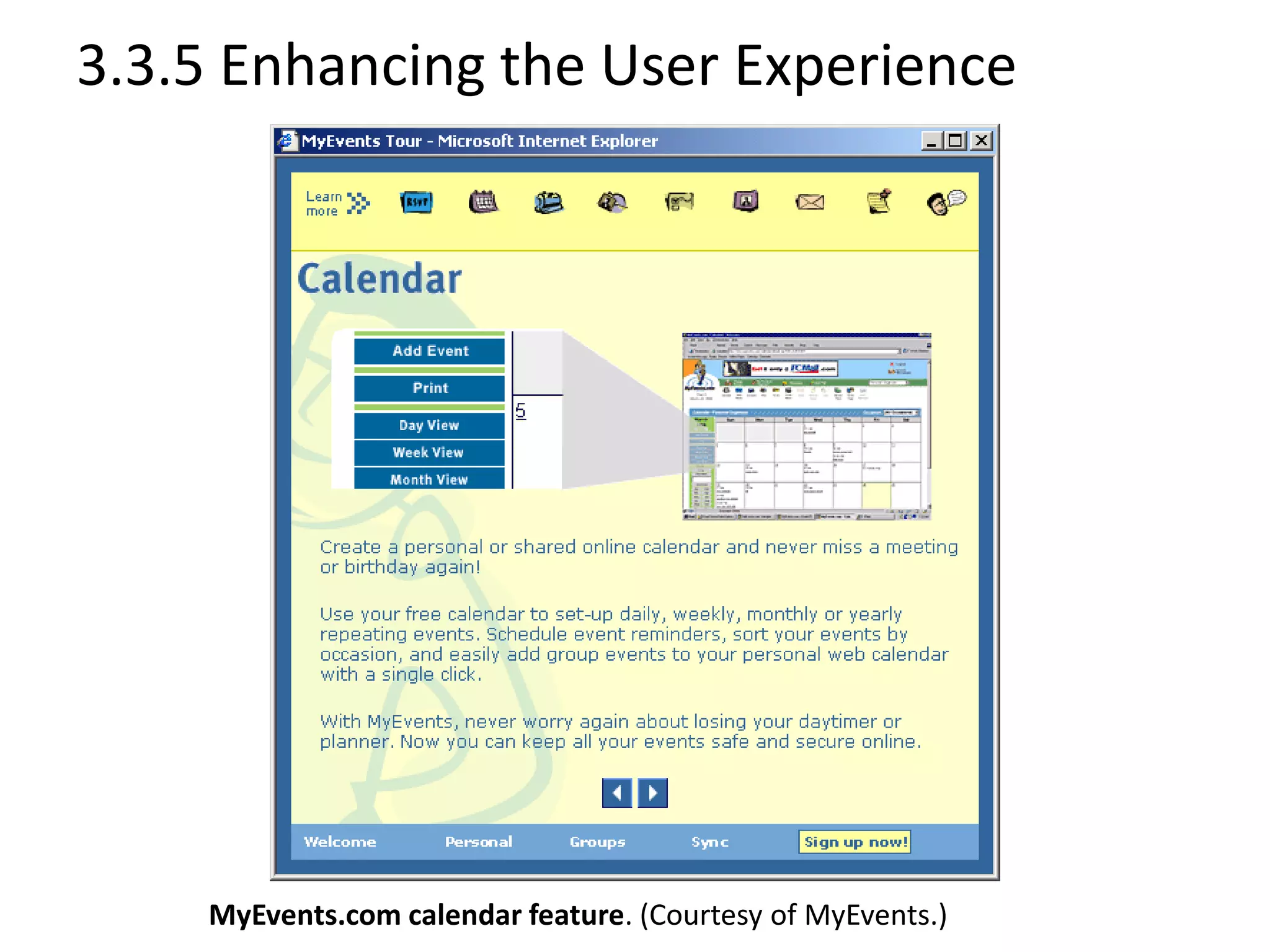
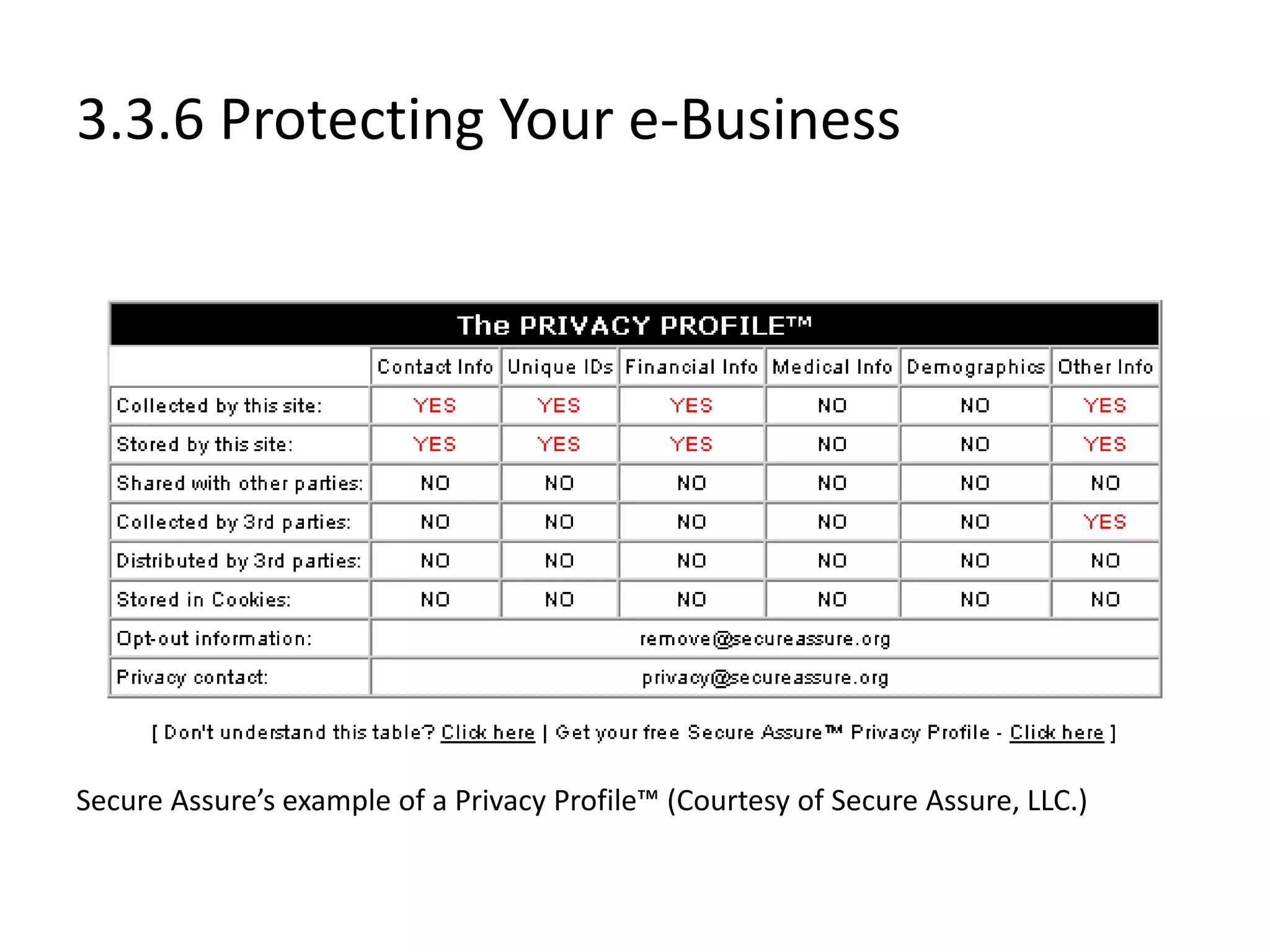
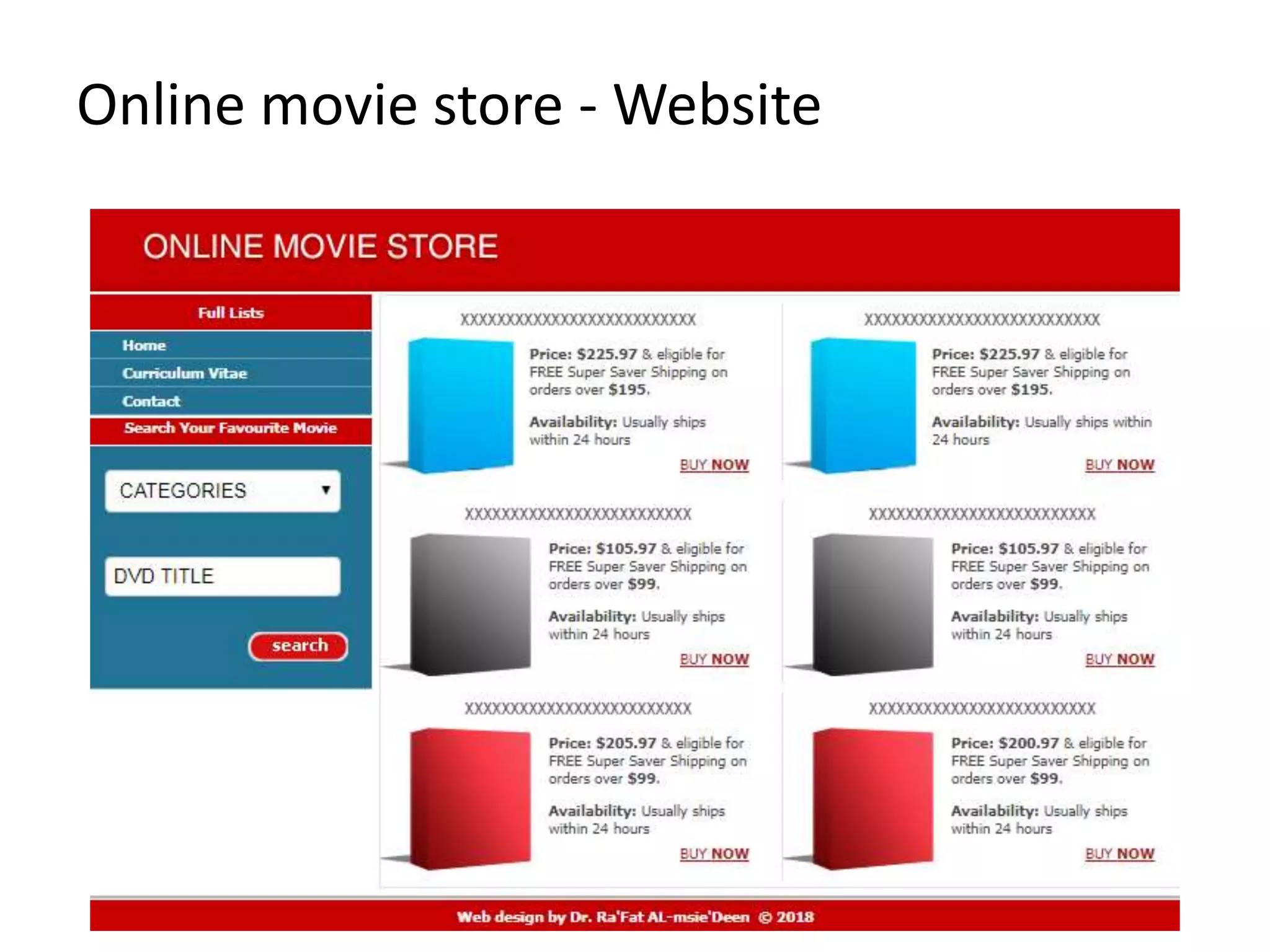
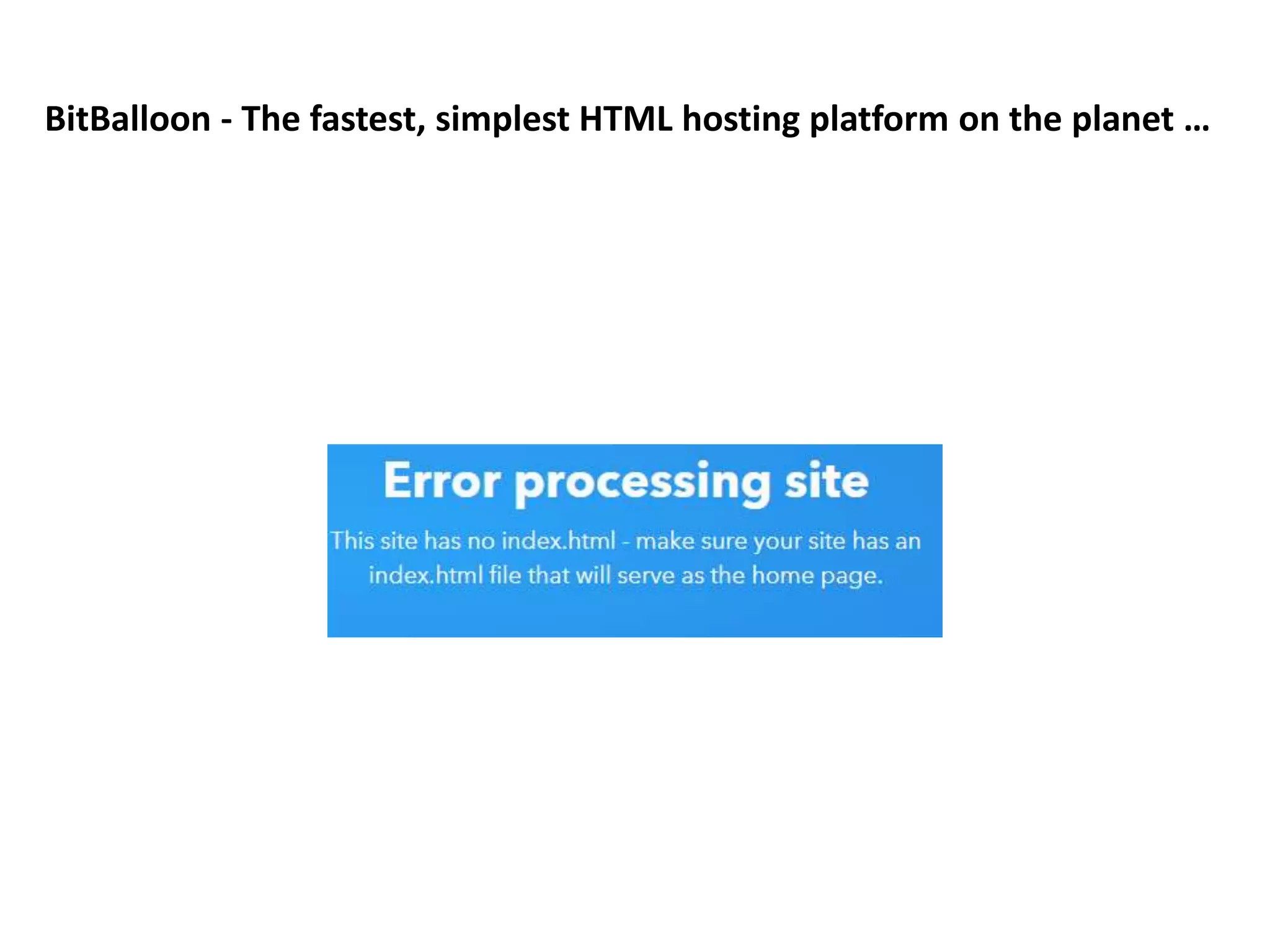
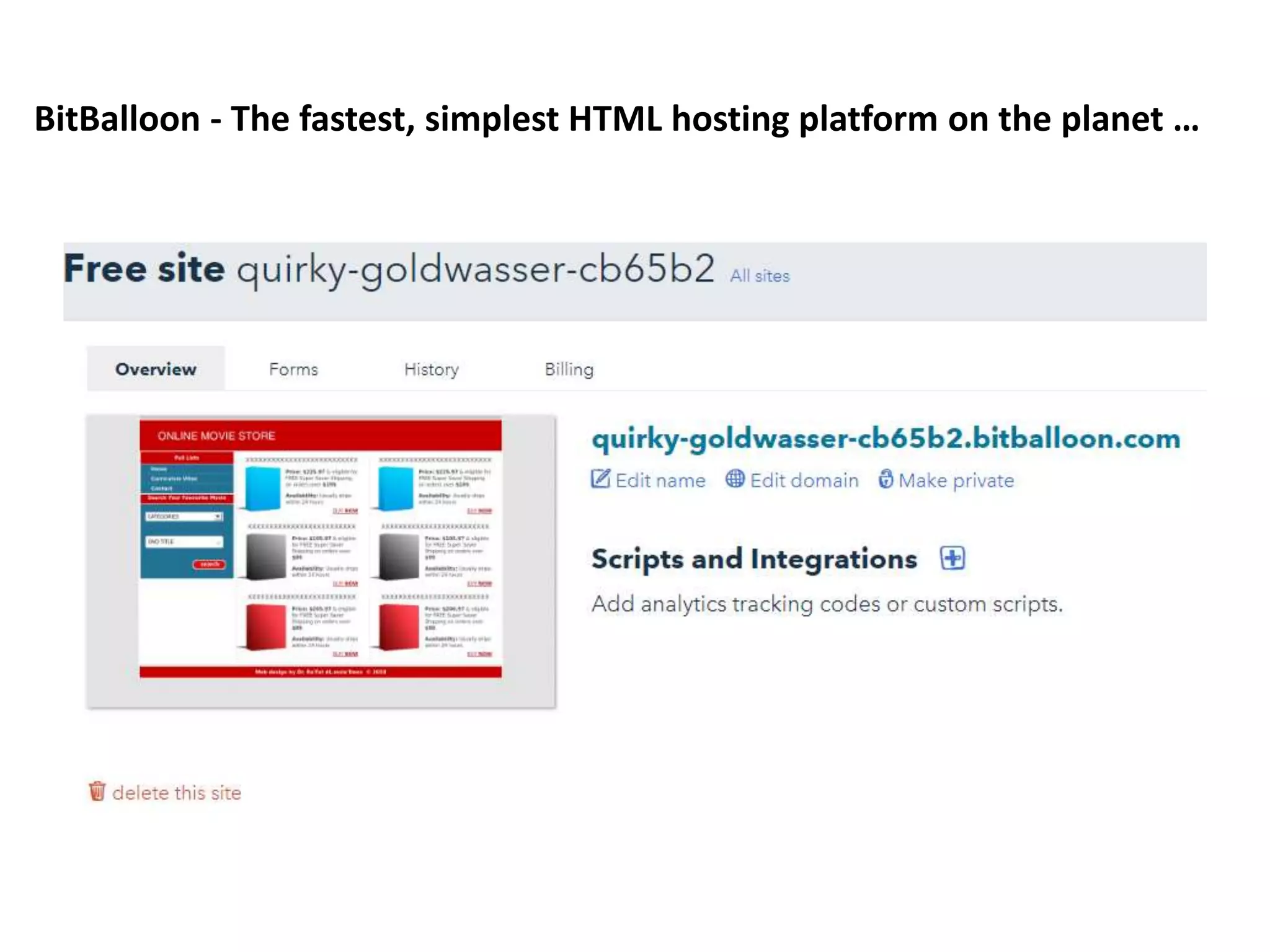
Chapter 3 provides a comprehensive overview of building, managing, and developing an e-business, covering aspects such as generating business ideas, risk evaluation, funding, and effective web design. It emphasizes the importance of a solid business plan, supply chain management, user experience enhancement, and robust website operations. The chapter also discusses various e-business solutions, including end-to-end service providers, and highlights the need for continuous adaptation to new technologies and market changes.