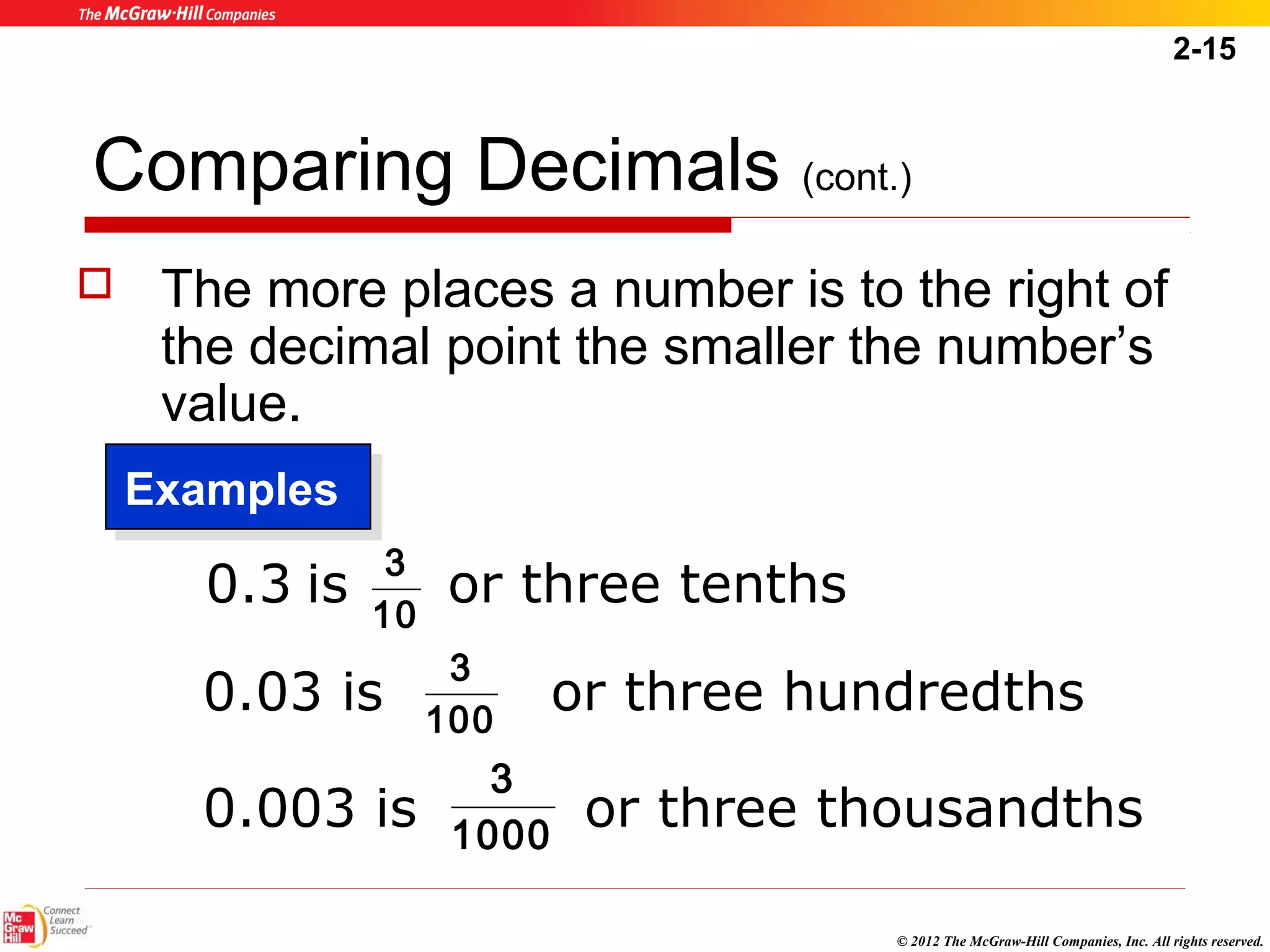
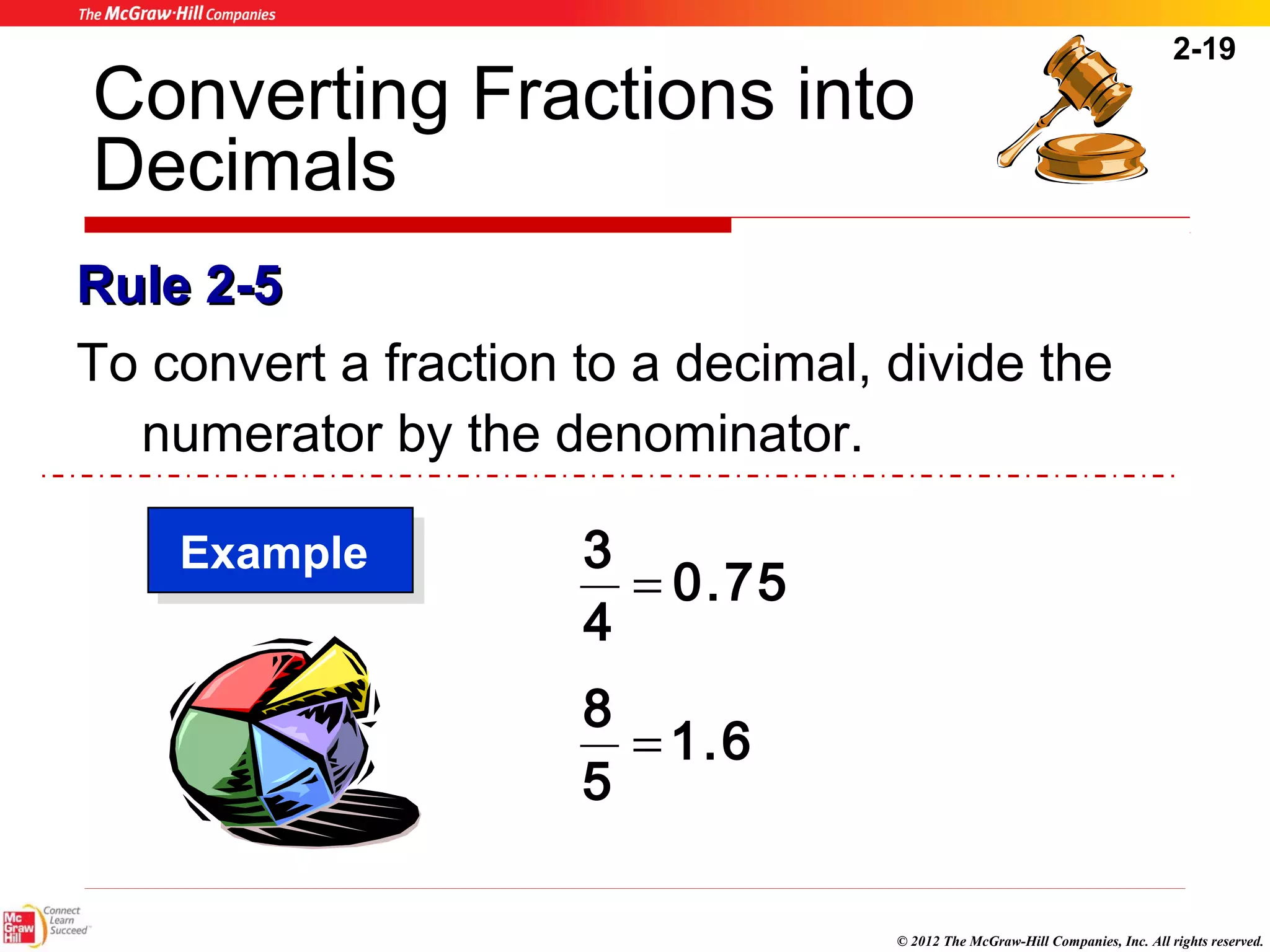
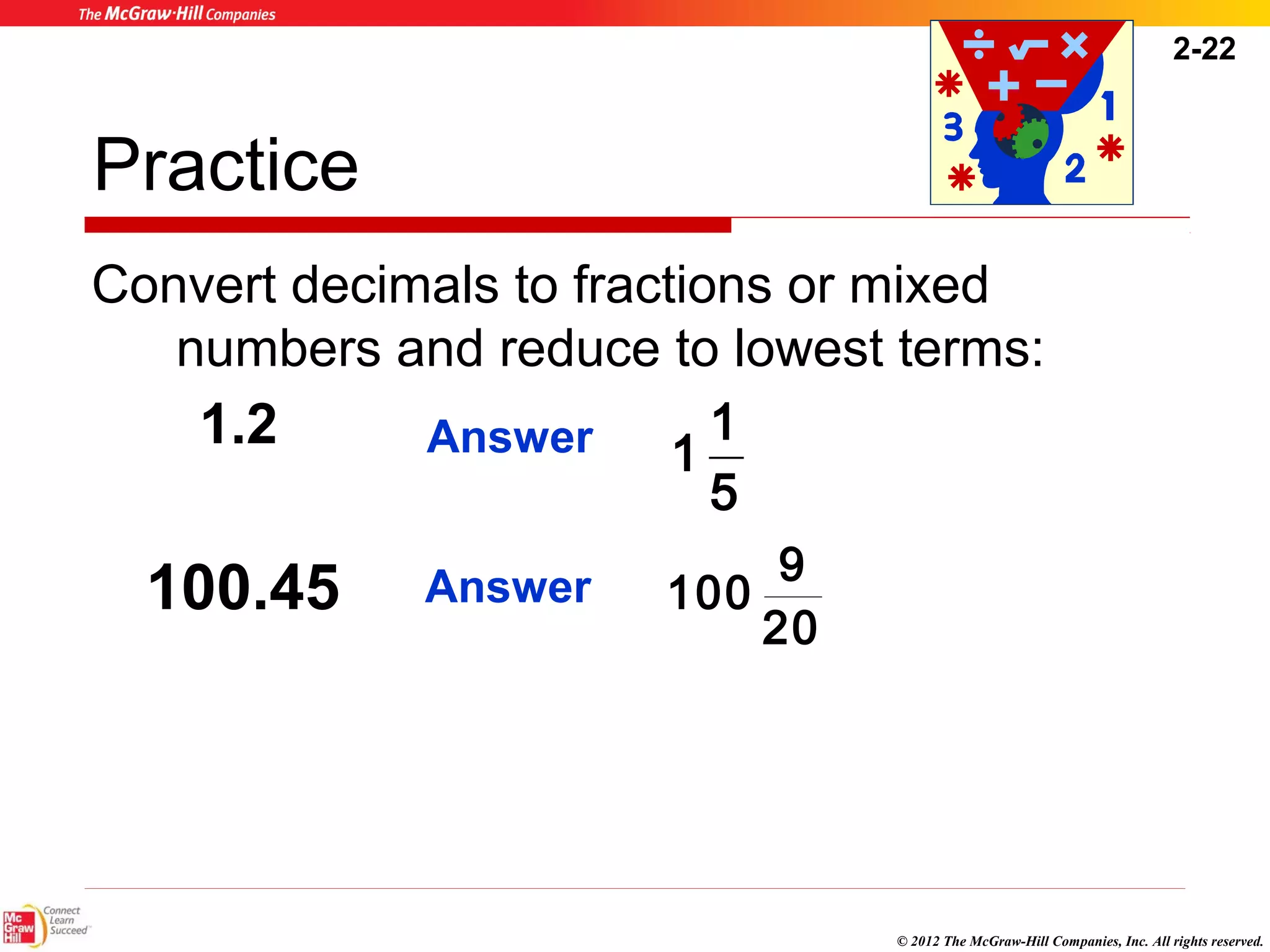
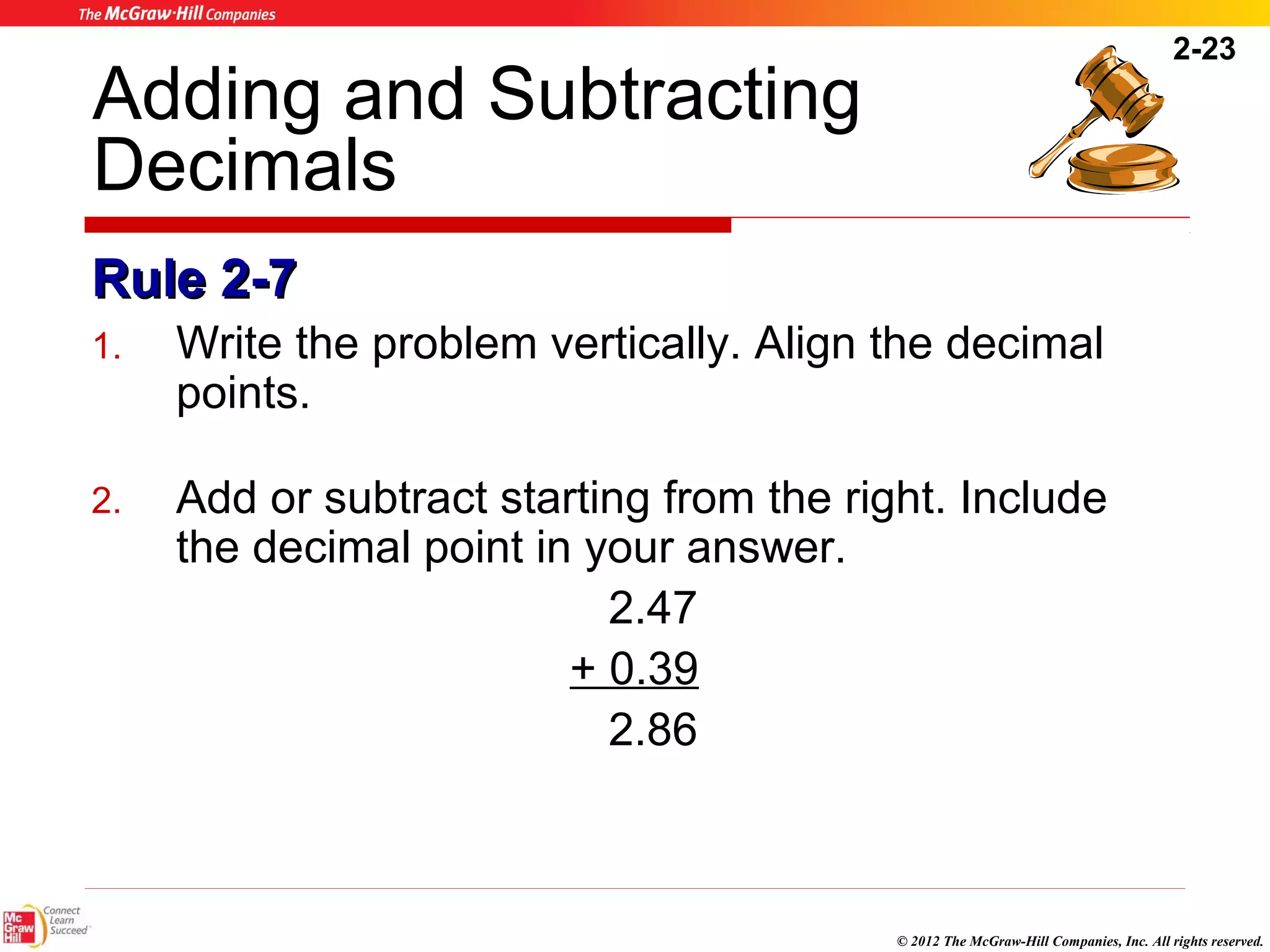
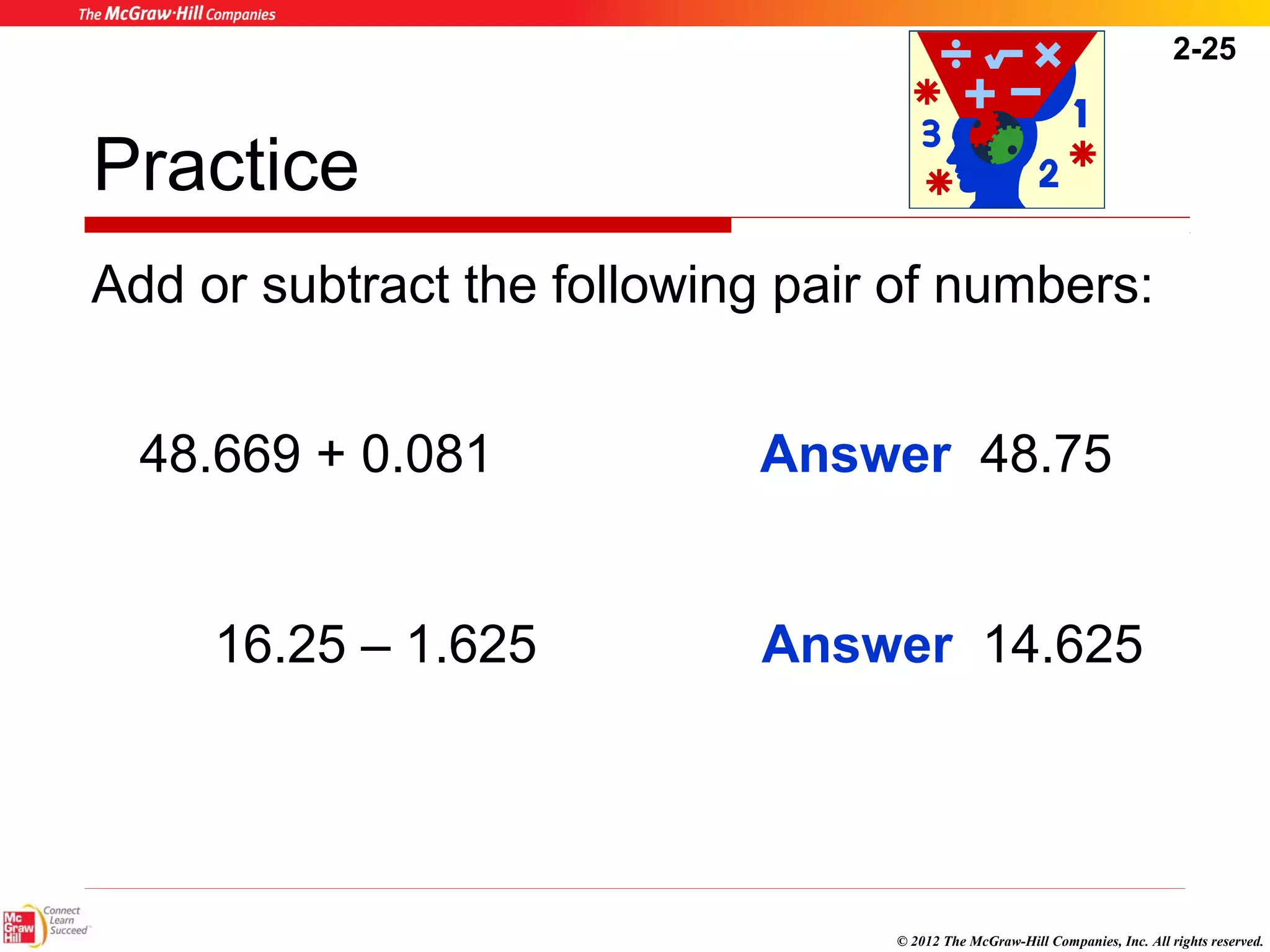
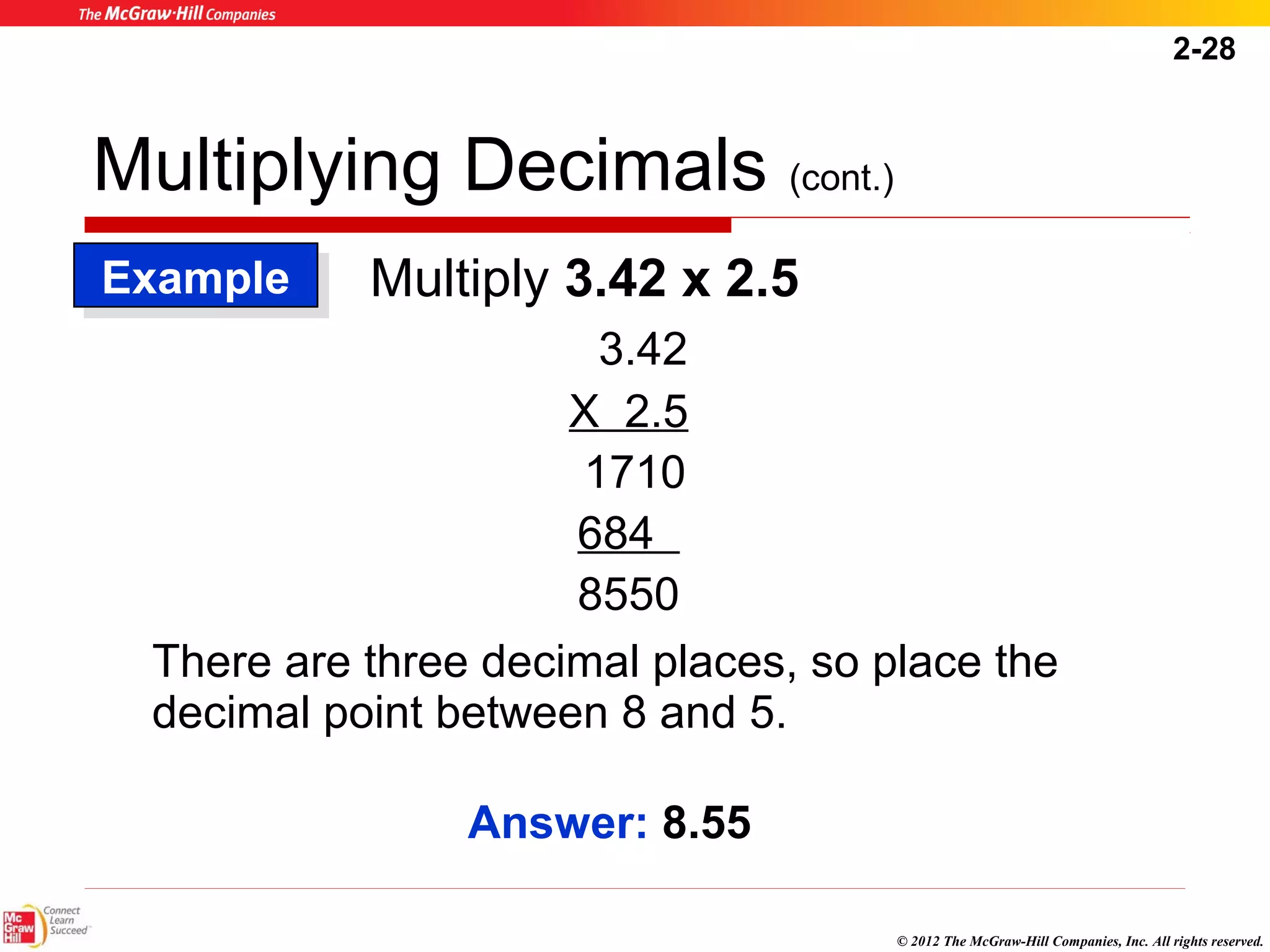
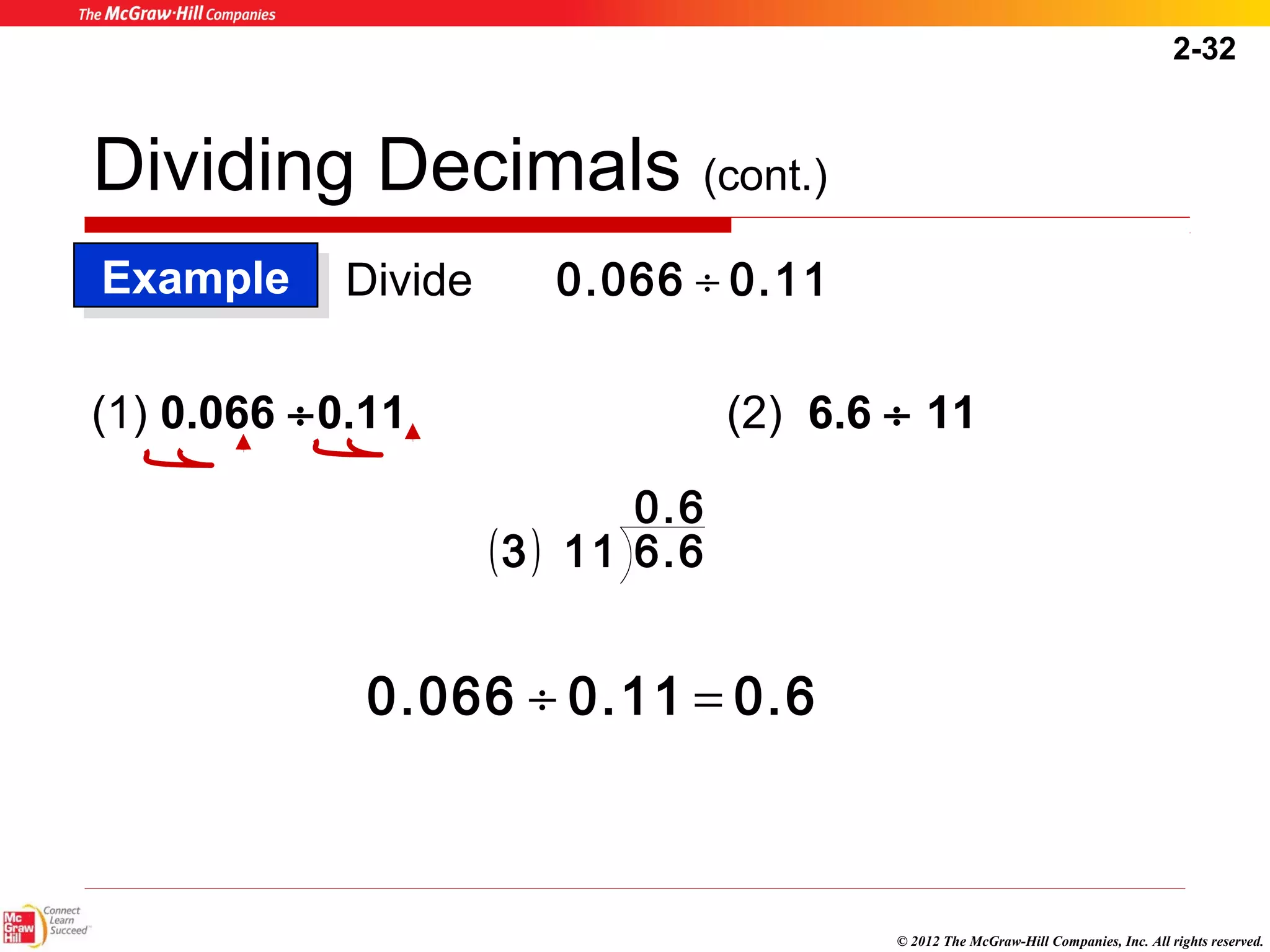
This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 2 of a textbook on decimals. It discusses writing, comparing, rounding, and converting decimals and fractions. Arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of decimals are also covered. Examples and practice problems are provided to illustrate the rules and steps for working with decimals. The goal is to help healthcare professionals feel comfortable using decimals for dosage calculations.