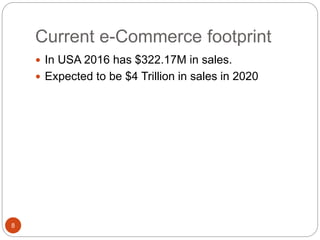
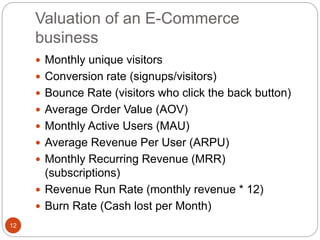
This document discusses electronic commerce (e-commerce) and starting an e-commerce business. It describes the main business models of e-commerce as business to consumer, business to business, consumer to consumer, and consumer to business. It outlines the benefits of e-commerce, how to start an e-commerce business, steps before and after launching, current e-commerce footprint, advantages and disadvantages, how to value an e-commerce business, how to sell an e-commerce business, and how to protect intellectual property rights for an e-commerce business.