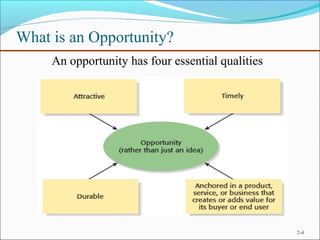
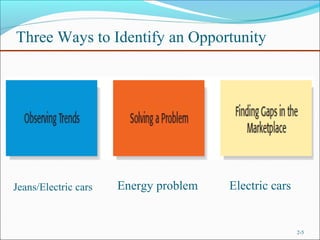
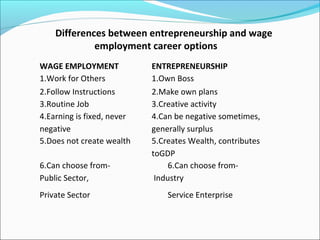
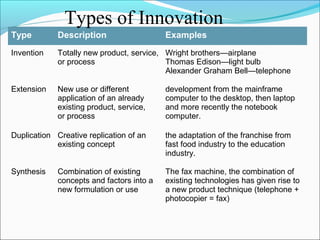
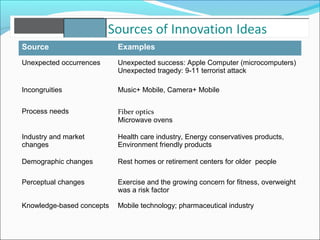
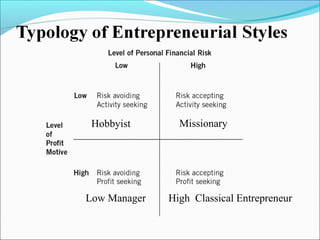
The document outlines the 5 main steps in the entrepreneurial process: 1) discovery, 2) concept development, 3) resourcing, 4) actualization, and 5) harvesting. It describes each step, including generating ideas, writing a business plan, acquiring resources, operating the business, and deciding on future plans. The document also discusses identifying opportunities, developing an innovative concept, and some of the challenges entrepreneurs may face like stress from risk, long hours, and balancing work and family commitments.