This document discusses decidable, semi-decidable, and undecidable problems in terms of Turing machines. It provides examples of each:
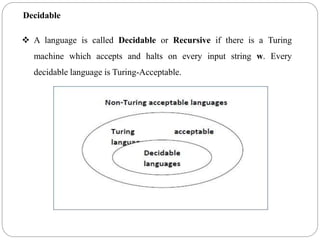
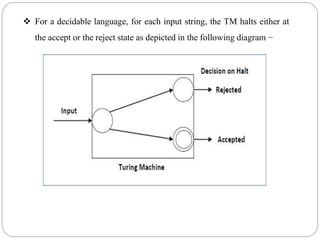
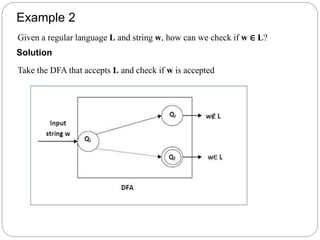
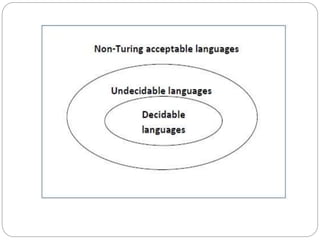
- Decidable problems are those where a Turing machine halts on every input and provides a yes or no answer. Examples given include checking if a number is prime or if a string is in a regular language.
- Semi-decidable problems are ones where a Turing machine halts on accepting inputs but may loop on rejecting inputs. Recognition of context-free languages is provided as an example.
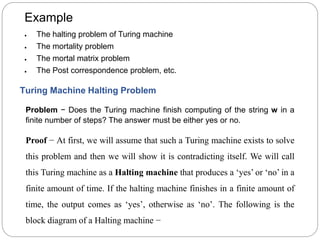
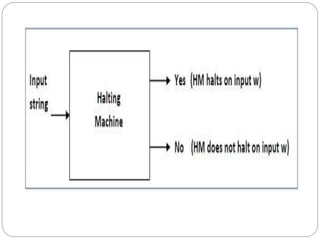
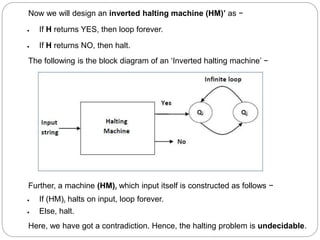
- Undecidable problems have no Turing machine that halts on every input. Examples mentioned include checking ambiguity of context-free grammars or equivalence of