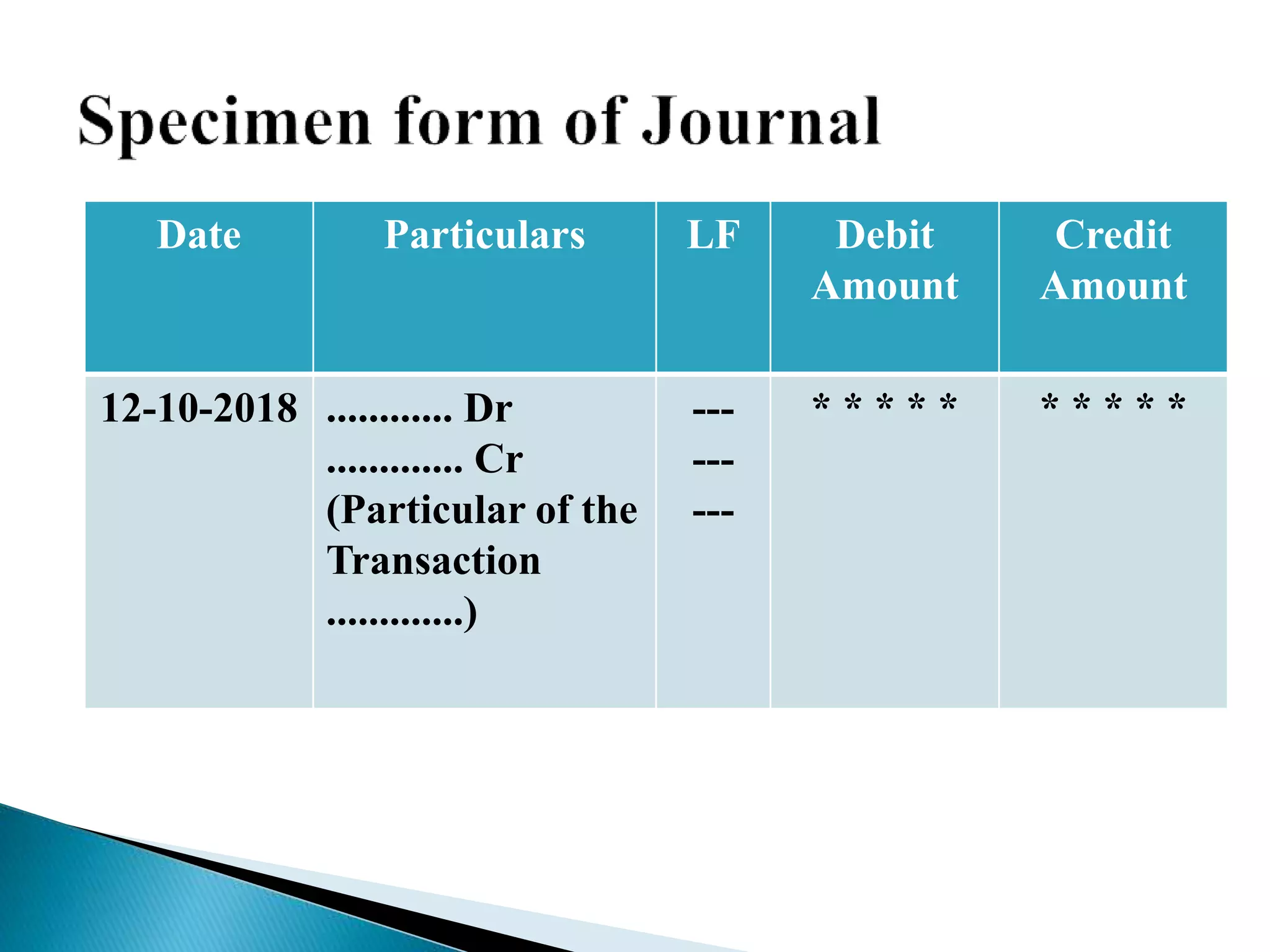
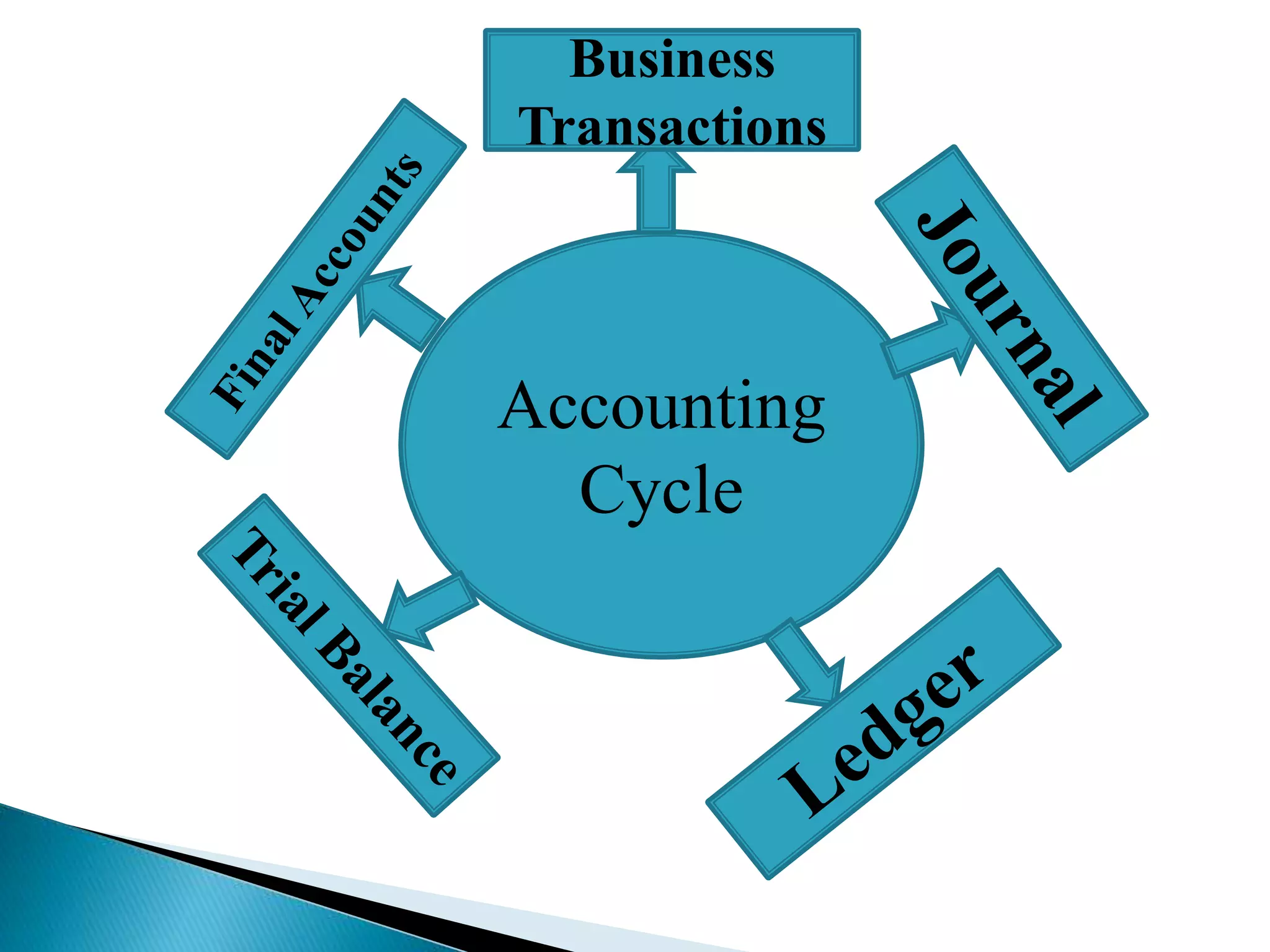
The document discusses accounting concepts and principles. It defines accounting as the process of recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions and interpreting the results. Accounting identifies, measures, and communicates economic information to allow for informed decisions. It notes that accounting is both a science and an art that follows systematic methods. The document also discusses accounting cycles, ledgers, journals, trial balances, and types of accounts.