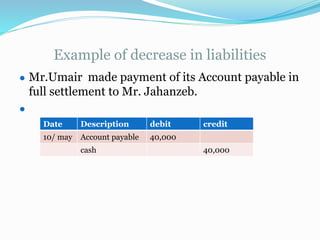
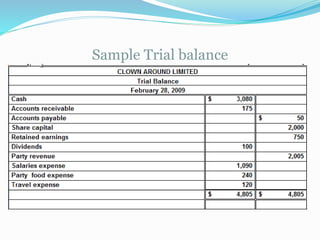
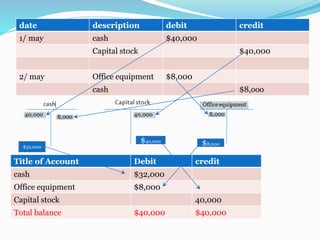
The document discusses the accounting cycle and key accounting concepts. It describes the steps of the accounting cycle as general journal, journal ledger, trial balance, adjusting entries, adjusted trial balance, financial statements, and closing entries. It also explains accounting principles such as debit/credit rules, double-entry accounting, recording of assets, liabilities, owner's equity, revenue, expenses and the purpose of the trial balance. To illustrate, it provides an example of Shehriyar investing $40,000 cash for capital stock and purchasing $8,000 of office equipment with cash.